CARBON CYCLE - Mo`Hearn Biology

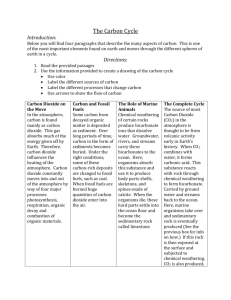
CARBON CYCLE
Introduction:
Carbon is a very important element that can combine with other elements to make many different molecules.
It is found in the tissues of living things and it is also found stored in things that are not living, like rocks. A very common form of carbon is called carbon dioxide and it is written as CO
2
. Carbon cycles over and over and it gets reused and turned into many different things.
As you go through this packet, draw and answer the questions as you go along.
This is due at the end of the period.
1.
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Carbon dioxide is found in the atmosphere. It is released by many different processes and accumulates in the atmosphere.
On your picture, label “CO
2
in the atmosphere”.
2.
Photosynthesis
During photosynthesis, plants take carbon dioxide out of the air, mix it with water and convert them into glucose.
A by-product of this reaction is the release of O
2
, or oxygen, that we breathe.
Draw on your poster: Some grass and trees.
Label: “Photosynthesis” by them and draw arrows to indicate the direction CO
2
would travel. Also put the arrows for O
2
3.
Cellular Respiration
Plants and animals need energy in order to survive.
When plants and animals break down food, carbon dioxide is released from their cells. Some of this carbon will become part of the tissues of the organism. Some carbon dioxide leaves the cells and is released when we breathe. That carbon dioxide then enters the atmosphere to be reused by plants to make sugar.
Draw on your poster: A person and an animal
Label: “Cellular respiration” by them and draw arrows to indicate the direction CO
2
would travel. Also do the arrows for O
2
Also, next to the plant mark cellular respiration.
4.
Decomposition
When a plant or animal dies, its tissues will be broken down by decomposers, like bacteria, in the soil. The decomposers will break down the tissues, releasing carbon back into the air or into the soil. This carbon can then be used by other organisms.
Draw on your poster: A dead animal (use “x” for eyes)
Label: “Decomposition” by it and draw arrows to indicate the direction CO
2
would travel.
5.
Burial
Some dead plants and animals get buried before decomposers have a chance to break them down. These buried dead organisms, over time and under the right temperature and pressure, will be converted into fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum. These fossil fuels serve as “carbon reservoirs” and hold carbon until the fuels are used.
Color on your poster: The dotted area in the soil
Label: “Fossil fuels” on it and draw arrows to indicate the direction CO
2
would travel.
6.
Burning of fossil fuels
Coal and petroleum are hot commodities in today’s market. Coal and petroleum are mined from the ground and burned at an enormous rate. Burning of these fossil fuels returns carbon dioxide back to the air at a rate faster than it is being taken out by trees and plants.
Draw on your poster: A building and car showing smoke coming from them (fossil fuels being burned)
Label: “Burning fossil fuels” by them and draw arrows to indicate the direction CO
2
would travel.
7.
Volcanic activity
Volcanic activity also puts carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. The carbon that was trapped inside of rocks is released when rocks melt under tremendous temperature and pressure. The carbon leaves the rocks and is released from volcanoes as carbon dioxide gas.
Draw on your poster: A volcano with gases escaping
Label: “Volcanic activity” on it and draw an arrow to indicate the direction CO
2
would travel.
8.
Carbon dioxide in oceans
Carbon dioxide is also found in oceans. The same processes that occur on land also occur in the ocean.
There is photosynthesis, cellular respiration, decomposition, and the formation of fossil fuels. The carbon dioxide from the ocean can be recycled both in the ocean and into the atmosphere.
Draw on your poster: Seaweed and fish
Label: “CO
2 in Ocean” and color the water blue
Label: “Photosynthesis” and “Cellular respiration” by them and draw arrows to indicate the direction CO
2 would travel.
9.
Human activities
Other human activities that can affect carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are mining and the cutting and burning of forests. Mining is the process of digging and removing fossil fuels from the ground. Cutting and burning of forests involves forests being cleared of trees to make room for cattle to graze and homes and roadways to be built. In tropical rainforests trees are cut for the beautiful and expensive woods that the trees produce. Answer some questions about this process.