Name: - lyneezajacbeck
advertisement

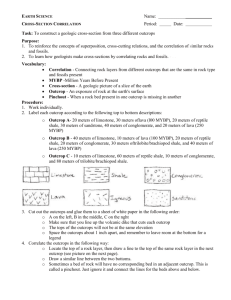
Geologic Correlation Activity Name _____________________ Block _____ Objective: To be able to construct a geologic cross-section from information provided from three different outcrops and interpret the geologic history based on the rock record. Purpose: 1) To demonstrate understanding of the processes that form different geologic units and how they are interrelated. 2) To reinforce the concepts of superposition, original horizontally, and cross-cutting relationships. 3) To learn how geologists evaluate geologic history by correlating rock units and fossil assemblages. Geologic Information: The following information has been determined by interpreting rock outcrops. The descriptions start at the top and work down the geologic section. OUTCROP A: 20 meters of limestone, 30 meters of lava (dated at 100 mybp), 20 meters of shale with reptile fossils, 30 meters of sandstone, 40 meters of conglomerate with an interbedded igneous dike (dated at 50 mybp), and 20 meters of lava (dated at 250 mybp). OUTCROP B: 40 meters of limestone , 10 meters of lava (dated at 100 mybp), 20 meters of shale with reptile fossils, 20 meters of conglomerate with an interbedded igneous dike, 30 meters of shale with trilobite/ brachiopod fossils, and 40 meters of lava (dated at 250 mybp). OUTCROP C: 10 meters of limestone, 60 meters of shale with reptile fossils (this unit has been cut by an igneous dike), 10 meters conglomerate, and 80 meters of shale with trilobite fossils. Procedure: 1. Work individually and identify each outcrop based on the information provided above. Cut out the outcrops and glue or tape them to a sheet of plain paper in the following order: Section A on the left, Section B in the middle, and Section C on the right. Label each of the sections at the top of the column. Make sure that you line up the volcanic dike that cuts through each unit. The tops of each unit will not necessarily be at the same elevation. 2. Space the three outcrops approximately one (1) inch apart on the paper. Make sure to leave room to place the legend you will create at the bottom of the page. 3. Correlate the three outcrops and evaluate the geologic history that is presented in the rock record. Start at the bottom of Section A and correlate the units between section A and Section B (section B should be to the right of Section A) as you work your way up the section of rock. Remember, not all units need to be present in both sections in order to correlate the sections. Sometimes a rock unit will have no corresponding unit in an adjacent outcrop, this is called a pinchout. This indicates that somewhere between the two areas the unit was either never deposited or was eroded away after deposition. 4. Draw lines between the sections to indicate where the different units are between them. In the areas between the outcrops, sketch in the appropriate pattern; dots for sandstone, blocks for limestone, etc. See example below. 1 5. Color each bed on your geologic cross section according to the following: Limestone = Yellow Shale = Gray Conglomerate = Orange Sandstone = Tan Igneous Dike = Pink Lava = Red 6. Construct a legend near the bottom of the page that shows the pattern, color, and type of each rock unit. 7. On a separate piece of paper, answer the analysis questions below. Analysis Questions 1. Identify and describe the oldest and the youngest rock units identified in the three outcrops. 2. Is the 100 mybp lava unit older or younger than the shale with the reptile fossils? Explain why? 3. Explain why the 50 mybp igneous dike may or may not be the youngest unit in your cross-section? Explain your answer. 4. Which set of fossils are older, the trilobites or the reptiles? Explain why? 5. Which geologic concept, or law, would you use to support this statement: “The igneous dike is younger than the shale unit with reptile fossils.” Explain your answer. 6. Which type of age dating would support the statement: “The two lava flows are separated by 150 million years of time”? 7. What explanation do you have for the 100 mybp lava being present in Outcrop A and B, but not in Outcrop C? 8. In your own words explain the terms; Law of Superposition, Law of Original Horizontality, and the Law of CrossCutting relationships. 2 3