Diarrhea syndrome - TMA Department Sites
advertisement

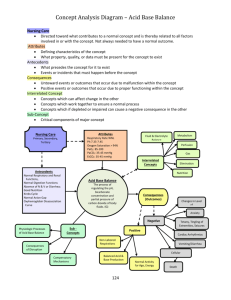
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OFTHE REPUBLIC OF UZBEKISTAN CENTER OF DEVELOPMENT OF MEDICAL EDUCATION TASHKENT MEDICAL ACADEMY Department of infectious and pediatric infectious diseases Subject: Infectious diseases THEME: Early and diffential diagnostics of infectious diseases Occurring with diarrhea syndrome Educational metholodical course book for lecturers and students Of Treatment Department TASHKENT MINISTRY OF HEALTH OFTHE REPUBLIC OF UZBEKISTAN CENTER OF DEVELOPMENT OF MEDICAL EDUCATION TASHKENT MEDICAL ACADEMY "A F F I R M E D" Pro-rector of educational work Professor Teshaev O.R. __________________________ «____»____________2012 Department of infectious and pediatric infectious diseases Subject: Infectious diseases THEME: Early and diffential diagnostics of infectious diseases Occurring with diarrhea syndrome Educational metholodical course book for lecturers and students Of Treatment Department "A F F I R M E D" at a DNC meeting of Therapeutic Faculty Protocol № ___from_________2012 Chairman of DNC, Professor Karimov M.Sh.___________ TASHKENT THEME: Early and differential diagnostics of infectious diseases occurring with diarrhea syndrome 1. Place of the lessons, equipping - The auditorium; - Box department; - Outpatients' clinic; - Diagnostic department; - Reception room; - Labs (clinical, biochemical, bacteriological, immunological); - Thematical patients with salmonellesis, cholera, dysentery, FTI, viral diarrheas, parasitical, amebic diarrheas, lamblyosis, slide projector, TV-video. 2.The duration of the study subjects – 6 hours - - 3.The purpose of classes Aim of lesson – to train integral approach to clinical diagnostics of infectious diseases with diarrhea syndrome, rational use of laboratory methods of testing. Teaching of rational therapy on house, means of individual prevention, prophylactic medical examination and rehab of diarrhea reconvalescents To accquant students with basic symptoms of diarrhea To teach an interest for the speciality, to stimulate the process of self-education and to develop responsibility and compassion to patient To develop scientific thinking, to stimulate creative approach for decision nonstandard clinical tasks and ability of independent decisions. To develop logical thinking Goals: Student has to know: Differential diagnosis of viral diarrheas and diarrheas from another infectious diseases Diff diagnosis of diarrhea syndrome causen from infect and noninfect diseases Early rational laboratory diagnostics of diarrhea syndrome Principles of complex therapy and rehab Student has to do: To lead the professional anamnesis collection and patient examination To form preliminary diagnosis To administrate purposeful examination To interpret laboratory and instrumental datas To own clinical logic of decision-making To diagnose emergency conditions and give first aid To carry out the rehab Skills of 1 order: Patient examination, stomach palpation To take a faeces on bacteriologic analysis To take a blood on Vidal reaction Skills of 2 order: Interpretation of laboratory data First aid First aid on dehydration 4. Motivation Wide spreading in Central Asia region diseases with diarrhea syndrome of infectious and non-infectious genesis, the ability of fast forming heavy status of patient define the necessity of doctor’s knowledge in differential symptoms of diarrhea syndrome and methods of fist aid providing. 5.Interdisciplinary communication Teaching of this theme is based on students’ knowledge of basics of water-mineral exchange, biochemistry of disbolism, microbiology, immunology, patanatomy, patphysiology, physiology of gastrointestinal tract and urinal system, endocrine and nerve systems. - - 6.The content of training 6.1.The theoretical part Diarrhea is a frequent defecation, when the stools have liquid consistention; disorder of different degree from simple inconvenience to acute disease which is dangerous to life. In present days diarrhea syndrome means a complex of different symptoms connected with intestinal evacuation disturbance, characterized by stools frequency elevation (more than 3 times a day) with discharging of big amount of liquid fieces. In diarrhea pathogenesis we mark out 4 mechanisms: Intestinal hypersecretion Elevation of osmotic pressure in intestine cavity Abnormalities in intestine contest transit Intestinal hyperexudation Intestinal hypersecretion – the mostly common mechanism of diarrhea conditioned by intestinal electrolyte transport abnormality which characterized by water and sodium content elevation in intestinal cavity. These processes are regulating and starting up by neuroendocrinal mediators, bilious acids, hormones, producing in organism or in intestine. Secretor diarrhea characterizing by equal meanings of osmollarity of faeces and blood plasma and the starvation (till 72 hours) doesn’t stop it. Salient feature of secretor diarrhea – polyfecalia, green color of faeces, steatorrhea (due to fatty acids with long carbon backbone chain), big loses of sodium, potassium, chlorine, metabolic acidosis, high pH. Hyperosmollar diarrhea is due to the elevation of chyme osmotic pressure which causes water delay in intestinal cavity; the reasons can be: carbohydrates digestion and suction disturbances (the lack of lactose), increased flux of osmotic stuffs (saline laxatives, sorbitol, some antacids), broken resorption syndrome. Characterized by polyfecalia, high chyme osmollarity, elevation of shortchain fatty acids and lactic acid, trivial loss of electrolytes with stools, low pH. Hypo- and hyperkinetic diarrhea – disturbance of intestinal content transit (increasing or decreasing of intestine motion). Characterized by retrograde motor activity decreasing, stimulation of secretor intestine processes, colicky abdominal pains (like intestinal colic) before stools and getting quietly after it, awaking diarrhea. Hyperexudative diarrhea – transudation in intestine lumen plasma, blood, mucus of intestinal cells. Characterized by frequent blood discharges, sometimes mixed with mucus or pus, moderate volume or like a spit. Infectious diseases: Acute (dysentery, cholera, salmonellesis, etc) Chronic (tuberculosis, intestine syphilis) Protozoa invasion (amebiasis, balantidiasis, lambliasis, trichomoniasis, etc) Helminthiasis (ascaridiasis, enterobiasis, hymenolepiasis) Nonspecific inflammatory processes (enteritis, enterocolitis, Crohn’s disease, diverticulitis) Disbacteriosis (the complication of antibacterial therapy, mycosis) Dystrophic changes of intestine wall (amyloidosis, intestinal lipodystrophy, celiacia-spru, collagenosis) Toxic influences (uremia, poisoning of heavy metals salts, alcoholism, medicamental intoxications) Dysentery. Causative agent is Sh. disenteria, sonnei, boydi, flexneri, incubation period 1-7 days, acute onset, chill, fever till 38-40°С, asthenovegetative syndrome, single vomiting, colitis, constant dull pain, tenesmus, false urges, 10-25 stools a day, decreasing in volume and has a potato smell, consist of mucus and blood, last portion only mucus – “rectal spit”. Salmonellisis. Causative agent is salmonella, incubation period is from 2-6 hours to 2-3 days, acute onset, chill, fever, repeated vomiting, watery liquid diarrhea, diffuse stomachache around the navel, headache, rumbling of sigma, 10-15 stools a day, abundant with mucus, like thin gruel, green color, fetid. Food toxic infection. Causative agent - St. aureus, proteus, incubation period 30 min – 7 hours, nausea, vomiting, colicky stomachache, frequent watery stools, no fever and muscle pain, in heavy cases tachycardia, hypovolemia, oliguria, dryness of skin and mucous. Botulism. Caus agent - Cl. Botulinum, incubation period – from 2 hours till 7 days, common indisposition, weakness, dryness in mouth, stomachache, liquid stools without impurities, sometimes vomiting, lesions of cerebral nerves, paresis, dysarthria, vision disturbance, diplopia, dysphagia, soft palate paresis, muscle weakness. Cholera. Causative agent is Vibrio cholerae classica, Eltor, incubation period is to 5 days, typical flow – acute onset, diarrhea without intoxication, fast turns to exicosis, painless stomach, watery stools, like a rice water with fish smell, defecation is painless, after diarrhea the vomiting without nausea begins, status cholericus, 10 l stools a day, colorless. Amebiasis. Causative agent is Е. histolytica, incubation period is from 1 till 3 months, gradually begins, weakness, headache, moderate stomachache, liquid stools with glassy mucus and blood, subfebril temperature, in case of long flow asthenic syndrome, decrease of appetite develop. Lambliasis. Causative agent is Lamblia intestinalis, incubation period is 1 to 3 weeks, during the acute period the clinical manifestations are rare, watery stools without mucus or blood, fetid, impurities of fat on the surface, pain in right subcostal area and around the navel, flatulence, decrease of appetite, nausea, may be vomiting, insignificantly temperature increase. Dysbacteriosis. Reasons are: fermentative insufficient, starving, avitaminosis, active hormonal therapy, allergization, antibiotics and chemiopreparations use, immunologic reactivity decrease, helminthic invasion, biliary tracts dyskinesis, chronic pancreatitis. In intestine the long running inflammatory process develops, in case of absence the infection generalization nausea, vomiting, fever, frequent stools with mucus, rarely with blood, abundant gases are registered. Because of abundant gases the sharp pains are appear when the peristaltic getting stronger. The process is longer, develops gradually, the abnormal stools can preserve for a long period of time even when the specific therapy is carried on. HIV-infection. Liquid stools to 15 times a day, significant dehydration sometimes, due to criptosporidosis development. The reasons of intestinal dysfunction are diff microorganisms, that’s why we need bacteriological scrutiny of feces. In case of zinc and copper poisoning the strong thirst, metallic taste in the mouth, the burning sensation behind the breastbone, elevated fatigability are registered. Diuresis is decreasing, urine become black, in biological liquids of organism the poison is registered. Noninfectious diarrhea. Poisoning of diff pesticides, diff surgical diseases, poisoning with mushrooms, poisoning with sea products, somatic diseases (heart attack). Poisoning with arsenic and mercury. Incubation period depends on dose, hours-days. Gastroenteritis or enterocolitis in all cases, fever sometimes, garlic smell from the mouth, on mercury poisoning strengthen sialorrhea, ulcerous stomatitis, gingivitis, rash, damage of kidneys are registered. Acute appendicitis. Liquid stools with mucus, sometimes with blood 5-6 times a day, stomachache can be primary and constant, diarrhea begins later. Appetite doesn’t disturbed. There is no intoxication in the beginning. Schotkin-Blumberg, Sitkovsky symptoms are typical. Important diagnostic role plays digital investigation of rectum. Local pain. Acute intestine invagination. Clinical picture is looks like dysentery. Invagination frequently occurs till 2 years. Suddenly in a state of total health strong colicky stomachache occurs, 1-2 min long, then repeat after 20 min and hour. In the initial period the temperature and stools are normal, then it becomes mucus-purulent. Stomach is soft, flatulence, compact painful sausage-look invaginate is palpated in the ileocaecal region. Dance’s symptom is positive. In digital investigation the rectal ampoule is empty. Intestinal diverticulum. Clinical picture is looks like acute dysentery. Frequently occurs on elderly people, long flow, pain is left iliac region or in stomach downstairs, flatulence, compaction in affected area, leukocytosis, elevated ESR. Intesinal tumours. In the cases of rectum and sigmoid intestines cancer the haemocolitis phenomenon is registered. Causeless diarrhea during 2-3 weeks with a blood impure frequently when the diet is broken. Ribbon-look shape of stools, stools is consist of a pure blood or meat slops. The flow is long and uninterrupted like a chronic dysentery. Stomachache occurs on later period. Untypical gigantic cells and insignificant amount of neutrofiles in coprology. Алгоритм диф. диагностики у больных с кровянистым стулом Кал с кровью НЯК Да Да Возможно дивертикулит Лихорадка Длительное течение кишечных язв НЕТ Длительное течение, не имеется воспалительные изменения Новообразование кишечнмка Боль в животе, геморрагический синдром Связан с менструацией Эндометриоз толстого кишечника Кишечное кровотечение у лиц выше 50 лет Тропический регион, признаки гиповитаминоза Да Да Да Пеллагра Да Болезнь Шенлейна-Геноха Кал с кровью Лихорадка Субфебрилитет Да Эозинофилия Да ДА Затяжное течение кишечных язв Анкилостомидоз или Шистосомоз Да Да Дизентерия Амебиаз Высокая температура Тенезмы, ложные позывы Да Водянистый стул, обезвоживание Боль в животе, артрит, эритема Да Да Болезнь Крона Кампилобактериоз New pedagogical technology. “The opinion review by rotation method” In lectionary room is hanging on some numerated tasks. Each little group (2-3 people) in 10 min discussing and writing its variant of question 8. The recommended literature 1. Majidov V.M. Infectional diseases. Т., 1992. 2. Maxmudov O.S. Children inflectional diseases, Т., 1995. 3. Uchaykin V.R. Manual by children inflectional diseases, М.,2005. 4. Shuvalova E.P. Infectional diseases, М.,1999. 5. Musabaev I.K. «the Management on intestinal infections», Т, 1999. 7. Pokrovsk Century И, Pak Of this year, etc. «Infectious diseases and epidemiology». - М, 2003 8. Jushchuk N.D., Vengerov J.J. «Lectures on infectious diseases». - М, 1999. 9. Uchajkin V. F «the Management on infectious diseases at children», - М, 1998. 10. Internet resources (www <http://www.medlinks.ru/> medlinks <http://www.medlinks.ru/><http://www.medlinks.ru/>ru <http://www.medlinks.ru/>, www.cdc.gov <http://www.cdc.gov/>).