Perspective
advertisement

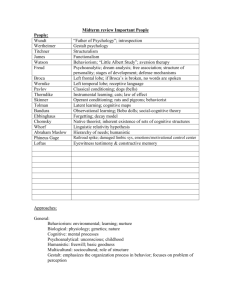
Perspective Biological Evolutionary Psychoanalytic (Psychodynamic- use more techniques and combination of perspectives) Cognitive Behavioral/Behaviorism/Behaviorist Humanistic Sociocultural Psychologists N/A Charles Darwin Freud Neo-Freudians: Jung, Adler, Horney, Erikson Piaget, Kohlberg, Gilligan, Beck, Ellis, Chomsky, Whorf Watson, Pavlov, Thorndike, Skinner, Bandura Carl Rogers, Abraham Maslow (Martin Seligman – Positive Psychology) N/A Chapter 1: Thinking Critically with Psychological Science Wilhelm Wundt William James Max Wertheimer Freud John Watson/Thorndike/Pavlov Structuralism Functionalism Gestalt – whole greater than the sum of the parts Psychoanalysis Behaviorism Chapter 2: Neuroscience - there are no specific psychologists to remember Chapter 3: Nature and Nurture - there are no specific psychologists to remember Chapter 4: Development Piaget Kohlberg Carol Gilligan Erikson Elisabeth Kubler-Ross Mary Ainsworth Harry Harlow Diana Baumrind Freud 4 stages of COGNITIVE development: Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operational, Formal Operational 3 stages of MORAL development: Preconventional, Conventional, Postconventional Opponent of Kohlberg’s theories (felt he was sexist) 8 stages of PSYCHOSOCIAL development: Trust v. Mistrust, Autonomy v. Doubt, Initiative v. Guilt, Industry v. Inferiority, Identity v. Confusion, Intimacy v. Isolation, Generativity v. Stagnation, Integrity v. Despair 5 Stages of Dying: Anger, Denial, Bargaining, Depression, Acceptance Attachment studies, Strange Situation Rhesus monkey studies: contact comfort important 4 Parenting Styles: Authoritarian, Passive, Permissive, Authoritative (the best one) 5 Psychosexual Stages: Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, Genital Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception Young-Helmholtz Weber’s Law Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision – red, green, blue receptors in retina Just Noticeable Difference, difference Threshold Chapter 6: Consciousness Ernest Hilgard Hidden Observer Effect in dissociation Chapter 7: Learning (behaviorism) John Watson Ivan Pavlov Edward Thorndike B.F. Skinner Garcia & Koelling (Garcia effect) Albert Bandura Wolfgang Kohler Baby Albert/white rat – classical conditioning Classical Conditioning Law of Effect Operant Conditioning Biological preparedness in classical conditioning. We are biological prepared to be conditioned for certain things Social Learning, modeling, Bobo doll experiment Insight learning in chimps Chapter 8: Memory Hermann Ebbinghaus Elizabeth Loftus Forgetting curve Constructed (false) memories Chapter 9: Thinking, Language and Intelligence Noam Chomsky Benjamin Whorf Binet Terman (at Stanford led to Stanford-Binet) Stern Spearman Goleman Gardner Language capability innate (born with a language acquisition device) Linguistic Relativity – language controls/influences thinking (this idea has been found to be mostly untrue except for the impact of labeling) Measure mental age Revised Binet’s tests Devised IQ (intelligence quotient) g – general intelligence Emotional Intelligence Multiple Intelligences Chapter 10: Motivation Abraham Maslow Yerkes-Dodson Hierarchy of Needs Arousal Theory Chapter 11: Emotions, Stress and Health James-Lange Cannon-Bard Schacter Two-Factor Theory Selye Physiological arousal precedes emotion Physiological arousal + cognition = emotion Physiological arousal and cognitive components interact to produce emotion. Explained the cognitive component more to differentiate theory from Cannon-Bard General Adaptation Syndrome (3 phase response to stress: 1. alarm 2. resistance 3. exhaustion) Chapter 13: Psychological Disorders Rosenhan Effects of diagnostic labels Chapter 12: Personality Freud Psychoanalytic – defense mechanisms, psychosexual stages Carl Jung Collective unconscious; Archetypes, personality traits (intuitive, sensing, feeling, thinking – the basis for Myers-Briggs personality inventory) Alfred Adler Birth order; inferiority and superiority complexes Karen Horney Women envy; felt Freud was sexist in saying that men have stronger superegos than women Gordon Allport Idiographic method: cardinal, central and secondary dispositions or traits specific to individual Eysenck-Cattell Nomothetic method: Used factor analysis to identify common traits in all people Julian Rotter Locus of control Carl Rogers Self Theory - Self-concept; ideal vs. real self; unconditional positive regard Abraham Maslow Hierarchy of Needs; top of the hierarchy – selfactualization Albert Bandura Social-cognitive theory: reciprocal determinism; self-efficacy Martin Seligman Positive psychology George Kelly (we didn’t talk about him, but know Personal-Construct Theory: people develop their him) own constructs to understand the world. Based on fundamental postulate – people are influenced by their cognitions. William Sheldon Somatotype Theory (3 body types): Endomorphs (fat) are friendly and outgoing, Mesomorphs (muscular) are aggressive, Ectomorphs (thin) are shy and secretive Barnum Effect (named after PT Barnum) The tendency for people to believe personality descriptions provided by palm readers, psychics, astrologers, etc. Chapter 14: Therapy Pinel and Dix Freud Carl Rogers Fritz Perls (we didn’t talk about him, but know him) Beck Albert Ellis Advocated humane treatment for mentally ill Psychoanalysis: free association, uncover unconscious, transference, resistance Humanistic: Client-centered Therapy using active listening Gestalt/Humanistic Therapy: get in touch with whole selves (even body position) and stressed the importance of the present time Cognitive Therapy: used the cognitive triad – beliefs about self, world and future Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT or RET): expose and confront irrational thoughts Chapter 15: Social Psychology Leon Festinger Rosenthal Sherif Asch Milgram Zimbardo Cognitive Dissonance Pygmalion Effect = self-fulfilling prophecy Superordinate goals promote cooperation Conformity – the line study Obedience – the shocking experiment Stanford Prison Study – role playing