Unit 1 National 5 notesB2
advertisement

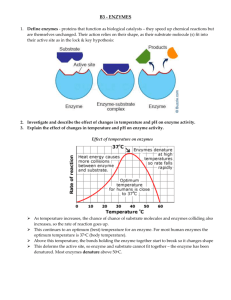
National 4 and 5 proteins enzymes and their use in industry Nat 5- Protein structure and function Proteins all have a 3-dimensional shape which is important in determining the proteins function this shape is determined by the order of amino acids the order of amino acids is determined by the order of the bases on the DNA Therefore, the structure and function of a protein is dictated by the order of bases on the DNA strand. The variety of protein shapes and functions arise from the sequence of amino acids. There gives rise to 3 different types of protein shape Proteins have many functions enzymes hormones e.g. insulin to regulate blood glucose levels antibodies (produced by white blood cells to fight infection) structural e.g. found in cell membrane and collagen in bone, tendon and ligament transport protein e.g. haemoglobin (found in red blood cells for transporting oxygen) National 4 and 5- Investigating Enzymes A catalyst is a substance that speeds up chemical reactions but is not changed in the process of doing so. Enzymes are made of protein and can be thought of as biological catalysts as they are found in living cells and speed up chemical reactions within the cell. 1 Enzymes are essential to living cells because without enzymes the cells chemical reactions would not proceed quickly enough to allow the cell to live. Examples of enzyme breakdown reactions Substrate Enzyme Catalase Hydrogen Peroxide End product(s) Water + Oxygen Amylase Starch Maltose Pepsin Protein Fats Peptides Lipase Fatty acids + Glycerol Examples of enzyme synthesis (building up) reactions Substrate Glucose Enzyme Phosphorylase End product(s) Starch Specificity of enzymes Every enzyme will act upon one substrate only and is said to be specific to that substrate, e.g. amylase will act on starch and nothing else, therefore amylase is specific to starch. National 5 - Effects of temperature and pH on enzymes Temperature Every enzyme has a temperature at which it is most active (works best). As the temperature is decreased below this value the enzyme becomes less and less effective until it is almost inactive. As the temperature is increased above this value the enzyme becomes less and less effective until it is denatured (destroyed). e.g. Pepsin breaks down most protein at 37oC, breaks down almost no protein at 4oC or below and is denatured at 60oC or above. 2 pH Every enzyme has a pH at which it is most active (works best). As the pH is decreased below this value the enzyme becomes less and less effective until it is almost inactive. As the pH is increased above this value the enzyme becomes less and less effective until it is almost inactive. pH’s which are very different from an enzymes optimum will denature the enzyme. e.g. Catalase will work from pH 7 to 11 but works best at pH 9. Most enzymes work best at pH 7 with pepsin being an exception as it works best at pH 2-3. Optimum conditions The temperature at which an enzyme is most active is said to be that enzymes optimum temperature. The pH at which an enzyme is most active is said to be that enzymes optimum pH. Each enzyme has a particular optimum temperature and pH at which it is most active. This temperature and pH is different for each enzyme depending upon the living cell it is in. National 4-Biological detergents Biological detergents contain enzymes produced by bacteria. Biological detergents remove stains because the enzymes they contain act upon the substance that is causing the stain (e.g. blood, grass) and break it down by digesting it. As the enzymes would be denatured at high temperatures, biological detergents work best at lower temperatures (around 40oC). Advantages of biological detergents 3 1. They will break down and remove biological stains like grass and blood that non-biological detergents cannot. 2. They save money on the cost of fuel and prevent fabrics being damaged because they work best at low temperatures. Biological detergents remove stains because the enzymes they contain act upon the substance that is causing the stain (e.g. blood, grass) and break it down by digesting it. As the enzymes would be denatured at high temperatures, biological detergents work best at lower temperatures (around 40oC). National 4- Production of cheese Cheese and yoghurt production requires lactic acid to make the milk curdle Certain bacteria are added to the milk and they produce the required lactic acid by fermentation Rennet is an enzyme that clots the milk and is used in cheese making. Check point B2 Level 4 E&O I have taken part in practical activities which involved the use of enzymes and microorganisms to develop my understanding of and their use in industry Nat 4 Properties of enzymes and their use in industry Enzymes are found in living cells. They are specific, speed up reaction and remain unchanged by the reaction. Enzymes build up and break down molecules. Enzymes xan be used in a range of biological industries. Enzymes are used in the detergent industry and in cheese making (rennet) Nat 5 5 Proteins and enzymes a. The variety of protein shapes and functions arises from the sequence of amino acids. b. Functions of proteins to include structural, enzymes, hormones, antibodies and receptors. c. Enzymes function as biological catalysts and are made by all living cells. They speed up cellular reactions and are unchanged in the process. The shape of the active site of enzyme molecules is complementary to a specific substrate. 4 d. Each enzyme works best in its optimum conditions. Enzymes and other proteins can be affected by temperature and pH. Enzymes can be denatured, resulting in a change in their shape, which will affect the rate of reaction. 5