Syllabus (Pharmacology) for the students of 3rd year (MPHL – 232)
advertisement

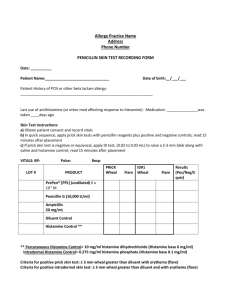
Syllabus (Pharmacology) for the students of 2nd year (MPHL – 231) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. General Pharmacology Cholinergic /Anticholinergic Drugs skeletal muscle relaxants Adrenergic /antiadrnergic drugs Autocoids Diuretics Drugs in heart failure Antiarrhythmic Drugs Antihypertensive Drugs Antianginal Drugs Drugs in hyperlipidemia Anticoagulants Fibrinolytics / Antiplatelet drugs Antianeamic Drug Antidiabetic Drugs Corticosteroids Thyroid /Antithyroid Drugs Fertility /antifertility Drugs Oxytocics and Uterine relaxants Prescription writing Syllabus (Pharmacology) for the students of 3rd year (MPHL – 232) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. Antimicrobial drugs Drugs to treat Tuberculosis (T.B) /Leprosy Immunopharmacology Cancer chemotherapy Antifungal drugs Local anesthetics General anesthetics Anthelmintic drugs Antischistosomal drugs Drugs to treat leishmaniasis Antiamoebic drugs Sedatives / hypnotics Antianxiety drugs Drugs in migraine Drugs in epilepsy Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs(NSAIDs) Drugs in gout Opioid analgesics Drugs in Parkinson's disease Antipsychotic drugs Antidepressant drugs Mood Stabilizing drugs Respiratory Pharmacology Drugs to treat peptic ulcer Drugs in bowel dysfunction PRACTICALS/EXPERIMENTS ON LIVE ANIMAL AND ISOLATED ANIMAL TISSUES MPHL – 231 1. Guinea pig ileum 2. Rabbit's eye 3. Isolated rabbit heart 4. Cat blood pressure. MPHL – 232 1. Local anaesthetics 2. Effects of anti-inflammatory drugs 3. Effects of anticonvulsant drugs 4. Sleeping time PRACTICAL # 1 EFFECTS OF AUTOCOIDS ON ISOLATED GUINEA-PIG ILEUM DRUGS 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Histamine Mepyramine Cimetidine Prostaglandins: PGE2 / PGF2 Acetylcholine Atropine 10 g / ml 10 g / ml 10 g / ml 10 g / ml 10 g / ml 100 g / ml METHOD: A piece (2-3 cm) of the ileum is suspended in an organ bath containing Tyrode solution through which air is blown. The temperature of the outer bath is maintained at 32C. Contractions of the ileum in response to drugs are recorded using one-channel electronic recorder. The following cycle is used: 0 min 1 min 1.5 min 3.0 min Start the recorder Add the drug Stop the recorder and wash the preparation Start the recorder Proceed to test the effects of different autacoid drugs as follows: 1. Study the relationship between the dose and response by testing the effect of different doses of histamine: 0.1 ml histamine solution 0.2 ml histamine solution 0.3 ml histamine solution 0.4 ml histamine solution You can measure the contractions to construct a dose-response curve. 2. Add 0.1 ml of mepyramine solution to the bath and allow it to act for 1 minute. Then without washing it, add histamine (the dose which produced the submaximal response in the previous step). 3. Add 0.1 ml cimetidine solution to the bath and allow it to act for 1 minute, then without washing, test the effect of the submaximal dose of histamine. 4. Study the effect of 0.1 ml of the prostaglandin solution you have. 5. Study the effect of 0.1 ml solution of acetylcholine. 6. Add 0.2 ml atropine solution to the bath, leave it to act for 1 minute, then without washing add 0.1 ml of acetylcholine solution. 7. Record your results and write your comments in the attached table. EFFECT OF DRUGS ON ISOLATED GUINEA – PIG ILEUM PREPARATION NO. 1. 2. DRUG Histamine (10 µg / ml) 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 Mepyramine (10 µg / ml) ml Wash ml “ ml “ ml “ 0.1 ml 3. No Wash Then: Histamine Cimetidine (10 µg / ml) 0.1 ml 4. No Wash Then: Histamine Prostaglandin (10 µg) 5. ACH 0.1ml (10 µg / ml) 6. 0.1 ml Atropine (10 µg / ml) 0.2 No Wash Then: ACH 0.1 ml ml OBSERVATION AND COMMENTS PRACTICAL # 2 MPHL – 231 (II YEAR) – EFFECTS OF DRUGS ON RABBIT’S EYE OBJECT: To test the effects of drugs on the rabbit’s eye. Drugs: 1. 2. 3. 4. Procedure: A. following: 1. 2. 3. Phenylephrine Pilocarpine Atropine Lignocaine = = = = 0.12% 1% 1% 2% Before adding the drugs examine the eyes for the Size of the pupil Light reflex Corneal reflex B. Add 2 drops of the drug to be tested into the conjuctival Sac. Wait for 5 minutes. Examine the eye. If there is no response, add another 2 drops of the same drug in the same eye. Wait again for 5 minutes and examine the eyes for any change in the above parameters. RECORD YOUR OBSERVATIONS IN A TABULATED FORM ON THE ATTACHED PAGE. Observations and Comments: Size of Pupil Light Reflex Corneal Reflex DRUGS Before Drug Phenylephrine Pilocarpine Atropine Lignocaine After Drug Before Drug After Drug Before Drug After Drug COM MENT S PRACTICAL # 3 PRACTICAL SHEET FOR MPHL – 231 EFFECTS OF DRUGS ON THE ISOLATED PERFUSED RABBIT HEART LANGENDORFF’S TECHNIQUE PROCEDURE: In this method, the heart is perfused through the aorta oxygenated Lock’s solution at a constant pressure from the reservoir. The pressure of the perfusing fluid closes the aortic valve, so the fluid passes only through the coronary vessels and escapes from the excised inferior vena cava, keeping the tissues warm and moist. The temperature of the Locke’s solution is maintained to 37 degree ceintigrade (37C). PARAMETERS TO BE RECORDER: 1. 2. AMPLITUDE OF CONTRACTION HEART RATE DRUGS TO BE STUDIED: Noradrenaline Adrenaline Isoprenaline Acetylcholine Atropine Propranolol Potassium Chloride Halothane 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Make sure you have a control recording of each parameter before injecting any drug. Always use separate syringe for each drug. Record your OBSERVATIONS in the attached sheets. Procedure 1. CONTROL Noradrenaline 5g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3-5 minutes CONTROL 2. Adrenaline 5 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3-5 minutes Amplitude of Contraction (mm) Heart rate (Beat/min.) Comments CONTROL 3. Isoprenaline 0.2 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3-5 minutes 4. CONTROL Acetylcholine 2 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3-5 minutes CONTROL 5. KCL 8 mg/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3-5 minutes CONTROL 6. Atropine 40 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 2 minutes CONTROL 7. Acetylcholine 2 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3-5 minutes CONTROL 8. KCL 80 mg/ml 0.5 ml Wait 5 minutes CONTROL 9. Isoprenaline 0.2 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3-5 minutes CONTROL 10. Propranolol 0.2 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3 minutes CONTROL 11. Isoprenaline 0.2 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 5-10 minutes CONTROL 12. Halothane 8 g/ml 0.5 ml Wait 3-5 minutes CONTROL. PRACTICAL #. 4 LAB PRACTICAL SHEET FOR MPHL-231 EFFECT OF AUTONOMIC DRUGS ON THE BLOOD PRESSURE OF THE CAT PROCEDURE: A cat is anaesthetized with pentobarbitone and chloralose (80 mg/kg). The trachea is cannulated and respiration is maintained by a respiration pump. The left carotid artery is exposed, cannulated, and connected to a pressure transducer for blood pressure recording. The femoral vein of the right leg is cannulated for i.v. injection of drugs. Drugs to be tested are administered i.v. followed by an injection of 2ml of 0.9% saline. The effects of the following drugs are to be recorded on the attached sheet. S.No. 1. 2. DRUG Noradrenaline (5 g /kg) Adrenaline (5 g /kg) 3. Tolazoline (10 mg /kg) 4. Adrenaline (5 g /kg) OBSERVATION COMMENTS 5. Isoprenaline (5 g /kg) 6. Pindolol (1 g /kg) 7. Isoprenaline (5 g /kg) 8. Acetycholine (1 g /kg) S.No. DRUG 9. Atropine (2 mg /kg) 10. Acetylcholine (A) - 1 g /kg 11. Acetylcholine (B) – 0.5 mg / kg OBSERVATION COMMENTS PRACTICAL # 1 MPHL -232 LOCAL ANAESTHTICS PRACTICAL # 2 – MPHL-232 ANTI-INFLAMMATORY DRUGS LAB PRACTICAL SHEET FOR MPHL-232 Demonstration of the Anti-inflammatory effects of some NSAIDS In Rats Methods: This method measures the increase in paw volume (oedema) of rats following the administration of the inflammatory substance carrageenan (1%). 1. 2. The paws of the right limbs of all animals are marked, and their volumes measured by using a plethysmometer. At zero time: The test drugs or their vehicles are administered to all the rat groups as follows: Group I : Diclofenac (5mg/kg, i.p.). Group II : Propylene glycol/i.p. (Control for group I). Group III Group IV III). : : Aspirin (300mg/kg, p.o.). Carboxymethycellulose/p.o. (Control of group (CMC) Group V Group VI group V). : : Ibuprofen (20mg/kg, p.o.). Carboxymethylcellulose /p.o. (Control for (CMC) 3. At 15 minutes: Carrageenan (0.1ml/paw) is injected in the right hind paws of rats in groups I and II. 4. At 30 minutes: Carrageenan (0.1 ml/paw) is injected in the right hind paws of rats in group III, IV, V and VI. 5. Carrageenan is allowed to act for 2 hours after which the volumes of the hind paws are measured. 6. The effect of the test drugs on the volume of edema is calculated. 7. a) Write your observations in the following table: Group TREATMENT PAW VOLUME (ml) Difference Reading Reading Before drugs After drugs Exp – 1 GP I Diclofenac, (5mg/kg, i.p.) Propylene glycol (i.p.) GP II Exp – 2 GP III Aspirin (300mg/kg.p.o.) CMC (p.o.) GP IV Exp – 3 GP V Ibuprofen 20mg/kg (p.o.) CMC (p.o.) GP VI b) Comment on the observations you have obtained: Exp. 1 ______________________________________________________ __ ______________________________________________________ __ ______________________________________________________ __ Exp. 2 ______________________________________________________ ___ ______________________________________________________ ___ ______________________________________________________ ___ Exp. 3 ______________________________________________________ ___ ______________________________________________________ ___ ______________________________________________________ ___ Note: i.p. = intraperitoneally; p.o. = per os (orally). PRACTICAL #. 3 EFFECTS OF ANTI-CONVULSANTS DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL PHARMACOLOGY MPHL-232 (III YEAR) EXPERIMENT ON ANTICONVULSANT DRUGS Materials and Doses: 1. Carbamazepine ml/mouse, i.p 50 mg/ml; 0.2 2. Phenobarbitone ml/mouse, i.p 36 mg/ml; 0.2 3. Phenytoin ml/mouse, i.p 50 mg/ml; 0.2 4. Strychnine hydrochloride 0.2ml/mouse, i.p 0.45 5. mg/ml; Mice , average weight 25 – 30 gm Procedure: Each group of students is provided with 4 groups of mice, each group consists 1. of three mice. All the assigned drugs are injected intraperitoneally. 2. Inject mice in group 1 with 0.2 ml strychnine hydrochloride. 3. Inject mice in group 2 with 0.2 ml carbamazeine, followed after 10 mins by strychnine hydrochloride solution. Record the time of onset of any convulsions or jerky movements. 4. Inject mice in group 3 with 0.2 ml Phenobarbitone sodium solution, followed after 10 mins by strychnine hydrochloride solution. Record the time of onset of any convulsions or jerky movements. 5. Inject mice in group 4 with 0.2 ml phenytoin solution, followed after 10 mins. by strychnine hydrochloride solution. Record the time of any convulsions or jerky movements. 6. Record your results and give your comments on the findings. Results of the Experiment Mouse No Drugs (1) Strychnine hydrochloride (2) Carbamazepine + Strychnine hydrochloride (3) Phenobarbitone + Strychnine hydrochloride (4) Time of onset of Convulsions or Jerks / min. Phenytoin + Strychnine hydrochloride COMMENTS: ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ _____________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ _____________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ _____________________ PRACTICAL #. 4 SLEEPING TIME MPHL-232 DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY SLEEPING TIME EXPERIMENT (A) Drugs: Dose 1. Thiopentone 30 mg/kg, i.p. 2. Cimetidine 50 mg/kg, i.p. 3. Phenobarbitone 40 mg/kg, i.p. (B) Animals (C) Procedure: 1. Rats – weight 150-180 gm The animals will be divided into three groups (A,B,C) with 4 rats in each group. Pretreat animals in group (B) with daily injections of cimetidine (50 mg/kg, i.p.) for 4 days. 2. Pretreat animals in group (C) with daily injections of phenobarbitone (40 mg/kg, i.p.) daily for 4 days. 3. Inject thiopentone (30 mg/kg, i.p)* in all groups (i.e., A,B,C) on the day of experiment. Leave the animals flat on the bench. 4. Start the stop watch and record the sleeping time of each rat in all groups. 5. When animals start moving their limbs or try to turn over. This marks the end point of sleep. 6. Note the difference in sleeping time (mins.) between the three groups. 7. Comment on the difference in sleeping time between the groups. * Animals were pretreated with daily injections of cimetidine (50 mg/kg, i.p.) or phenobarbitone (40 mg/kg, i.p.) for 4 days before this injection of thiopentone. This is needed to inhibit or stimulate liver microsomal enzymes, respectively. Name:___________________________Reg. No. ___________________Sl.No.____________ MPHL-232 DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY RECORD OF SLEEPING TIME IN RATS Group”A” Thiopentone alone (30 mg/kg, i.p.) Sr. No. Group “B” Cimetidine, 50 mg/kg, i.p. + Thiopentone, 30 mg/kg, i.p. SLEEPING TIME Group “C” Phenobarbitone, 40mg/kg, i.p. + Thiopentone, 30 mg/kg, i.p. (min) 1. 2. 3. 4. Mean Comments: 1. ____________________________________________________________ ___________ 2. ____________________________________________________________ ___________ 3. ____________________________________________________________ ___________ 4. ____________________________________________________________ ___________