math_tools
advertisement

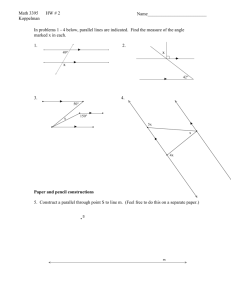
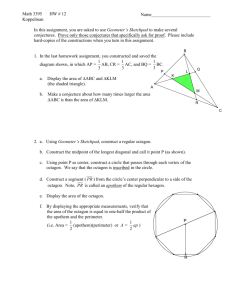
COMPUTATIONAL TOOLS Introduction: Software like Mathematica® and Math CAD® are powerful computational and programming tools. In this assignment you will become familiar with the basic features of Math CAD®, a program that is particularly attractive to secondary school mathematics teachers because the text editing features resemble standard mathematical form rather than standard computer form. Before you get started: • Review Getting Started Under the Help Menu from within Mathcad • Review the Topics Under the Help Menu • Use Balloon Help to Identify all icons on the screen. Click on the top icon to get additional palates. Assignment: Demonstrate competence using MathCAD and Geometer's Sketchpad by providing a printout of the following. Use the text tool to identify your work MATHCAD (1) Calculations: Five different calculations using a variety of functions. (2) Variables: Write three or more different equations relevant to your subject such as those shown below. Solve each equation for one or more specific situation. Biology Chemistry Physics Logistic Growth Curve K N Ir N K Where I= rate of increase K=carrying capacity r=intrinsic rate of increase=(b-d)=birthsdeaths N=number of individuals in the population Force between charges QQ F k 12 2 d F=Force between two point charges k=constant of proportionality Q1 and Q2 =charges V=potential difference Relativity 2 E mc E=energy m=mass c=speed of light (3) Iterative Calculations: Solve an equation for a range of variables. Computational Tools - 1 (4) Graphs: Create a graph of a function relative to the subject you teach. (5) Integration/Summation: Use the integral and summation functions to solve problems of your choice. (6) Implications for Teaching: (a) What are the implications of tools such as Mathematica and MathCAD for the teaching and learning of mathematics? What are the issues, problems, benefits, challenges, and dangers? (b) Should mathematics teachers be required to have mastery of such programs? Why or why not? (c) How should such software be incorporated into the mathematics or science curriculum? GEOMETER'S SKETCHPAD (a) Illustrate the concept of Pi using Geometer's sketchpad. Computational Tools - 2 (b) Solving real-life problems: (a) Knowing that P waves travel approximately 740 km/minute faster than S waves, determine the epicenter of an earthquake that produced the seismograms shown. Copy a map of showing three of the cities into Geometer's Sketchpad, and use the circle tool to draw circles around each with a radius equivalent to the distance to the epicenter. The location where all three circles meet is the epicenter. Include a screen shot showing how you determined the epicenter using Geometer's Sketchpad. Computational Tools - 3 (c) Using Geopeter's sketchpad develop a lesson to show how to calculate the height of a building or the diameter of the moon. The average distance to the moon is 384,402 km. Include graphics in your drawing. (d) Using the Sketchpad, develop a lesson to illustrate one or more theorems. Pythagorean Theorem Computational Tools - 4 Computational Tools - 5