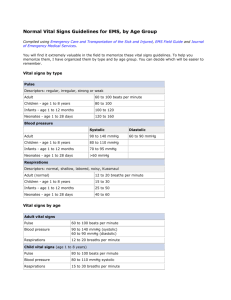
Pediatric Formulas Estimated body weight Age 1 to 8 years: weight
advertisement

Pediatric Formulas Estimated body weight Age 1 to 8 years: weight = 8 + (2 x age in years) Over 8 years of age: weight = 3 x age in years Estimated blood pressure Systolic BP = 80 + 2(age in years) Diastolic BP = 2/3 x systolic BP Heart rate Age < 1 – 110-160 bpm Age 2 -5 – 95-140 bpm Age 5-12 – 80-120 bpm Over 12 – 60-100 bpm Normal maintenance fluid requirements First 10 kg – 4ml/kg per hour (100ml/kg/day) Second 10 kg – add 2ml/kg/hour for every kg over 10 kg to above (40ml/kg/hr + x) (+50ml/kg/day) Over 20 kg – add 1ml/kg/hour for every kg over 20 kg to above (60ml/kg/hr + y) (+25ml/kg/day) Normal respiratory rates Age < 1 – 30-40 rpm Age 2-5 – 25-30 rpm Age 5-12 – 20-25 rpm Over 12 - 15-20 rpm Guide to Endotracheal tube size (internal diameter) ETT size (mm) = Age in years / 4 + 4 Rough guide to tube length o Oral ETT length (cm) = Age in years / 2 + 12 o Nasal ETT length (cm) = Age in years / 2 + 15 Cuffed tube recommended after age of 12 years but considered where high pressure ventilation is anticipated Practically correct diameter is that which results in a small leak at an inspiratory pressure of about 25 cm of water Tube should be at mid-trachea – between the clavicles on an AP CXR Severe croup patients may need one size smaller than calculated Calculating replacement fluid therapy following resuscitation Volume of rehydrating fluid (ml) = body weight (kg) x % estimated dehydration(up to 5%) x 10 Calculating amount of sodium repletion in hyponatremia Mmol Na required = (proposed serum Na – present serum Na) X 0.6 X body weight in kg Replaced over a 24 – 48 hour period. 1) Formulas and General Rules (Children over 1 year old) a) Formulas (Systolic Blood Pressure) i) Median SBP = 90 mmHg + (2 x Age in years) ii) Minimum SBP = 70 mmHg + (2 x Age in years) b) Rough Approximations i) Pulse or Heart Rate (HR) (1) Infant Pulse: 160 (2) Preschool Pulse: 120 (3) Adolescent Pulse: 100 ii) Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP) (1) Infant SBP: 80 (2) Preschool SBP: 90 (3) Adolescent SBP: 100 iii) Respiratory Rate (RR) (1) Infant RR: 40 (2) Preschool RR: 30 (3) Adolescent RR: 20 2) Indications for rapid cardiopulmonary assessment a) Systolic Blood Pressure is observed to drop 10 mm Hg b) Respiratory Rate >60 c) Heart Rate outside ranges shown below d) Increased work of breathing i) Retractions ii) Nasal Flaring iii) Grunting e) Cyanosis or decreased Oxygen Saturation f) Altered LOC (irritability, lethargy) g) Seizures h) Fever with Petechiae i) Trauma j) Burns >10% of body surface area 3) Age associated Vitals a) Term Newborn (3 kg) i) Blood Pressure: (1) Age 12 hours: 50-70 / 25-45 (2) Age 96 hours: 60-90 / 20-60 (3) Age 7 days: 74 +/- 22 mmHg (Systolic BP) (4) Age 42 days: 96 +/- 20 mmHg (Systolic BP) ii) Pulse: 80-200 iii) Respiratory Rate: 40-60 b) Infant (6 months old) i) Blood Pressure: 87-105 / 53-66 ii) Pulse: 80-180 c) Toddler (2 years old) i) Blood Pressure: 95-105/53-66 ii) Pulse: 80-180 iii) Respiratory Rate = 24 d) School age (7 years old) i) Blood Pressure: 97-112 / 57-71 ii) Pulse: 60-160 e) Adolescent (15 years old) i) Blood Pressure: 112-128 / 66-80 ii) Pulse: 60-160 iii) Respiratory Rate = 12