Problem solving for a set of data - variance and standard
advertisement

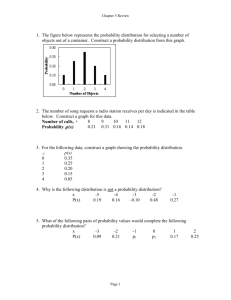
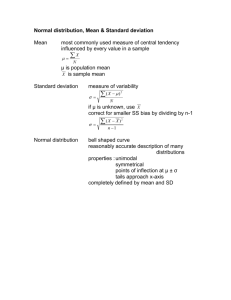
Unit 1: Mathematics for engineering LO6: Be able to apply statistics and probability in the context of engineering problems Problem solving for a set of data – variance and standard deviation A manufacturer of nuts and bolts performs quality control of the bolts by measuring their diameter. The nominal diameter of the bolt is 25mm. During a production run, they suspect that one of their CNC machines manufacturing the bolts is malfunctioning, and take a sample of 18 bolts to measure. The sample is believed to be representative of the whole batch being produced. Here are the measured diameters (in mm): 25.11 25.02 25.08 24.93 24.98 25.01 25 25.03 24.99 24.97 24.95 24.94 25 25.07 25.15 24.9 25.18 24.89 Version 1 The contract they are working to specifies that no more than 10% of the bolts are to be further than one Standard Deviation (1 SD) away from the mean. (a) Determine the mean for the sample (b) Determine the variance (c) Determine the Standard Deviation (d) Identify all bolts in the sample that are greater than 1 SD from the mean (e) Determine the percentage failure rate for the sample, and if the CNC machine should be investigated as malfunctioning Activity 2 During the production of sulphuric acid in a chemical engineering plant, the population data for 20 readings of sulphuric acid concentration (mol/l) is as follows: 9 2 5 4 12 7 8 11 9 3 7 4 12 5 4 10 9 6 9 4 The processing of the sulphuric acid batch requires that none of the readings are more than two Standard Deviations (2 SD) from the mean. (a) Determine the mean for the population (b) Determine the variance (c) Determine the Standard Deviation (d) Identify if any of the readings are more than 2SD from the mean and if the batch passes or fails Version 1