Observing Cells Pre-Lab
advertisement
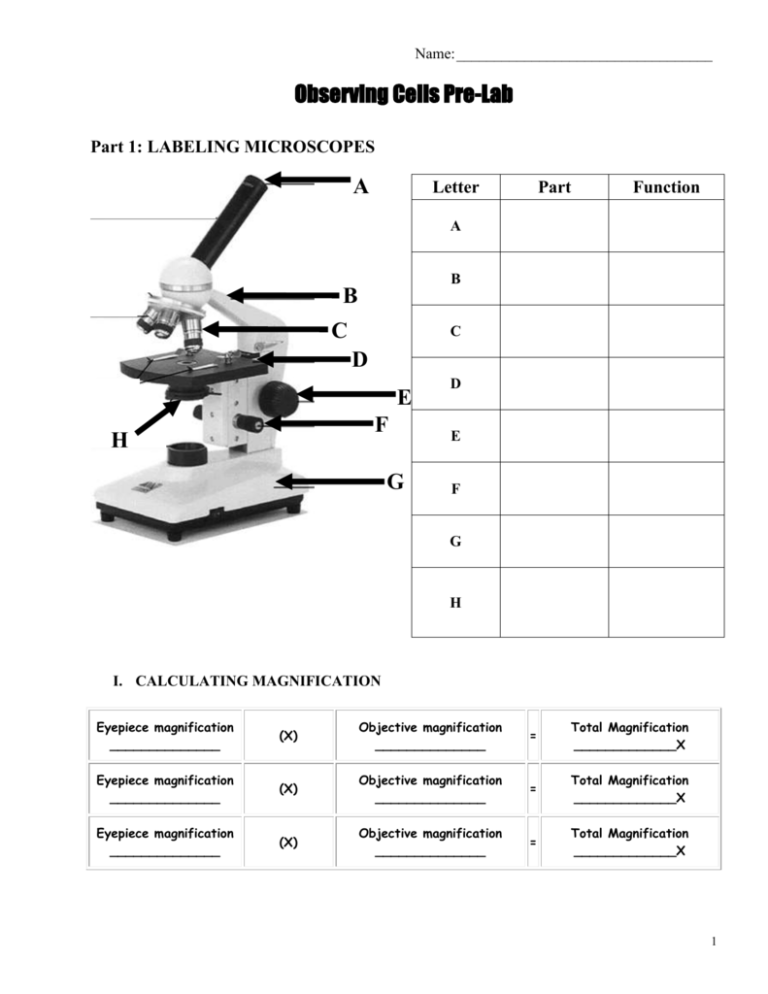
Name: __________________________________ Observing Cells Pre-Lab Part 1: LABELING MICROSCOPES A Letter Part Function A B B C C D E F H G D E F G H I. CALCULATING MAGNIFICATION Eyepiece magnification ______________ (X) Objective magnification ______________ = Total Magnification _____________X Eyepiece magnification ______________ (X) Objective magnification ______________ = Total Magnification _____________X Eyepiece magnification ______________ (X) Objective magnification ______________ = Total Magnification _____________X 1 Part 2: LABORATORY DRAWINGS Laboratory drawings can be done in several ways depending on the lab. Some drawings are made in circles that represent the microscope field of view. Always label the magnification you used when doing any laboratory drawing. Most laboratory drawings are labeled. Use the following guidelines to help make your laboratory drawings clear and legible: o Make all drawings in pencil. o Label lines should point to the center of the structure being labeled. o Do not write on the label lines. o Print all labels horizontally. o Label the right-hand side of the drawing, if possible. o Do not cross label lines. The following laboratory drawing was completed without using the guidelines for laboratory drawings. Circle 5 things that are wrong with this drawing. Onion cell magnification:_____X 2 Name: ________________________________________ Period: ___________ Observing Cells Lab Introduction: Living things are made of cells. All cells have parts that do certain jobs. These parts are called organelles. Cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cell membranes give the cells their shape and control what enters and leaves the cell. The clear, jelly-like material inside the cell is the cytoplasm. Also present in all eukaryotic cells is the nucleus. The job of the nucleus is to control the activities of the cell. Plant cells have two organelles that animal cells do not have, cell wall and chloroplasts. The cell wall is what gives plant cells their shape. Chloroplasts are the site of photosynthesis in the plant. The chloroplast contains the pigment chlorophyll. This is the pigment that gives the cell its color and allows it to use the sun to make energy. Plant cells also have an organelle called a vacuole, which is a large sac that stores water. Purpose: The purpose of this laboratory exercise is to observe and identify structures of cells. You will also learn about the structural difference between plant and animal cells. Materials: slide dropper & water frog blood slides cover slip microscope onion slides tooth picks methylene blue (stain) Elodea paper towels Part 1: Onion Cells Procedure: 1. Prepare a wet mount of the onion. 2. Examine the slide under scanning power. 3. Examine the slide under low power and high power. In the space below, draw the onion cells as your see them under high power. Use good scientific drawing procedures. Make sure you record the total magnification of each diagram. 3 Part 2: Elodea cells Procedure: 4. Prepare a wet mount of an Elodea leaf. 5. Examine the slide under scanning power. 6. Examine the slide under low power and high power. In the space below, draw the Elodea cells as your see them under high power. Label the cell wall, a chloroplast, and cytoplasm. Use good scientific drawing procedures. Make sure you record the total magnification of each diagram. 7. Look closely at the cells. Do you observe any movement within the cells? If so, describe the movement. _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Analysis Questions: 1. When you looked at the Elodea cells you should have seen movement. This movement is called cytoplasmic streaming. Describe the movement you saw below:_________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the small green organelle visible in the Elodea cells? ___________________________ 4 Part 3: Cheek Cells 1. Prepare a slide of cheek epithelial cells. Directions are as follows: a. Obtain a toothpick and gently scrape the inside of your cheek with the toothpick. b. Place the scraping on a clean, dry slide. c. Discard the toothpick into the garbage can. d. Add a drop of methylene blue and cover with a cover slip. 2. Observe under scanning power, low power, and then high power. 3. Draw the cheek cells as you see them on high power. 4. Label the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane. 5. Discard the slide of cheek cells into the broken glass container (green bucket). Part 4: Bacterial Cells 1. Obtain a slide of different bacterial types. There are three types of bacteria to observe on each slide. 2. Observe the bacterial cells under scanning power, low power, and high power. 3. Draw the three different types bacterial cells as you see them on high power. Label the cell membrane. 4. What are the three shapes are the bacterial cells? __________________________________________________________________________ 5 Analysis Questions: 1. Which of the slides you looked at were plant cells and which were animal cells?_____ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 2. What were some of the differences between plant and animal cells that you observed while using the microscope?_______________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 3. If you got a “mystery” slide and you had to determine if it contained plant cells or animal cells, what would you look for to determine what type of cells it contained?_________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 4. Which of the slides that you looked at were prokaryotic cells? How did you know? Explain. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 5. Which of the slides that you looked at were eukaryotic cells? How did you know? Explain. _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 6. How were the bacterial cells different from the plant and animal cells you looked at? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 6 Conclusion Questions: 1. How did the invention of the light microscope change the way scientists looked at the world? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 2. What are the major differences between plant and animal cells?______________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?_______________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ IF TIME PERMITS, obtain a survey kit and start exploring!! 7