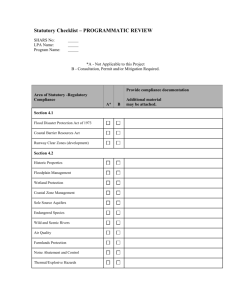
This document reviews commonly asked questions for the
advertisement

Echelon Biosciences Inc. 675 Arapeen Drive, Suite 302 Salt Lake City, UT 84108 Telephone 866-588-0455 Fax 801-588-0497 echelon@echelon-inc.com www.echelon-inc.com Question and Answer Sheet For research use only Not intended or approved for diagnostic or therapeutic use. The LPA Assay Kit was co-developed using the proprietary monoclonal antibody of Lpath Inc. (San Diego, CA). Lpath, Inc. has a number of patent applications pending or issued covering material(s) incorporated into this assay. The assay’s sole permitted use is for non-clinical research to measure LPA in biological samples. Any other use, including drug discovery, requires a license from Lpath (www.lpath.com). This document reviews commonly asked questions for the Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) Assay kits; catalog numbers K-2800 and K-2800B LPA standard and % recovery of different acyl chains. Q: What version of LPA is used for the standard in the LPA assay, catalog number K-2805? A: In preparing the LPA standard (K-2805) we use C18:3, Echelon catalog number L-0183. Product Name: D (+)-sn-1-O-linolenoyl-glyceryl-3-phosphate (Sodium Salt) Product Number: L-0183 Formula: C21H35Na2O7P, FW: 476.45 ONa H O P OH O 0.2 0.1 0.0 DHS Rat serum Figure 3: Background control (No Anti-LPA) was run with both delipidized human sera (DHS) and Rat serum in the K-2800 and K-2800B LPA assay kits. Non-specific binding from antibodies present in serum was observed in the K-2800 kit when rat serum was used. C18:3 0.00 0.1 C20:0 0.5 100 1000 Note: It is assumed that these results apply to both the K2800 and K-2800B since the K-2800B assay utilizes the same primary antibody and similar assay format 10000 LOG10 [LPA], nM Figure 2: Different mixtures of LPA in the K-2800. Mixtures were designed based on biological activity1. Each LPA mixture was prepared by mixing LPA at 1:1 ratio. LPA Mixture = C14:0. C16:0. C18:0, C18:1, C18:2, C18:3, C20:0, C20:4. High (Biological) Activity = C18:1, C18:2, C18:3. Low (Biological) Activity = C18:0, C14:0 LPA Spike-in (µM) Calculated (µM) % Recovery LPA Mixture High Activity LPA Mixture Low Activity LPA Mixture 5 5 5 1.22 2.70 0.49 24% 54% 10% 1 10 100 1000 10000 Q: Has this assay been verified LOG10 [LPA], nM by mass spec analysis? Figure: 3 A comparision of the K-2800 and K-2800B standard curves A: Mass spectrometry analysis, performed by an outside lab, found that undiluted human serum Parameter K-2800 K-2800B samples run in the LPA assay gave 230 nM 15 nM EC50 comparable LPA values. The same 0.99 0.99 R2 patient samples were anylized 160 nM 12 nM Sensitivity using mass spectrometry and K0.87 0.98 Z’ 2800 ELISA. The samples were run in triplicate. For more information please see “AACR poster” (available on website) for further details of the mass spectrometry/ ELISA comparison study. Q: What lipids interfere with the assay? A: We have analyzed Structuraly Simular Lipid crossreactivity structurally similar lipids (Figure 4), and membrane Glycerol Phosphate lipids (Figure 5) in the KMG C18:1 2800 ELISA with no cross MG C16 (migrated) MG C18:1 (migrated) reactivity observed at the LBPA C18 concentrations tested. LBPA C12 (biotin) LBPA C12 LPA C18:3 0. 00 LPA mixtures were prepared based on biological activity1,2 100 1000 10000 LOG10 [LPA], nM and assumed LPA species Figure 1: Sensitivity and specificity of the K-2800 assay present in serum. The percent for different acyl chains of LPA. recovery of the different LPA LPA Mixture % recovery mixtures was 1.0 0 LPA LPA C18:3 calculated using the LPA Mixture LPA C18:3 curve for High Activity LPA comparison. Low Activity LPA C20:4 0 10 Abs 450nm . 2. 00 C18:2 1 Ba .50 se lin 1. e 75 C18:1 1 1. 25 C18:0 Assay sensitivity and cross-reactive data with similar lipids. Q: What is the LPA assay’s LPA standard Curve Comparision sensitivity? 1.00 A: The sensitivity of the LPA ELISA (K-2800) is 0.16 μM. 0.75 K-2800B However, the Universal LPA K-2800 0.50 ELISA (K-2800B) has a much higher sensitivity of 12 nM 0.25 (Figure 3; Table 2). 1. 00 C16:0 2 Different LPA chain lengths and saturation were run in the K-2800 LPA assay (See figure 1). A decrease in chain length and saturation resulted in decreased potency in the assay. 0. 75 C14:0 0 LPA O.D.450 0.3 0. 50 LPA Acyl Chain Comparison O.D.450 0.4 O 3 0.0 10 K-2800B K-2800 0.5 0. 25 O Non-specific binding 0.6 Q: I am running mouse samples, why do they contain such high levels of LPA? A: The K-2800 assay kit utilizes an anti-mouse-HRP conjugated secondary antibody. This antibody has been known to cause high background in mouse and rat serum samples due to endogenous antibodies present in the serum. The K-2800B kit does not use this secondary antibody and therefore does not have elevated non-specific binding from these sample sources (Figure 3). O.D.450 NaO Primary and/or secondary antibody questions. Q: What is the isotype of the primary antibody? A: Mouse IgG Ab450 Assay platform: Q: Why do higher levels of LPA cause a decrease in the assay signal? A: The LPA assays are competitive assays, in which the LPA bound to the plate, competes for binding to the antibody with the LPA in solution. As the LPA in solution increases the amount of anti-LPA antibody that binds the plate is reduced, lowering the observed signal. Figure 4: Structuraly simular lipids to LPA were ran in the LPA ELISA (K-2800) at 2 M concentration. -1- 533566990 Common membrane lipids crossreactivity References: 2.0 baseline OD 450 nm 1.5 1. Jalink K, Hengeveld T, Mulder S, Postma FR, Simon MF, Chap H, van der Marel GA, van Boom JH, van Blitterswijk WJ, Moolenaar WH. Biochem Lysophosphatidic acid-induced Ca2+ mobilization in human A431 cells: structure-activity analysis. Biochem J. 1995 Apr 15;307 ( Pt 2):609-16 2. Tokumura A, Sinomiya J, Kishimoto S, Tanaka T, Kogure K, Sugiura T, Satouchi K, Waku K, Fukuzawa K.Human platelets respond differentially to lysophosphatidic acids having a highly unsaturated fatty acyl group and alkyl ether-linked lysophosphatidic acids. Biochem J. 2002 Aug 1;365(Pt 3):617-28. 1.0 10 M 0.5 2 M pl e D ilu en t SP C Sa m P SP PS S1 PE PG PC PA G A LP C D LP A 0.0 Lipids Figure 5: Cell membrane lipids were tested for cross reactivity in the K-2800 assay kit. All lipids were prepared in DHS at 10 µM and 2 µM. Run in triplicate. LPA = Lysobisphosphatidic Acid C18:3, DAG = Diacylglycerol, LPC = Lysophosphotidylcholine, PA = Phosphatidic Acid, PC = Phosphatidylcholine; C16, PE = Phosphatidylethanolamine; C16, PG = Phosphatidylglycerol, PS = Phosphatidylserine; C16, S1P = Sphingosine 1 Phosphate, SP = Sphingosine, SPC = Sphingosylphosphorylcholine, Sample = Random Human Sera, tested in 1X & 10X dilution, Diluent = Delipidized Human Sera (DHS), use as baseline Sample Preparation for other sources of LPA Q: What other types of samples have been verified in the LPA assays and what is the proper dilution? A: The K-2800 and K-2800B were developed for the determination of LPA in human serum and plasma. However, due to the interest in other sources of LPA we are currently working to broaden the use of these kits (see table). An example of human, goat and rat serum is shown below (Figure 5). Sample Source Cat # K-2800/K-2800B K-2800B K-2800B Dilution factor of sample Neat * * Human Sera/Plasma Tissue Cell lysate Animal sera/plasma Mouse/Rat Diluted in DHS DHS DHS K-2800B * DHS * To be determined; work in progress. Performance of different serum sources 1.75 1.50 K-2800B uM LPA 1.25 K-2800 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 oa t G um H H um an (# 62 ) an R at (# sp 36 ik ) ed 0. 5 M G oa ts R pi at ke d 0. 5 M 0.00 Figure 5. An example of Human, Rat, and Goat serum with and without 5 M LPA spike. Goat and rat serum anylized in both LPA assays. . -2- 533566990