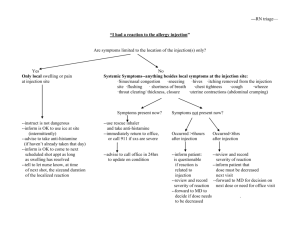
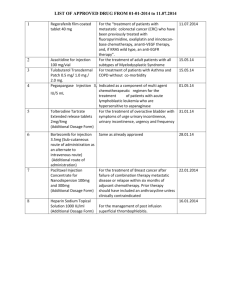
P-RMS
advertisement
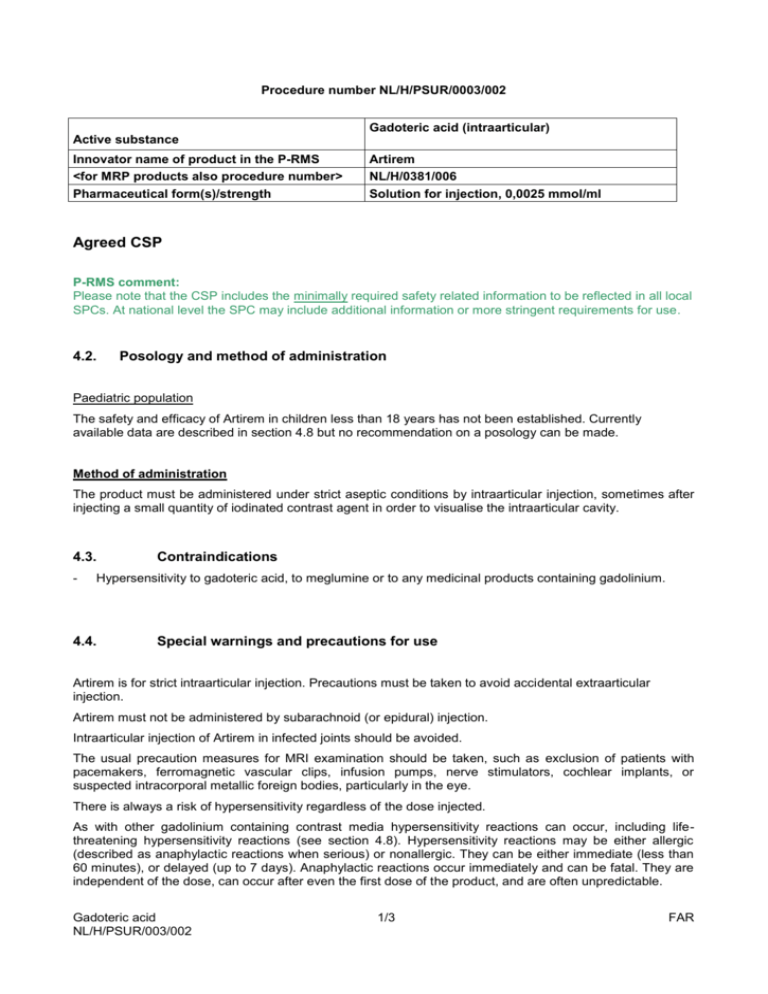
Procedure number NL/H/PSUR/0003/002 Gadoteric acid (intraarticular) Active substance Innovator name of product in the P-RMS <for MRP products also procedure number> Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength Artirem NL/H/0381/006 Solution for injection, 0,0025 mmol/ml Agreed CSP P-RMS comment: Please note that the CSP includes the minimally required safety related information to be reflected in all local SPCs. At national level the SPC may include additional information or more stringent requirements for use. 4.2. Posology and method of administration Paediatric population The safety and efficacy of Artirem in children less than 18 years has not been established. Currently available data are described in section 4.8 but no recommendation on a posology can be made. Method of administration The product must be administered under strict aseptic conditions by intraarticular injection, sometimes after injecting a small quantity of iodinated contrast agent in order to visualise the intraarticular cavity. 4.3. - Contraindications Hypersensitivity to gadoteric acid, to meglumine or to any medicinal products containing gadolinium. 4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use Artirem is for strict intraarticular injection. Precautions must be taken to avoid accidental extraarticular injection. Artirem must not be administered by subarachnoid (or epidural) injection. Intraarticular injection of Artirem in infected joints should be avoided. The usual precaution measures for MRI examination should be taken, such as exclusion of patients with pacemakers, ferromagnetic vascular clips, infusion pumps, nerve stimulators, cochlear implants, or suspected intracorporal metallic foreign bodies, particularly in the eye. There is always a risk of hypersensitivity regardless of the dose injected. As with other gadolinium containing contrast media hypersensitivity reactions can occur, including lifethreatening hypersensitivity reactions (see section 4.8). Hypersensitivity reactions may be either allergic (described as anaphylactic reactions when serious) or nonallergic. They can be either immediate (less than 60 minutes), or delayed (up to 7 days). Anaphylactic reactions occur immediately and can be fatal. They are independent of the dose, can occur after even the first dose of the product, and are often unpredictable. Gadoteric acid NL/H/PSUR/003/002 1/3 FAR To permit immediate emergency countermeasures, appropriate drugs (e.g. epinephrine and antihistamines), an endotracheal tube and a respirator should be ready to hand. Patients who have already experienced a reaction during previous administration of a gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agent present an increased risk of experiencing another reaction on subsequent administration of the same product, or possibly other products, and are therefore considered to be at high risk. The injection of Artirem may aggravate symptoms of an existing asthma. In patients with asthma unbalanced by the treatment, the decision to use Artirem must be made after careful evaluation of the risk/benefit ratio. Before any contrast medium is injected, the patient should be questioned for a history of allergy (e.g. seafood allergy, hay fever, hives), sensitivity to contrast media and bronchial asthma as the reported incidence of adverse reactions to contrast media is higher in patients with these conditions and premedication with antihistamines and/or glucocorticoids may be considered. 4.5. Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction No interactions with other medicinal products have been observed. Formal drug interaction studies have not been carried out. In the absence of specific studies, Artirem should not be mixed with other substances. Iodinated contrast media must not be administered simultaneously with Artirem, since the efficacy of Artirem may be reduced (see section 6.6). Concomitant medications to be taken into account Beta-blockers, vasoactive substances, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists: these medicinal products decrease the efficacy of the mechanisms of cardiovascular compensation for blood pressure disorders: the radiologist must be informed before injection of gadolinium complexes, and resuscitation equipment must be at hand. 4.6. Fertility, pregnancy and lactation Pregnancy There are no data from the use of gadoteric acid in pregnant women. Animal studies showed no direct or indirect harmful effects in animals receiving high intravenous doses of gadoteric acid with respect to reproductive toxicity (see section 5.3). Artirem should not be used during pregnancy unless the clinical condition of the woman requires use of Artirem. Lactation Gadolinium-containing contrast agents are excreted into breast milk in very small amounts (see section 5.3). At clinical doses, no effects on the infant are anticipated due to the small amount excreted in milk and poor absorption from the gut. As the dose of gadoteric acid injected in an arthrographic examination is very low and the administration is local (intraarticular), it is not necessary to interrupt breastfeeding following an examination carried out with Artirem. 4.7. Effects on ability to drive and use machines No studies of the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed. Effects on the ability to drive and use machines are not expected. However, joint effusions may impair the ability to drive because of a reduced mobility of the joint. Gadoteric acid NL/H/PSUR/003/002 2/3 FAR 4.8. Undesirable effects Adverse reactions related to the use of Artirem are generally mild to moderate, and transient. The adverse reactions most commonly reported during administration of Artirem since marketing are mild pain or local discomfort in the examined joint and hypersensitivity reactions. The effects most commonly observed during hypersensitivity reactions are skin rashes, which can be localized, extensive or generalized. These reactions are usually immediate (during the injection or over the hour following the start of the injection) or sometimes delayed (one hour to several days after the injection), and then appear in the form of adverse skin reactions. Immediate reactions comprise one or several, successive or concomitant effects, usually including skin reactions, respiratory and/or cardiovascular disorders, which may be the first signs of shock, which can rarely be fatal. Adverse reactions are presented in the following table by system organ class and by frequency according to the following categories: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100 to 1<1/10), uncommon (≥1/1 000 to 1<1/100), rare (≥1/10 000 to <1/1,000), very rare (<1/10,000), undetermined frequency (cannot be estimated on the basis of available data). The frequencies presented are derived from the data of an observational study on 463 patients. System Organ Class Frequency: adverse reaction Immune system disorders Uncommon: hypersensitivity Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Uncommon: arthralgia Adverse reactions in children The expected nature of adverse reactions related to Artirem is identical to that reported in adults. The frequency of these reactions can not be estimated on the basis of available data. 4.9. Overdose No signs of intoxication secondary to an overdose have so far been observed or reported in clinical practice with Artirem. On the basis of the results of the toxicity studies conducted with gadoteric acid solutions at higher concentrations, a risk of acute intoxication is highly unlikely following the use of Artirem by intra-articular injection. Gadoteric acid NL/H/PSUR/003/002 3/3 FAR