Administration of Blood and Blood Products MLP Eng

AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
Instructor Serial/Semester Location Start/Finish Time Date
LESSON OBJECTIVE
Performance: Students will gain an understanding of the administration of blood and blood products.
Conditions:
Standard: 1. Given the five elements of the nursing care process and a privileged provider’s order to administer blood or blood products by correctly responding to written, oral, and experiential assessment measures.
TEACHING POINTS
1. Explain the indications for administration of the following blood products: whole blood, RBC’s, fresh frozen plasma, serum albumin and plasma protein factor, fibrinogen, platelets, cryoprecipitate anti-hemophilic factor, and granulocytes
2. Identify the equipment required for the administration of blood and blood products
3. Discuss the nursing considerations prior to the administration of blood or blood products include patient understanding and consent, blood verification, patient identification, assessment, and patient teaching
4. Describe the procedure for implementing the infusion of blood or blood product
5. Discuss the procedure for monitoring a patient during a transfusion
INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGY
Method:
Media:
Interactive Lecture
Instructor
Environment: Classroom
OTHER LESSON SPECIFICATIONS
Type of Lesson:
Ratio:
Knowledge Lesson
1/50
Resources:
Instructor Materials: Lesson plan and multimedia presentation. Student Materials: Student handout .
End of Lesson Test:
Instructional Time:
Reference(s):
DEWIT, S. C. (2)
None
48 Minutes
Fundamental Concepts and Skills for Nursing, 1st
Edition, W B Saunders (ISBN: 0721669239)
01 Jan 2001.
ISBN 0-323-01727-4, Foundations of Nursing, 4th
Edition, 01 Jan 2003.
ISBN 0-323-01728-2, Adult Health Nursing, 4th
Edition
01 Jan 2003., ISBN 0-7817-3553-X, Introductory
Medical-Surgical Nursing, 8th Edition
01 ISBN 0-7817-3696-X, Introductory Clinical
Pharmacology, 7th Ed.
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
01 Jan 2004 Jan 2002., Chapter 19, pages 448-451,
Foundations of Nursing, 4th Edition, Christensen and Kockrow;
Adult Health Nursing, 4th Edition Christensen and
Kockrow p 259
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology, 7th Ed. p 633-
638
LESSON PLAN APPROVAL
Signature of Standards Officer Date
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
INTRODUCTION
Allocated Time:
Review:
Objective:
Importance:
Fit:
Approach:
5 Minutes
You have had previous anatomy and physiology lectures in your combat medic training, this lecture will build upon prior instruction.
To discuss/describe topics related to the nursing process.
Nurses work in various health care settings so it is important to gain an understanding of this subject as it will apply to your clinical practice.
Administration of blood and blood products can be a lifesaving procedure.
However, it has many dangers associated with it, especially transfusion reactions. The most severe transfusion reactions occur from errors in verification of the client, product, product type and cross-match. Therefore is vital that the nurse understands and complies with the guidelines in place to prevent these errors.
You will be presented the subject in lecture format and will be tested using a written exam at a later date.
If you have any questions during the lesson please feel free to ask. Control Statement:
BODY
1. Teaching Point: Explain the indications for administration of the following blood products: whole blood, RBC’s, fresh frozen plasma, serum albumin and plasma protein factor, fibrinogen, platelets, cryoprecipitate antihemophilic factor, and granulocytes.
Allocated Time:
Introduction:
Learner Participation:
Knowledge Lesson
Skill Lesson
Learning Support:
Minutes
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products a. Whole blood:
(1) Cardiac surgery and acute hemorrhage
(2) Replaces blood volume and all blood products: RBCs, plasma, plasma proteins, fresh platelets, and other clotting factors b. RBCs:
(1) Used to increase the oxygen carrying capacity of blood in anemias, surgery, and disorders with slow bleeding c. Fresh frozen plasma:
(1) Expands blood volume and provides clotting factors
(2) Contains no RBCs d. Serum albumin and plasma protein factor: blood volume expanders e. Products that provide clotting factors:
(1) Fibrinogen: the largest plasma protein. Plays a key role in forming blood clots.
(2) Platelets: restores or improves the ability to control bleeding. Assists in making the “plug” or clot stop leakage of blood from damaged vessel.
(3) Cryoprecipitate: mixture of clotting factors. Treats blood clotting disorders like hemophilia.
(4) Antihemophilic factors: replaces specific clotting factors deficient in hemophilia disorders f. Granulocytes: improves the ability to overcome an infection
Knowledge Lesson:
Question:
Answer:
Skill Lesson:
Check on Learning
In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class.
What product would you expect the physician or order if client needed an increase in oxygen carrying capacity?
Packed RBCs.
In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill.
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
2. Teaching Point: Identify the equipment required for the administration of blood and blood products
Allocated Time: Minutes
Introduction:
Learner Participation:
Knowledge Lesson
Skill Lesson
Learning Support: a. Blood product administration set:
(1) Y blood tubing: contains two spikes with separate lines that come together into one chamber
(a) One spiked line goes to the blood component to be infused.
(b) The other spiked line goes into a bag of normal saline.
(2) If a reaction occurs while transfusing the blood component, the blood can be instantly shut off and normal saline infused.
(3) Most infusions are done via an IV infusion pump (unless otherwise specified by local institutional policy.) b. Filter:
(1) Filters have a surface area large enough to allow blood components through easily but are designed to trap clots.
(2) Some clients require an extra filter to trap other substances such as common viruses. c. Normal saline:
(1) The ONLY product that can be infused with blood components is normal saline. Only product that is compatible.
(2) It is used in a Y blood infusion set to prime the line.
(3) Decrease the viscosity of the blood product when infusing RBCs.
(4) Is used to keep vein open between and after product administration d. IV site:
(1) An IV with an 18 to 19-gauge cannula is necessary when administering blood cell components.
(a) Blood components: whole blood, RBCs and granulocytes
(b) Smaller cannula sizes may break up cell components.
1
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
(2) Plasma products may be infused via a 22-gauge cannula. e. Valid physician’s order:
(1) A physician’s order is necessary prior to administration of any blood or blood product.
(2) The orders should specify the rate of the infusion.
(a) Each unit should be infused within 2 to 4 hours of initiation.
(b) The risk of blood cell damage and infection increases after 2 to 4 hours. f. Signed patient consent: Client must sign an informed consent within 72 hours of administration of the product.
Knowledge Lesson:
Question:
Answer:
Skill Lesson:
Check on Learning
In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class.
Why should the IV tubing for the administration of blood products contain a filter?
Prevent infusion of clots.
In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill.
3. Teaching Point: Discuss the nursing considerations prior to the administration of blood or blood products include patient understanding and consent, blood verification, patient identification, assessment, and patient teaching.
Allocated Time:
Introduction:
Learner Participation:
Knowledge Lesson
Skill Lesson
Minutes
Learning Support: a. Patient understanding and consent:
(1) Client must be informed thoroughly about the options, benefits and risks of blood and blood product transfusion.
(2) There is never a completely risk-free transfusion. However, extra care is taken to ensure the products and process is as safe as possible.
(3) Consent must be signed no more than 72 hours prior to the administration of the product.
(a) Indicates the client was informed of the reason for and possible adverse effects of the transfusion.
2
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
(b) Signature of the client is must be verified. b. Blood product verification:
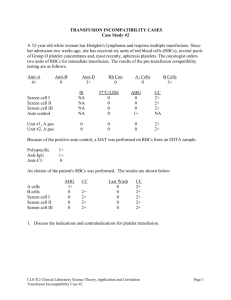
(1) Two witnesses and some form of client identification are required to obtain a blood product from the blood bank.
(a) Note time blood unit is obtained from blood bank.
(b) Transfusion must be started within 30 minutes of obtaining the product.
(2) Two licensed nurses must verify the blood component. One nurse must be an RN.
(a) Compare the donor numbers.
(b) Compare the ABO grouping and Rh type.
(c) Check the expiration date.
(3) Compare the paperwork with the unit of blood product container.
(4) Check the blood product for clots or unusual appearance: abnormal color, clumping, gas bubbles, and extraneous material. c. Patient identification: Proper identification of the client should be conducted in same manner as if administering any medication.
(1) Check the room number and bed number.
(2) Check the client’s identification bracelet.
(a) Some facilities use a special Identification band for blood product administration. If this is so, identification number on client’s bracelet must match transfusion number on blood product.
(b) Blood products should never be administered to a client without an identification bracelet.
(3) Ask the client to state his/her name. d. Assessment:
(1) Obtain baseline vital signs for comparison later. Changes in vital signs during transfusion are sign of possible transfusion reaction.
(2) Assess the client’s physical status for baseline. Comparison of changes might indicate a reaction during the procedure. e. Patient teaching:
(1) Ensure client understands the risk, benefits and indications for the blood product transfusion.
3
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
(2) Explain the process to the client:
(a) Remain with the client for the 1st 15 minutes of the transfusion.
(b) Frequent vital signs during the process.
(c) Precaution of verifying client and blood product identification.
(3) Instruct the client to report any discomfort or changes that may occur during the transfusion.
Knowledge Lesson:
Question:
Answer:
Skill Lesson:
Check on Learning
In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class.
Why is it important to obtain baseline vital signs?
So they can be used for comparison later for possible changes that might indicate transfusion reaction.
In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill.
4. Teaching Point: Describe the procedure for implementing the infusion of blood or blood product
Allocated Time:
Introduction:
Learner Participation:
Knowledge Lesson
Skill Lesson
Learning Support:
Minutes a. Gather necessary equipment and ensure client has patent IV site that is appropriate for product administration. b. Obtain blood product from the blood bank. c. Verify the blood component and client identification with another nurse. d. Prepare IV tubing:
(1) Close all clamps on the Y blood tubing administration set.
(2) Spike the normal saline container.
(3) Prime the filter and tubing with normal saline.
(4) Spike the blood product bag.
(5) For RBCs, invert and lower the packed RBCs bag. Open the clamp to the normal saline and allow approximately 50 cc of saline to run into the bag. Close the clamp.
4
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products e. Obtain baseline vital signs. f. Don gloves and connect the administration tubing directly to the cannula hub. Do not use a heplock device. g. Start the normal saline to clear the cannula and verify patency of the IV site. h. Start the blood product transfusion:
(1) Clamp off the saline and open the clamp to the blood product.
(2) Set the flow rate at 2 ml/minute for the 1st 15 minutes.
(3) Stay with the client and monitor for any changes.
(4) At the end of 15 minutes, obtain vital signs. If no adverse reaction is noted, increase the transfusion to the ordered flow rate. i. Monitor client and obtain vital signs as indicated. j. When blood component is complete, flush the line with normal saline. k. Maintain IV access per physician orders. l. Document:
(1) Add the amount infused to the client’s I &Os record.
(2) Record starting of the blood, including vital signs, type of blood, blood unit number, sequence number, site of venipuncture, size of needle cannula, and drip rate.
(3) Record completion of the transfusion, time, amount of blood product infused, the blood unit number, vital signs and client’s response.
Knowledge Lesson:
Question:
Answer:
Skill Lesson:
Check on Learning
In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class.
After how long should the nurse increase the blood transfusion rate to that which the physician ordered?
After 15 minutes.
In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill.
5. Teaching Point: Discuss the procedure for monitoring a patient during a transfusion
Allocated Time:
Introduction:
Learner Participation:
Minutes
5
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
Knowledge Lesson
Skill Lesson
Learning Support: a. The nurse must remain with the client for the 1st 15 minutes while blood is administered slowly. If no reaction occurs within this time frame, the blood product transfusion rate can be increased to the ordered rate. b. Vital signs are taken frequently during the procedure:
(1) Baseline vital signs
(2) 15 minutes after transfusion is started
(3) 30 minutes after transfusion is started
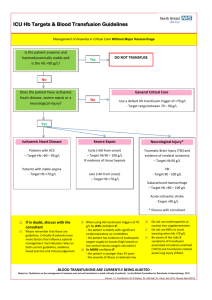
(4) Every 30 minutes until the transfusion is complete c. Monitor for transfusion reactions:
(1) Signs and symptoms:
(a) Client may report feeling “funny”, “not feeling right” or “anxious”.
(b) Chills, fevers
(c) Low back pain (flank pain)
(d) Pruritus, rash
(e) Hypotension
(f) Nausea and vomiting
(g) Decreased urine output
(h) Chest pain, dyspnea, wheezing, and rales
(i) Flushed skin, cyanosis
(2) Types of transfusion reactions:
(a) Hemolytic reaction: incompatibility between client’s blood and donor’s blood
(b) Febrile reaction: sensitivity of the client’s blood to white blood cells, platelets or plasma proteins
(c) Allergic reaction: severe antibody-antigen reaction
(d) Circulatory overload: blood administered faster than the circulation can accommodate
6
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
(e) Sepsis: contaminated blood administered
(3) Nursing interventions:
(a) Discontinue the transfusion immediately.
(b) Keep the vein open with normal saline.
(c) Notify the charge nurse and physician.
(d) Obtain vital signs.
(e) Prepare to send the following to the laboratory for testing:
1) Remaining blood and tubing used in administration
2) Sample of the client’s blood with tests ordered per agency protocol
3) Urine sample from client
Knowledge Lesson:
Question:
Answer:
Skill Lesson:
Check on Learning
In a knowledge lesson, pose questions to the class.
What is the first thing the LPN should do if a transfusion reaction is suspected?
Immediately stop the transfusion.
In a skill lesson, provide practice and watch students perform a skill.
END OF LESSON TEST
Allocated Time:
Instructions:
0 Minutes
Determine if the students have learned the material presented by soliciting student questions and explanations. Ask the students questions and correct misunderstandings.
Test Questions or
Performance
Expected:
Test Key:
CONCLUSION
Allocated Time:
Summary:
5 Minutes
Review and re-emphasize the difficult Teaching Points below.
1. Explain the indications for administration of the following blood products: whole blood, RBC’s, fresh frozen plasma, serum albumin
7
Closing Statement:
Re-motivating
Statement:
AFAMS Master Lesson Plan (MLP)
Nursing Program
Administration of Blood and Blood Products
2.
3.
4. and plasma protein factor, fibrinogen, platelets, cryoprecipitate antihemophilic factor, and granulocytes
Identify the equipment required for the administration of blood and blood products
Discuss the nursing considerations prior to the administration of blood or blood products include patient understanding and consent, blood verification, patient identification, assessment, and patient teaching
Describe the procedure for implementing the infusion of blood or blood product
5. Discuss the procedure for monitoring a patient during a transfusion
Proper administration of blood and blood products can significantly improve a client’s condition. Because of the inherent risks, the nurse must be sure that extreme care and careful monitoring occurs before, during and after the transfusion.
Administration of blood and blood products can be a lifesaving procedure.
However, it has many dangers associated with it, especially transfusion reactions. The most severe transfusion reactions occur from errors in verification of the client, product, product type and cross-match. Therefore is vital that the nurse understands and complies with the guidelines in place to prevent these errors.
8