Writing formal lab reports

Lab Reports For Organic Chemistry
In this course there are 3 types of labs; the discovery lab, the purification technique lab and the synthesis lab. It is very important that you understand what kind of lab you are doing as the report must reflect what type of lab it is.
All types of labs will begin with a Purpose and end with a Conclusion. The
Purpose is the reason for doing the lab, the question you are asking. The
Conclusion should
Purpose
The Question
Analysis
Conclusion
The Answer establish if you accomplish the purpose and/or answered the question. That which leads from the Purpose to the Conclusion is the Analysis.
I. Discovery Lab: What is the relationship between certain variables?
The first type of experiment is the Discovery Experiment. In this experiment, one looks for a relationship or pattern that is unknown. The relationship is between one variable and another. So the goal or purpose of a Discovery Lab can be to answer a question such as:
What is the Relationship between “Variable 1” and “Variable 2”?
The pattern or relationship can be qualitative or quantitative. A qualitative pattern might be: “The solutions turns red when heat is added.” or “The light bulb is brighter when the current is increased.” Qualitative patterns do not have numbers; they do not answer questions like “How much does it change?” A quantitative pattern usually answers the question “How much does that change when I change this.
A block diagram for a Discovery Lab might look like this:
PURPOSE
To Discover a relationship or pattern.
ANALYSIS
Carry out experiment, take measurements/make observations—use
CONCLUSION
Describe the relationship or pattern. reasoning to explain any patterns observed
II.
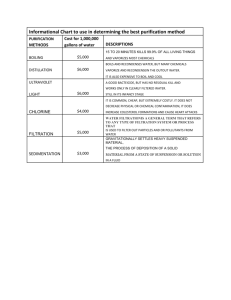
Purification Technique lab: Does a given technique purify the sample?
In the purification technique lab you learn the theory of a purification technique (the principles upon which a sample can be isolated/purified) and then you carry out this technique to purify an impure sample. In the end you will assess the purity of the sample and from this determine how well the technique worked Later in the course, these
techniques will be used at the end of the synthesis labs to purify the final product of a reaction.
A block diagram for a Purification Lab might look like this:
PURPOSE
To carry out the purification technique on an impure sample--Can this technique purify the sample?
ANALYSIS
Measurement of physical properties (including interpretation of spectra) of the sample to determine purity.
CONCLUSION
Did the results of the measurement indicate that the sample was purified?
III.
Synthesis lab: Did you synthesize the molecule you intended?
In the synthesis lab you will carry out a classical organic reaction and isolate the expected products of that reaction.(this often involves a purification of the product using one of the purification techniques learned in the purification labs).
A block diagram for a Synthesis Lab might look like this:
PURPOSE ANALYSIS
CONCLUSION
Did the measurements To carry out a given reaction and isolate the expected product (show balanced reaction equation).
Measurement of physical properties (including interpretation of spectra) of the mixture to determine the indicate that you synthesized and purified the expected product? identity and purity of the final product.
You should be aware that the data and procedure are also a part of all the 3 lab types.
They are part of the path from Purpose to the Conclusion. The procedure tells how the data was collected (so that anyone could repeat it) and the data is used in the analysis.
Writing Formal Lab Reports:
Formal Lab Reports must follow a format. The block diagrams should be the big picture plan for your lab report. On the next page is an outline for a standard Lab Report Format.
The outline contains 6 sections: Purpose, Theory, Data, Analysis, Conclusion and
Questions. Read the outline carefully to see how these sections differ depending on lab type.
Note : Lab reports are due one week from the completion of a lab.
LAB REPORT FORMAT
Title of Lab Name
Date
Partners
I PURPOSE:
For the discovery lab: What are you trying to find or show in this experiment? It is best to write the purpose in the form of a question.
For the purification lab . What purification technique are you using and what are you trying to purify?
For the synthesis lab.
What reaction are your carrying out— write the balance reaction equation for the reaction. Also state how the product is to be purified.
II THEORY:
For the discovery lab, the theory generally describes what led to the question asked in the purpose. What kinds of things might suggest that there is a pattern? In a comparison lab, the calculations and explanations should be given to support the expected model.
This expected model should also be described.
For the purification lab . What is the theory or idea behind the purification technique?
What physical property variable/difference is being manipulated in order to purify?
For the synthesis lab . Write the mechanism for the reaction.
III DATA: For all the labs the data should be displayed in neat tables , with all units and labels clearly given. Attach all spectra acquired (IR and NMR spectra).
IV ANALYSIS:
For the discovery lab: The analysis is the section where all manipulation of data is reported. Also included is all the reasoning that leads to the conclusions that are made.
Comments on any patterns or trends that shed light on the question posed in the purpose.
For the purification and synthesis labs you will show calculations for % recovery
(purification lab) and % yield (synthesis lab). Interpret all IR and NMR data in this section. Also comment on melting point, boiling points, and spectra in regards to purity of the sample.
V CONCLUSION: For all 3 type of lab you should describe briefly the results of your analysis.
VI ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS . Additional question may be assigned from the text.
These will be announced in class and posted on the web site.