Density
advertisement

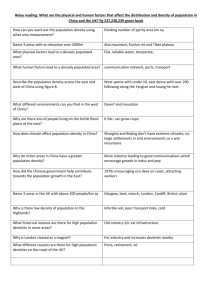
Michigan Geographic Alliance Presents Population Density & Natural Environments Amy Perkins Lakeshore Middle School Population Density & Natural Environments Amy Perkins, Lakeshore Middle School, Lakeshore Public School, Stevensville, MI 49085 Grade Level: 9th Grade Grade Level Content Expectation(s): Describe how processes like population growth, economic development, urbanization, resource use, international trade, and global communication are affecting different world regions. II.4.HS3 Interpret geographic information from maps, tables, graphs, charts, and text. V.1.HS.3 Lesson Overview This lesson will challenge students to identify how the natural environment (e.g. climate, availability of natural resources, landforms) affects human settlement patterns throughout the world. They will use a world population distribution map and a physical map of the world to examine the correlation between environmental factors and human population density. Objectives Students will be able to: Identify the environmental reasons for human settlement patterns throughout the world. Use data to compose a short essay explaining the correlation between environmental factors and human population density. Materials World Map of Natural Vegetation http://www.mapsofworld.com/thematic-maps/world-natural-vegetation.htm World Map of Minerals http://www.mapsofworld.com/world-mineral-map.htm World Map showing Energy Balance, Principal Oilfields, Coalfields, and Gasfields http://www.mapsofworld.com/thematic-maps/world-energy-balance-map.htm 1994 Population Distribution Map of the World http://soils.usda.gov/use/worldsoils/mapindex/popden.html) Physical Map of the World http://www.odci.gov/cia/publications/factbook/reference_maps/physical_world.html Requirements for Short Essay Composition Teacher Background Notes The population of the world in 1950 was 2.5 billion people and in 2000 it was approximately 6 billion. The increase in population over the 50 year period resulted in numerous changes in the human-environment interactions that occur in regions. For example, forested regions have been converted to grasslands. There are three aspects of the increase in population. First, it has not increased at the same rate in all parts of the world. Second, the population density of countries and regions increases as their total population increases. It is the increase in population density that usually has the greatest impact since most countries have some regions that have a better natural environment in which to live and other regions of a country are often not so well-suited. For example, China has the best environmental conditions (climate and soil fertility) in the southeastern coastal region and the interior is either mountainous or arid. Therefore, the population density of southeastern China is far greater than the northwest region. Finally, the third aspect is that where the population density is highest, the impact of the population on the environment is greatest. Students should have a basic understanding of the natural resources required to sustain a human population prior to the lesson. Students should be familiar with how governments have divided land and sea areas into different region prior to the lesson. Students should have experience composing short essays using data from maps/charts prior to the lesson. Procedure for Activity 1. Distribute copies of the 1994 Global Population Density of the World Map. b) Have students list the countries/global regions with the greatest population density. (Record list on the board) c) Have students list the countries/global regions with the lowest population density. (Record list on the board) d) Show students a physical map of the Earth. Divide students into small groups (34 students per group). Using the physical map, have students compare the two groups of countries/regions (i.e. those with the greatest and those with the lowest population densities) using the following questions or statements. Note: They should record their answers on their worksheets (see attachment). 1) Locate the most densely population regions on the physical map. a) What do the densely populated regions have in common? -rich in natural resources -easily accessible (near major transportation routes) -fertile soil b) Explain this phenomenon: Why do people tend to settle in these regions? -Natural resources enable economic growth, attract industry -Fertile soil is necessary for farming—feeding large populations -People typically settle in convenient locations—places that are easy to access and located along major trade routes 2) Locate the least populated regions on the physical map. a) What do the least populated regions have in common? -dry, infertile soil -difficult to access (mountains, deserts, landlocked—distant from major transportation routes) b) Explain this phenomenon: Why do few people settle in these regions with low population densities? -Few natural resources to attract industry, jobs -No fertile soil for farming; unable to produce enough food to feed a large population -The region is relatively inaccessible—not a convenient destination for people and distant from established trade routes. e) Instruct students to respond to the following question using a short essay format: How have natural environments (e.g. climate, availability of natural resources, landforms) influenced human settlement patterns in various world regions? Be sure to include specific examples to support your argument. *Suggestions for lesson extension: -Identify and discuss other factors that dramatically influence population density in various world regions (e.g. disease, war, environmental disasters). -How have recent advances in technology and transportation enabled humans to inhabit regions that are devoid of natural resources, fertile soil and hospitable climates? (Ex. Las Vegas, NV) 6. Assessment See the rubric below to assist with grading student essays. **See “Six Trait Analytic Writing Rubric” (http://www.ade.state.az.us/sbtl/6traits/) for additional information regarding assessment. 7. References -World Map of Natural Vegetation http://www.mapsofworld.com/thematic-maps/world-natural-vegetation.htm -World Map of Minerals http://www.mapsofworld.com/world-mineral-map.htm -World Map showing Energy Balance, Principal Oilfields, Coalfields, and Gasfields http://www.mapsofworld.com/thematic-maps/world-energy-balance-map.htm -1994 Population Distribution Map of the World (see http://soils.usda.gov/use/worldsoils/mapindex/popden.html) -Physical Map of the World http://www.odci.gov/cia/publications/factbook/reference_maps/physical_world.html 8. Student sheets (blackline masters) Worksheet: “Population Density and Natural Environments” 9. Answer keys and scoring guides Worksheet key: “Population Density and Natural Environments” Rubric for grading student essays Population Density and Natural Environments Using the physical map of the world, examine the correlation between population density and natural environments. Record your answers in the space provided. 1) Locate the most densely population regions on the physical map. a) What do the densely populated regions have in common? b) Explain this phenomenon: Why do people tend to settle in these regions with low population densities? 2) Locate the least populated regions on the physical map. a) What do the least populated regions have in common? b) Explain this phenomenon: Why do few people settle in these regions? 3) Short essay response: How have natural environments (e.g. climate, availability of natural resources, landforms) influenced human settlement patterns in various world regions? Be sure to include specific examples to support your argument. (Record your answer on the back side of this worksheet) Grading Rubric for Student’s Essay Student’s name: _______________ __/4 points that __/6 points Lists four or more environmental characteristics of regions/countries are densely populated. Uses three or more examples (2 points each) to demonstrate the correlation between the natural environment (climate, natural resources, landforms) and the human population density in various world regions. __/4 points Uses correct spelling and grammar. __/2 points Presents information in an organized manner. (Introduction, body, conclusion) __/16 points Total points awarded Comments: Student name:__Key______ Population Density and Natural Environments Using the physical map of the world, examine the correlation between population density and natural environments. Record your answers in the space provided. 1) Locate the most densely population regions on the physical map. a) What do the densely populated regions have in common? -rich in natural resources -easily accessible (near major transportation routes) -fertile soil b) Explain this phenomenon: Why do people tend to settle in these regions with low population densities? -Natural resources enable economic growth, attract industry -Fertile soil is necessary for farming—feeding large populations -People typically settle in convenient locations—places that are easy to access and located along major trade routes 2) Locate the least populated regions on the physical map. a) What do the least populated regions have in common? -dry, infertile soil -difficult to access (mountains, deserts, landlocked—distant from major transportation routes) b) Explain this phenomenon: Why do few people settle in these regions? -Few natural resources to attract industry, jobs -No fertile soil for farming; unable to produce enough food to feed a large population -The region is relatively inaccessible—not a convenient destination for people and distant from established trade routes. 3) Short essay response: How have natural environments (e.g. climate, availability of natural resources, landforms) influenced human settlement patterns in various world regions? Be sure to include specific examples to support your argument. (Record your answer on the back side of this worksheet) Student name:_________________