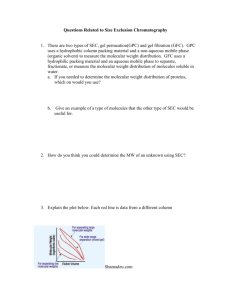
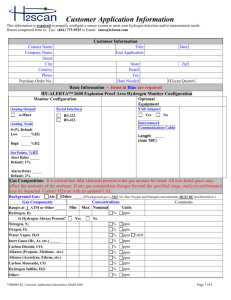
Supporting information
advertisement

Supporting information Gel permeation chromatography: Molecular mass analysis of the degraded samples was conducted by dissolving the samples in chloroform and filtering through a 0.2 m polyamide membrane prior to the chromatography measurement. The GPC system was equipped with PLgel guard plus 2mixed bed-B column (30 cm 10 m) and a flow rate of 1.0 mL min-1 was used at a temperature of 30°C. The eluted polymer was detected with a differential refractometer. The data were collected and analysed using Viscotek ‘Trisec 2000’ and ‘Trisec 3.0’ software. The GPC system was calibrated with polystyrene calibrants. (a) (b) In vitro degradation study of P(3HB)/BG composites in SBF depicting (a) % reduction in weight average molecular weight (Mw) and (b) % reduction in number average molecular weight (Mn) (bioactive glass particles used for molecular weight study only were micron sized (<5 m)) Ion release study in water For cation (Na+, Ca2+) release, an ICS-1000 ion chromatography system (Dionex, UK) was used. A 30 mM MSA (methanesulfonic acid, BDH, UK) solution was used as the eluent. Cations were eluted using a 4x250 mm IonPac® CS12A separator column and auto suppression. All results were calculated against a four-point calibration curve using the predefined calibration routine. Chromeleon v5.0 software package was used for data analysis. Sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium chloride (CaCl2.2H2O) were used as reagents. A 100 ppm mixed (sodium and calcium) stock solution was made, from which serially diluted 50, 25, 10 and 1 ppm standard solutions were prepared. The phosphate anion measurements were carried out using a Dionex ICS-2500 ion chromatography system (Dionex, UK), consisting of a gradient pump with a 25 μL sample loop. In this method, polyphosphates were eluted using a 4x250 mm IonPac AS16 anion exchange column packed with anion exchange resin. A Dionex ASRS (anion self regenerating suppressor) was used at 242 mA. The Dionex EG40 eluent generator equipped with a KOH (potassium hydroxide) cartridge was used in conjunction with the ASRS. The sample run time was set for 15 min. The gradient program started from 30 mM KOH, and after 8 min increased from 30 to 60 mM KOH up to 10 min, and then reduced to 30 mM KOH for up to 15 min. Orthophosphate (PO43-) ion release was used as reference for total anion release in this study. A 100 ppm (parts per million) working solution of Sodium phosphate tribasic (Na3PO4) was made, from which serially diluted 50, 20, 10 and 1 ppm standard solutions were prepared. All the above standards and dissolution studies were conducted using high purity water (18.2 MΩcm-1 resistivity), obtained from a 120 10 wt% BG (a) 20 wt% BG 100 4 cumulative release of PO 80 60 40 20 0 10 20 30 40 50 Time (Days) cumulative release of Ca 2+ (ppm) 10 wt% BG 20 wt% BG (b) 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 80 P(3HB) 300 cumulative release of Na + (ppm) P(3HB) 3- (ppm) PURELAB UHQ-PS system (Elga Labwater, UK). P(3HB) 10 wt% BG 20 wt% BG 0 10 20 30 Time (Days) 40 50 (c) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 10 20 30 Time (days) 40 50 Cumulative ion release of P(3HB) and P(3HB)/n-BG composites with given wt% of n-BG particles in water over a 45 day period (a) PO43- (b) Na+ (c) Ca2+ Biocompatibility analysis Experiments were performed using Sprague Dawley rats (Harlan Ltd. UK). All animals were maintained and handled in accordance with the Animals (Scientific procedures) Act 1986 and the study performed following guidelines stipulated by the Home Office (UK). All animals were kept under standard laboratory conditions and fed commercial pellet diet. Four adult rats weighing 235-280 g were anaesthetised using 0.25 mL IM Hypnorm (0.315 mg/mL fentanyl citrate and 10 mg/mL fluanisone) and 1 mg IP diazepam and an abdominal ventral midline incision made through the skin. Four films, one per animal (0.5cm x 0.5cm), were implanted into subcutaneous pockets formed on the right hand side in 4 rats. Skin was closed with 3/0 Mersilk® sutures (Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson Medical Ltd, UK). 8 mg/kg IM gentamicin was administered postoperatively. Rats were sacrificed by a lethal injection of sodium pentobarbitone at 1 and 2 weeks and the film and adjacent associated tissue removed resulting in 2 films for each time point. The films were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formal saline and allowed to fix for a minimum of one week. Following fixation each sample was cut in half before being processed for paraffin/wax embedding. Full-face histological sections were cut at 5 µm and stained with haematoxylin and eosin. (a) (b) P(3HB) film (c) Histological examination of P(3HB) films implanted subcutaneously in rats after 2 weeks. Figure (a) shows a biorefringent image of the film (x200), with both sides attaching to the surrounding tissues. A high density of cells is evident from this image (b) Histological image showing the presence of a fibrous capsule surrounding the film and the adjacent muscles (x200). (c) Presence of well-developed blood vessels were evident (marked by arrow) (x400). The results indicate a mild response, predominantly a foreign body response by the P(3HB) implant. In all the images, no penetration or growth of the cells through the substrate was observed.


![R)-3-Hydroxybutyrate] Formation in Escherichia coli from Poly[(](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/010484641_1-0eeadd20cec68424bd4bfd5be9a45c45-300x300.png)
