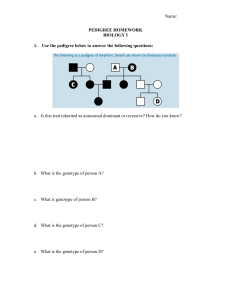
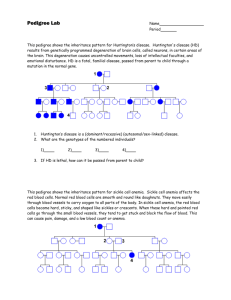
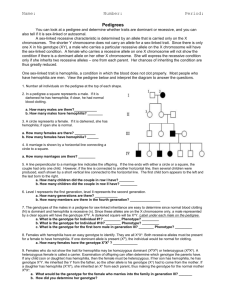
Human Pedigree Activity
advertisement
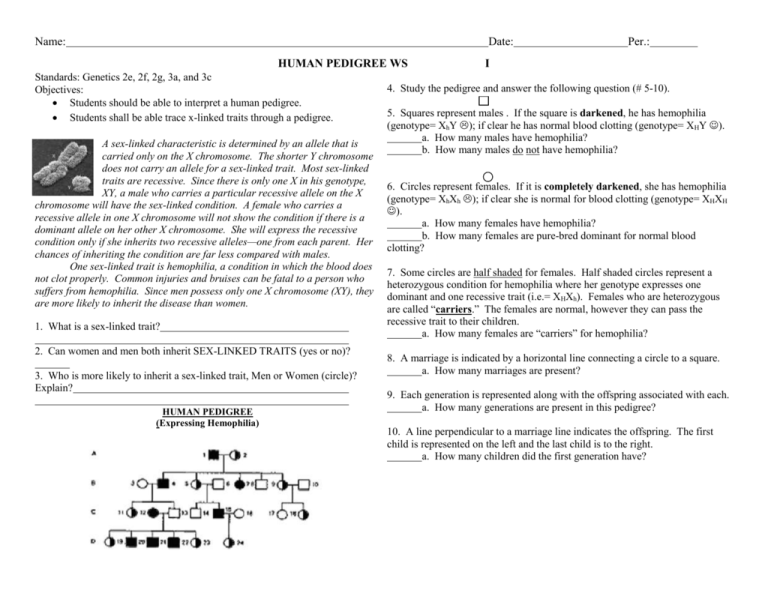
Name: Date: HUMAN PEDIGREE WS Standards: Genetics 2e, 2f, 2g, 3a, and 3c Objectives: Students should be able to interpret a human pedigree. Students shall be able trace x-linked traits through a pedigree. A sex-linked characteristic is determined by an allele that is carried only on the X chromosome. The shorter Y chromosome does not carry an allele for a sex-linked trait. Most sex-linked traits are recessive. Since there is only one X in his genotype, XY, a male who carries a particular recessive allele on the X chromosome will have the sex-linked condition. A female who carries a recessive allele in one X chromosome will not show the condition if there is a dominant allele on her other X chromosome. She will express the recessive condition only if she inherits two recessive alleles—one from each parent. Her chances of inheriting the condition are far less compared with males. One sex-linked trait is hemophilia, a condition in which the blood does not clot properly. Common injuries and bruises can be fatal to a person who suffers from hemophilia. Since men possess only one X chromosome (XY), they are more likely to inherit the disease than women. 1. What is a sex-linked trait? 2. Can women and men both inherit SEX-LINKED TRAITS (yes or no)? 3. Who is more likely to inherit a sex-linked trait, Men or Women (circle)? Explain? HUMAN PEDIGREE (Expressing Hemophilia) Per.: I 4. Study the pedigree and answer the following question (# 5-10). 5. Squares represent males . If the square is darkened, he has hemophilia (genotype= XhY ); if clear he has normal blood clotting (genotype= XHY ). a. How many males have hemophilia? b. How many males do not have hemophilia? 6. Circles represent females. If it is completely darkened, she has hemophilia (genotype= XhXh ); if clear she is normal for blood clotting (genotype= XHXH ). a. How many females have hemophilia? b. How many females are pure-bred dominant for normal blood clotting? 7. Some circles are half shaded for females. Half shaded circles represent a heterozygous condition for hemophilia where her genotype expresses one dominant and one recessive trait (i.e.= XHXh). Females who are heterozygous are called “carriers.” The females are normal, however they can pass the recessive trait to their children. a. How many females are “carriers” for hemophilia? 8. A marriage is indicated by a horizontal line connecting a circle to a square. a. How many marriages are present? 9. Each generation is represented along with the offspring associated with each. a. How many generations are present in this pedigree? 10. A line perpendicular to a marriage line indicates the offspring. The first child is represented on the left and the last child is to the right. a. How many children did the first generation have? Name: Date: HUMAN PEDIGREE WS Per.: I Applying the skill: Translate the following symbols into a genotype and phenotype, and assess the health status of individuals with sexlinked traits. Analysis: Use the pedigree above to answer questions #11-13 11. Why did family members in the second generation experience some Symbol Genotype 14. form of hemophilia? 15. 16. 12. a. How many children did couple 3-4 have? b. Why did child #11 receive a recessive hemophilia trait and #13 did not? 17. 18. 13. Child #13 did not have hemophilia and the family history with hemophilia could have ended with him. Why did his children end up with hemophilia? Phenotype Hemophilia, Normal, or Carrier. Affected or NOT Affected Name: Date: #11-18. The pedigree below is NOT HUMAN PEDIGREE WS I STOP! Do not answer the following until question #191-18 has been completed! correct. You will need to shade in the males and females correctly with the information already given (Hint: Work bottom –up. #7 will need to be shaded. Try to make the family as HEALTHY as possible Genotype Genotype Per.: 19. (#) How many marriages? 20. XY represents? 21. (#) How many XHY? 22. (#) How many XhY (Men with hemophilia)? 23. XX represents? 24. (#) How many XHXH? 1. 10. 25. (#) How many XHXh “CARRIERS”? 2. 11. 26. (#) How many XhXh (Women with hemophilia)? 3. 12. 27. Y or N Carrier females XHXh are affected with sex-linked traits. 4. 13. 5. 14. 6. 15. 7. XHXh “Carrier” 16. 8. 17. 9. 18.