Chapter 11
advertisement

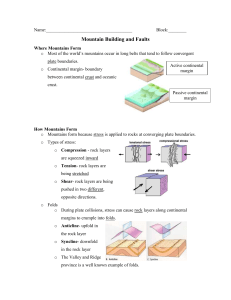
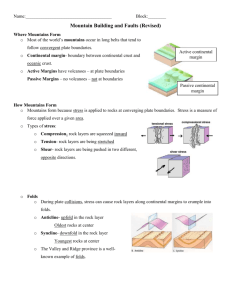
Chapter 11 Mountain Building Vocabulary: Mountain: A large mass of rock that rises a great distance above its base Continental Margin: The underwater part of the continental crust, which includes the continental shelf and the continental slope. Key Idea: Events at plate boundaries and at continental margins result in the formation of mountains. The process of mountain creation and erosion is cyclical (cycle). 1. Mountains form at an active continental margin ↓ 2. The active continental margin becomes a passive continental margin ↓ 3. Mountains begin to erode ↓ 4. Sediments carried by rivers to oceans ↓ 5. Sediments accumulate in the oceans ↓ 6. Passive continental margins becomes active continental margin ↓ 7. Sediments from oceans are deposited on continental crust ↓ The cycle begins again! The top picture is an ACTIVE Margin, the bottom picture is a PASSIVE Margin. Notice that the Active Margin has volcanic activity! 11.2 – How Mountains Form Vocabulary: Anticline: An upfold in rock layers Syncline: A download in rock layers Normal fault: A fault where the hanging wall moves down with respect to the footwall. Reverse fault: A fault where the hanging wall moves up with respect to the footwall. Thrust fault: A reverse fault in which the fault plane dips 45° or less from the horizontal Strike-slip fault: A fault where the rocks on opposite sides of the fault plane move horizontally. Joint: A crack or break in the bedrock along which no movement has occurred. Key Idea: Rocks at converging plate boundaries are under stress, and this stress may lead to deformation. 1. Types of stress, including: Compression Tension Shear 2. Folds Lead to 3. Faults classified as a. Normal b. Reverse c. Thrust d. Strike-slip 4. Joints Folded rock layers tend to occur along continental margins. Folded rock layers to occur deep beneath Earth’s surface. Folded mountains can be found in New Zealand and the Appalachians. Sidling Hill in Maryland is an example of syncline Anticline ic.ucsc.edu/.../Lectures/Joints/joints.htm Fault photo www.dukelabs.com/.../19Primer.htm 11.3 – Types of Mountains Vocabulary: Folded mountain: Mountains formed when two plates carrying continental crust collide, folding the rocks and earth with great force. Dome mountain: A nearly circular folded mountain. Fault-block mountain: Mountains formed from blocks of crust that have been faulted and tilted at the same time. Key Idea: Mountains can be classified by features that result from forces involved in plate interactions. The process by which each type of mountain is created: 1. Folded Mountains Two continental plates move toward each other The plates collide and subduction stops Rocks at the edges of the plates crumple up into folded mountains Examples: Appalachians, Alps, northern Rocky Mountains, Urals, Himalayans 3. Dome Mountains Uplifting forces or igneous intrusions push rock layers up into a dome Examples: mountains on the border of the Colorado Plateau or the Rocky Mountains. 2. Volcanic Mountains Volcanic activity tends to form mountains Examples: the Cascades, some Himalayan mountains 4. Fault-block Mountains Tension due to uplifting forces stretches the Earth’s crust Faults form along the surface Blocks of crust are thrust upward Examples: Sierra Nevada, Wasatch Range, Teton Range Ongoing examples of changes in the Earth’s surface include: 1. The Indian plate is pushing into the Eurasian plate 2. In some parts of the western United States, the crust is being uplifted 3. In the Great Rift Valley, rising magma is forcing the crust upward. Indian plate into Eurasian plate Crustal Uplift Great Rift Valley FOLDED MOUNTAIN Folded Mountain and diagram Folded mountain diagram with anticline and syncline Fault Block Mountains Fault Block Mountain diagram http://pirate.shu.edu/~schoenma/mountains.htm Dome Mountains Dome mountains are the result of a great amount of melted rock pushing its way up under the earth without folding or faulting resulting in a rounded dome. As the dome is raised above its surroundings erosion occurs, and as a result of erosion, peaks and valleys are formed.