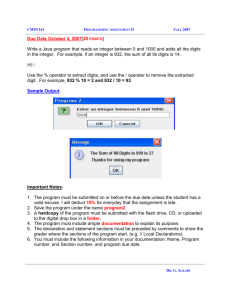
Measurement, Mass, Volume (Ch 2 labs)
advertisement

Accelerated Physical Science Study Guide: Volume, Mass, Measurement, Significant Digits, Conversions Covers IPS book sections 2.1-2.5, 2.10-2.12, 2.14-2.15 Lab review – know procedures, measurements, calculations, principles 2.3 – Measuring Volume by Displacement of Water 2.10 – Mass of Dissolved Salt 2.11 – Mass of Ice and Water 2.12 – Mass of Mixed Solutions 2.14 – Mass of a Gas Units and Measurement Know these SI units o mass (gram, g) o length (meter, m and centimeter, cm) o volume (cubic meter, m3; cubic centimeter, cm3; and liter, L) Know metric prefixes (mega, kilo, deci, centi, milli, micro, nano) and be able to convert between units using them. e. g. 1 L = 1000 mL, 1 gigameter = 109 meters Know scientific notation, how to convert a number into scientific notation and how to go from scientific notation back to a regular number. Know how to multiply and divide in scientific notation Uncertainty – comes from equipment and from estimation o Any measurement value contains certain digits and one uncertain digit o The uncertain digit is estimated Precision – a reliable measurement – one that gives about the same result again and again Accuracy – a measurement that is close to the accepted or true value Significant Digits Significant digits – certain AND estimated digits o Non-zero digits – ALWAYS significant o Leading zeros – NEVER significant o Trapped zeros – ALWAYS significant o Trailing zeros – ONLY significant when the number contains a decimal point o When using scientific notation, ALL significant digits are used Calculating with significant digits o Exact numbers (counting numbers, numbers in conversions) do NOT affect the number of significant digits in answer o Multiplication and division – answer has the same number of significant digits as the measurement with the fewest number of significant digits o Addition and subtraction – answer has the same uncertainty as the number with the largest uncertainty Conversions, Dimensional Analysis (converting from one unit to another) Start with unit equalities e. g. 1 L = 1000 mL, 1 mL = 1 cm3 Make conversion factors from the unit equalities. A conversion factor always = 1. Using the unit equalities above, the conversion factors are: 1L 1000 mL 1000 mL 1L 1 mL 1 cm3 1 cm3 1 mL Multiply the number you wish to convert by the conversion factor that results in canceling the first unit and leaving the correct unit for the answer. The correct conversion factor will have the unit to be canceled in the denominator and the unit for the answer in the numerator. Converting 350 mL to L: 350 mL x 1L = 1000 mL 0.35 L Converting 350 mL to cm3: 350 mL x 1 cm3 1 mL = 350 cm3