NURSING PROCESS FOCUS: Patients Receiving Levodopa
advertisement

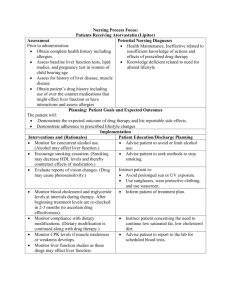
NURSING PROCESS FOCUS: Patients Receiving Levodopa (Larodopa) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration: Falls, risk for Obtain complete health history including Knowledge deficit related to allergies, drug history and possible drug medication effects interactions. Mobility, impaired Obtain baseline evaluation of severity of Self-care deficit, ADLs, feeding, Parkinson’s disease to determine toileting medication effectiveness. Constipation Obtain baseline vital signs, especially blood pressure and pulse Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes Patient will Report increased ease of movement and decreased symptoms of Parkinson’s disease Demonstrate an understanding of the drug’s action by accurately describing drug side effects and precautions, and measures to take to decrease any side effects Immediately report side effects and adverse reactions Adhere to the medication regimen Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Education/Discharge Planning ● ● ● ● ● Monitor vital signs closely when levodopa dose is being adjusted. (Hypotension could occur as result of dose adjustment. Dysrhythmias can occur in patients predisposed to cardiac problems.) Provide for patient safety. (Orthostatic hypotension may occur.) Instruct patient to: Report signs of hypotension, dizziness, light-headedness, feelings that heart is racing or skipping beats, or dyspnea Have routine EKGs and vital signs taken Instruct patient: To change position slowly and to resume normal activities slowly. How to protect self from falls. Monitor for behavior changes. (Drug Instruct patient and caregiver to: increases risk of depression or suicidal Watch for and report immediately any thoughts, and may cause other mood signs of changes in behavior or mood. disturbances such as aggressiveness and Seek counseling or a support group to help confusion.) deal with these feelings; assist patient to find such resources if needed. Monitor for symptoms of overdose. Instruct patient or caregiver to be aware of (Muscle twitching and blepharospasm are newly occurring muscle twitching, early symptoms.) including muscles of eyelids and to report immediately. Monitor for improved functional status Instruct patient or caregiver to report rapid, followed by a loss of therapeutic effects unpredictable changes in motor symptoms (on-off phenomenon), due to changes in to healthcare provider immediately, and dopamine levels that may last only that this can be corrected with changes in ● ● minutes, or days. (Usually occurs in patients on long-term levodopa therapy.) Evaluate diet. (Absorption of levodopa decreases with high protein meals or high consumption of pyridoxine-containing foods.) levodopa dosage schedule. Instruct patient to: Take on empty stomach, but food may be eaten 15 minutes after, to decrease GI upset. Avoid taking levodopa with high protein meals. Avoid high consumption of foods containing vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) such as bananas, wheat germ, green vegetables, liver, legumes. Watch for vitamin B6 in multivitamins, fortified cereals, and antinauseants, so these products should be avoided. Monitor glucose levels in patients with Instruct diabetic patient to: diabetes mellitus. (Loss of glycemic Consistently monitor blood glucose both control may occur in the diabetic patient.) by self and with periodic lab studies. Report symptoms of hypo- or hyperglycemia. ● Monitor for decreased kidney or liver Instruct patient to keep all appointments function. (Decrease in these functions for liver and kidney function tests during may slow metabolism and excretion of therapy. drug, possibly leading to overdose or toxicity.) ● Monitor for side effects in the elderly. Instruct elderly patients to report any (Elderly patients may experience more symptoms involving cardiovascular rapid and severe side effects, especially system: changes in heart rate, dizziness, those affecting cardiovascular system.) faintness, edema, or palpitations. ● Monitor for other drug-related changes. Inform patient that urine may darken and (Drug may cause urine and perspiration sweat may be dark colored, but not to be to darken in color, but it is not a sign of alarmed. overdose or toxicity.) Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”) Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Benztropine (Cogentin) Assessment Prior to administration: Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history and possible drug interactions. Obtain baseline of severity of Parkinson’s symptoms to determine effectiveness. Assess for use of other medications, Obtain lab work to include a complete blood count, liver and renal function studies Obtain baseline vital signs, especially pulse. Potential Nursing Diagnoses Constipation, risk for related to side effects of drug Injury, risk for related to effects of drug Risk for imbalanced body temperature Sleep pattern, disturbed, insomnia or extreme drowsiness related to action of drug Therapeutic regimen management, ineffective Urinary retention relation to side effect of drug Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes Patient will Experience relief of Parkinson’s symptoms or EPS due to anti-psychotic medications Immediately report any occurrence of adverse reactions Demonstrate an understanding of the drug’s action by accurately describing drug side effects and precautions, and measures to take to decrease any side effects Maintain compliance with drug regimen Maintain normal bowel pattern Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Monitor adherence to recommended Instruct patient to take benztropine as therapy. Benztropine should be begun with ordered, unless side effects occur; then low dose, then gradually increased. notify health care provider that it usually takes 2-3 days before desired effect will be noticed Monitor proper storage of benztropine. Advise patient to store benztropine in tightly covered, light resistant container at moderature room temperature. Monitor environmental temperature. Advise patient to avoid strenuous activity (Patient will have decreased ability to in hot weather, to plan rest periods, and to tolerate heat, and may develop heat stroke.) avoid strenuous activity during heat of day to decrease risk of heat stroke. Instruct patient to: Monitor patient’s ability to void, as well as intake and output. (Benztropine can cause Report infrequent voiding, or feeling of urinary hesitation or retention, secondary to fullness after emptying the bladder its anticholinergic effect.) Keep a record of intake and output with times of occurrence, and to report imbalance in intake and output Evaluate medication regimen for drugs that interact with benztropine. (Concurrent use of phenothiazines causes increased risk of adverse anticholinergic effects; patient will need decreased phenothiazine dose, and close monitoring for worsening symptoms of psychiatric disorder.) Monitor drug use in elderly. (Increased sedative effects of benztropine may occur and lower doses may be needed.) Monitor for anticholinergic effects such as dry mouth. Instruct patient to: Disclose any history of psychiatric problems or other medication use to all health care providers Report urinary problems, blurred vision, constipation, dry skin, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, dysphagia, photophobia Advise patient to report any drowsiness. Teach patient measures to use sugarless hard candy or gum, frequent drinks of water, frequent rinsing of mouth. Review with patient and family: Observe for increased symptoms of Parkinson’s or EPS. (If involuntary Exactly how to take medication. movements or increased rigidity occur, To report increased muscle rigidity, medication levels may not be therapeutic.) difficulty changing position, muscle spasms or other involuntary movements Advise patient to: Monitor for constipation and for signs of paralytic ileus. (This may be caused by Take benztropine after meals to decrease decreased GI motility due to drug’s GI irritation anticholinergic effects.) Decrease constipation by increasing fluids, fruits and vegetables, exercise if possible Report signs of paralytic ileus (abdominal pain, intermittent constipation, abdominal distention, nausea, and vomiting) Observe for unsafe activities. (Benztropine Instruct family to supervise ambulation may cause sedation or dizziness.) until response to medication is known Advise patient not to drive until response to medication is known Monitor for symptoms of overdose. (Some Advise patient to report immediately: adverse reactions may result from atropinehallucinations, confusion, disorientation, like toxicity, and may be eliminated by delusions, anxiety, hyperthermia, lowering dose of benztropine.) tachycardia, increased respirations. Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”).