Gagne`s Learning Domains
advertisement

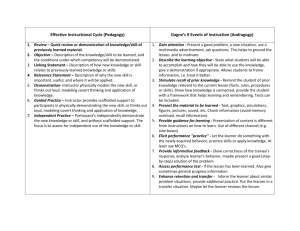
A prerequisite to writing goals (overarching statements) and objectives (specific statements of what it takes to achieve a goal) is a having a familiarity with how people learn. As you think back on your previous instructional design classes remember Gagne’s organization of learning domains as a guide for writing performance objectives. If you need to review your ability to use the domains correctly try evaluating several goal statements by the learning domain they address. You can do this with the exercise that follows the chart. If you are unsure about writing objectives try identifying the three parts of objectives. In the document entitled “3 Part Objectives.” You will need to associate learning domains with instructional strategies in the lesson plan that you design for ITED 8300. You will also need to use 3 part performance objectives. If after practicing with these exercises you are still unclear about these topics, you should let Dr. Schmertzing know so that more instruction can be given. What is a Goal? A goal is a statement of what learners should be able to do at the conclusion of instruction. It is a broader statement than an objective The focus of a goal is on outcome or performance of the learner. Writing Goals Use clear, concise statements of learner outcomes. Use verbs like: Choose Discriminate State Demonstrate Generate Summarize Discover Do not use the following verbs: Know Appreciate Understand An example of a goal: Student will design and produce a lesson for delivery via multimedia demonstrating effective designing skills and effective computer skills according to criteria established in the class. Behavior that learner will do: design & produce a lesson Indicator of behavior: use of effective design & computer skills Evaluation statement: according to criteria established in class Gagne’s 5 domains of Learning Outcomes Learning Domain What the domain covers 1. Verbal Information Basic description of knowledge and facts 2. Cognitive Strategy Learner develops a strategy for learning 3. Attitude Predisposition to learning 4. Psychomotor Skills Learn to physically perform a certain function. 5. *Intellectual Skills Deals with rules, concepts and ideas 5.a. Discrimination Determine if 2 objects are the same or different 5.b. Concrete concepts Something you can see or face Something you have to give a name to. You can’t touch it, but you know it (democracy). How to print documents (if this then do that) 5.c. Defined concepts 5.d. Rules and procedural relationships 5.e. Higher order rule Diagnose a problem and address solutions to the problem Verbs to Use “Learner will…” State Recite Summarize List Discover Adapt Choose Avoid Execute Draw Perform Discriminate Identify same or different Identify What will be reflected if the goal is achieved Reflects ability to recall information Reflects ability to assess learning task, to select a strategy, apply the strategy, assess and modify the strategy Reflects what learner does to show acquisition of attitude. Reflects learners ability to control the muscular activity required for a specific task. Ability to apply rules to previously unencountered situations and handle the situation effectively. Ability to differentiate between 2 stimuli (example: match this with that) Reflects learner’s ability to classify and label ideas, objects, events. Classify Demonstrate Explain Predict Fix Generate Apply Evaluate Analyze Ex. – Is this an example or nonexample of a particular concept? Indicates that learner can use the rule to predict, explain, control something or successfully complete a procedure. Requires learner to assess the problem/situation, determine which rule applies and synthesize for a solution. Practice using Gagne’s list to identify the Learning Domain associated with the following statements. 1. The learner chooses to exercise one hour a day while on vacation. Learning Domains 1. Verbal Information 2. The learner must invent a way to remember the steps to Dick and Carey’s Instructional Design Model. 2. Cognitive Strategy 3. Attitude 3. The learner must list relevant dates and locations of the wars fought with United States involvement during the past 75 years. 4. Psychomotor Skills 4. The learner will demonstrate a knuckle ball in a baseball game. 5. *Intellectual Skills 5.a. Discrimination 5. Given an architectural drawing of a house, the learner must select all of the doublewide doorways. 5.b. Concrete concepts 5.c. Defined concepts 6. Using the formula provided, the learner must convert a series of measurements from miles to kilometers. 7. Given a map and a budget, the learner must determine how to reach the West Coast from Valdosta, Georgia, in less than 48 hours and with money left over in the budget. 5.d. Rules and procedural relationships 5.e. Higher order rule Answers 8. The learner will run one mile in twelve minutes. 9. Given sample uses of technology in the classroom and lesson plan guidelines the learner will generate a lesson plan that can be used in his/her classroom and incorporates technology into its design. 1. Attitude 2. Cognitive Strategy 3. Verbal Information 4. Psychomotor skill 5. Concrete concept 6. Rule and procedures 7. Intellectual skill: higher order rules, problem solving 8. Psychomotor 9. Intellectual skill: Higher Order, problem solving