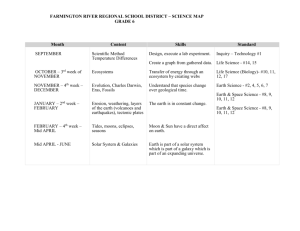
Binary Search Average Case Complexity Analysis
advertisement

Average case complexity analysis for binary search
function binsrch2(low, high: index)
if low > high then return(0)
else
mid (low + high)/2
if x = A[mid] then
return(mid)
else if x < A[mid]
return(binsrch2(low, mid - 1))
else
return(binsrch2(mid + 1, high)
endif
Main program function call:
location binsrch2(1, n)
The binary search is done on the elements in array A. There are n values in A and n+1 gaps,
so a given value of x may lie in any of 2n + 1 places. To keep the analysis manageable, we will
assume x is equally likely to lie in any of these places. That is,
pr(x = ai) = pr(x gj) = 1/(2n + 1) so
Ta(n) = pr(I)*c(I)
IDn
Let's sum the values level by level in the binary search tree that corresponds to the algorithm.
k
Ta(n) = [1/(2n+1)]•2i-1•i + [1/(2n+1)]•(n+1)•k (successful + unsuccessful)
i=1
k
Ta(n) = [1/(2n+1)] • ( Σ 2i-1•i + (n+1)•k)
i=1
k
k
Notice that (i•2i-1) = ½ (i•2i)
i=1
i=1
k
Let Sk = (i•2i )= 1•21 + 2•22 + 3•23 + ... + k•2k so
i=1
k
2 Sk = (i•2i) = 1•22 + 2•23 + 3•24 + ... + k•2k+1 Subtracting we get
i=1
k
k
Sk = k•2k+1 - (21 + 22 + ... + 2k ) = k•2k+1 - 2i = k•2k+1 –( 2i – 1)
i=1
= k•2k+1 - (2k+1 - 1) + 1 = (k-1)•2k+1 + 2
i=0
Thus,
k
Ta(n) = [1/(2n+1)] • ( (i•2i-1) + (n+1)•k) = [1/(2n + 1)]•{ ½ [(k-1)•2k+1 + 2] + (n+1)•k }
i=1
= [1/(2n + 1)]•[(k-1)•2k + 1 + (n+1)•k]
Since n = 2k - 1 we have
Ta(n) = (k-1)2k + k•2k = (2k - 1)•2k + 1 = 2k•(2k - 1) +
1___
k+1
k+1
k+1
k+1
2 -1
2 -1
2 -1
2 -1
= __2k • (2k - 1)
2k - ½
2
+
1__
2k+1 - 1
which is approximately (2k - 1)/2 = k - 1/2 = lg n + ½