Earthquake Epicenter
advertisement

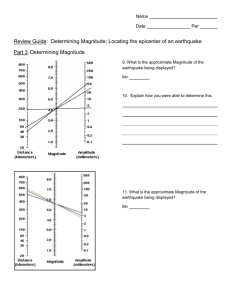
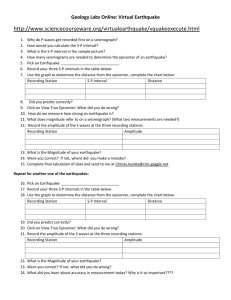
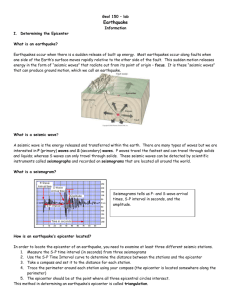
Name: Section: Date: Earthquake Epicenter Problem: An earthquake has occurred, and as a seismologist your job is to locate the epicenter and determine what the cause of that earthquake could have been. Ex: is there a fault near by, a volcano, a plate boundary, etc. Procedure: 1. Use the following seismograms to determine the time interval between the arrival of the P-wave and the S-wave. 2. For each time interval use the S-P interval graph to figure out how far each seismograph was from the epicenter of the earthquake. 3. Next use a compass and the scale on the map to draw the circles around each of your seismic stations. 4. If your circles intersect mark that has the epicenter. If they do not go back through and check your measurements. 5. Using a different color writing utensil, box out the area that you think is the epicenter. Seismograms: Chichuahua Seismic Station Chichuahua Seismic Station S-P Interval = seconds Name: Section: Date: Mazatlan Seismic Station Mazatlan Seismic Station S-P Interval = seconds Rosarito Seismic Station Rosarito Seismic Station S-P Interval = seconds Name: Section: Date: S-P Time Interval: Station Chihuahua Mazatlan Rosarito Distance (km) Name: Section: Date: Epicenter Map: 1. How many seismic stations are required to locate an epicenter? 2. In what three ways are P-waves different from S-waves? 3. How long does it take for a P-wave to travel 4,400 km? 4. Which type of E.Q. wave arrives first? 5. The second and most intense wave is called what? 6. If a P-wave arrived at a seismograph station 6,200 km away at a time of 6:43:30 pm, what time did the E.Q. actually occur? 7. How far from the epicenter is a seismic station if the time between the P and S waves is 16 min 30 sec?