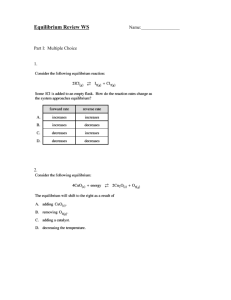
Tall: 1) The decomposition of CaCO3 is an endothermic process:
advertisement

Chemistry – Equilibrium Tall: 1) Name: _______________________Date: _________- Period: _______ The decomposition of CaCO3 is an endothermic process: CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) a) Use LeChatelier’s Principle to explain how an increase in temperature would affect the equilibrium. b) If more CaCO3 is added to a flask in which this equilibrium exists, how is the equilibrium affected? c) If pressure within a flask in which this equilibrium exists is increases, how is the equilibrium affected? 2) Write equilibrium constants for the following reactions: a) (NH4)2CO3(s) 2 NH3(g) + CO2(g) + H2O(g) b) CO(g) + ½ O2(g) CO2(g) d) Fe2+(aq) + Sn(s) Sn2+(aq) + Fe(s) e) N2O4(g) + O3(g) N2O5(g) + O2(g) 3) Neither PbCl2 nor PbF2 are appreciably soluble in water. If solid PbCl2 and solid PbF2 are placed in separate beakers, in which beaker is the [Pb2+] greatest? Explain your choice. The equilibrium constants for the solids dissolving in water are: PbCl2(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2 Cl¯(aq) PbF2(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2 F¯ (aq) K = 1.7x10-5 K = 3.7x10-8 Chemistry – Equilibrium Name: _______________________Date: _________- Period: _______ Grande 4) The reaction below has an equilibrium constant, Keq, of 171 at 25oC. Using the reaction conditions given, determine if the reaction is product-favored, reactant-favored, or at equilibrium. Don’t forget to find Molarity first! 2 NO2(g) N2O4(g) a) 2.0x10-3 mol NO2, 1.5x10-5 mol N2O4, 10.0 L flask b) 1.5x10-4 mol NO2, 2.0x10-3 mol N2O4, 10.0 L flask c) 2.0x10-3 mol NO2, 1.5x10-3 mol N2O4, 5.0 L flask 5) At room temperature the equilibrium constant Keq for the reaction: 2NO(g) N2(g) + O2(g) is 1.4x1030. In the atmosphere at room temperature the concentration of nitrogen gas is 0.33 mol/L and the concentration of oxygen gas is about 25% that value. Calculate the equilibrium concentration of nitrogen monoxide in the atmosphere. Venti 6) A 1.00 mol sample of CO2 is heated to 1000K with excess graphite in a container of volume 40.0 L. At this temperature, Kc is 2.11x10-2 for the reaction: C(graphite) + CO2(g) 2 CO(g) a) b) What are the equilibrium concentrations of each species? If the volume of the flask is changed so a new equilibrium is established in which the amount of CO2 in the flask equals the amount of CO, what is the new volume of the flask?