MCV4U Introduction to Geometric Vectors
advertisement

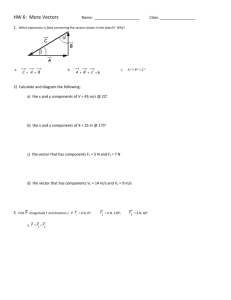
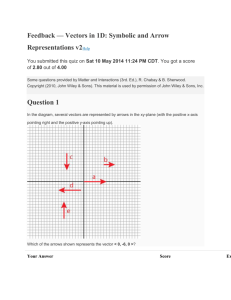
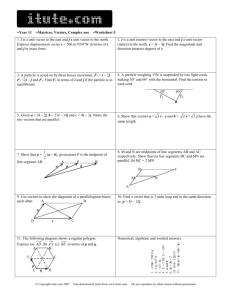
MCV4U Introduction to Geometric Vectors (Independent Study) Work through the following sections in the text book at your own pace. Make notes for yourself as you go, and complete practice exercises. Three days of class time will be allocated for this work. Expectations: 1. demonstrate an understanding of vectors in two-space and three-space by representing them algebraically and geometrically and by recognizing their applications; 2. perform operations on vectors in two-space and three-space, and use the properties of these operations to solve problems, including those arising from realworld applications 6.1: Characteristics of Vectors – p. 275 Scalars vs. Vectors (examples) Speed vs. Velocity Magnitude of a Vector Equivalent Vectors Coordinate system to represent vectors Connecting Vectors to 2-dimensional figures (Example 1) Practice: p. 279 # 1,2, 4, 6ace, 8bd, 9, 11 6.2: Vector Addition – p. 282 Parallelogram representation Triangle representation Resultant Vector Zero Vector Difference of Two Vectors Practice: p. 290 # 2, 3, 4, 7, 10, 11, 13, 17[TBF] Gizmos: On-line: Vector Addtion (self-test) 6.3: Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar – p. 293 Effect of k on k a Collinear / Parallel vectors Unit Vectors Vector Diagrams Direction Notation / Bearings Problem Solving Practice: 1, 3, 4, 5ad, 7, 11, 14, 17, 18, 22[TBF] 6.4: Properties of Vectors – p. 302 Commutative, Associative, Distributive with sketches Using Properties to perform vector operations Practice: p. 306 # 1, 8, 9, 11 Consolidation / Extra Practice Mid-Chapter Review - p. 308/309 (as needed)