03. Workplace monitoring - Radiation Protection of Patients
advertisement

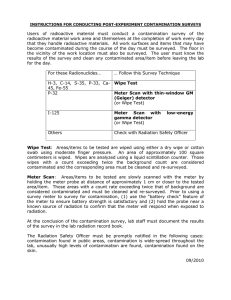
Radiation Protection in Nuclear Medicine PRACTICAL SESSION 3 WORKPLACE MONITORING BACKGROUND One requirement in a radiation protection programme is to perform a regular workplace monitoring. This should be sufficient to enable: evaluation of the radiological conditions in all workplaces; exposure assessment in controlled and supervised areas; and review of the classification of controlled and supervised areas The primary objective of monitoring is to reduce or prevent exposure of staff and the public to radioactive material. The secondary objectives are to detect any loss of control resulting from failures of containment or departures from good operating practice, and to assist in preventing the spread of contamination from a controlled area. Frequently such contamination spread must be restricted for reasons other than control of exposures, e.g. to avoid contamination of low-level counting equipment in analytical or research laboratories. In most countries the Regulatory Authority will specify the required frequency of documented workplace monitoring. AIM The aim of this practical session is to learn how to set up a programme for workplace monitoring and how to make the measurements using the correct instrument. MATERIAL A plan of the facilities should be available. Instrumentation Dose rate monitor Contamination monitor Activity meter or gamma counter Other equipment Protective clothing (laboratory coat or plastic apron, gloves and overshoes) Swabs, moistened with alcohol Tubes for samples Forceps PROCEDURE Use the plan to identify the points where the measurements should be performed. Contamination monitoring should be done in areas where there is an increased risk of contamination such as the work benches and equipment in the preparation area, patient bed where injections are made, patient toilet etc. Dose rate monitoring should 1 Radiation Protection in Nuclear Medicine PRACTICAL SESSION 3 be made in rooms where radionuclides are stored and in rooms permanently occupied by workers. Wipe an area of a workbench, typical 10x10 cm 2 using a moistened swab. Wipe from the periphery and inwards. Put the swab in a tube and measure the activity in a calibrated gamma counter or an activity meter. Calculate the contamination according to: contamination (Bq/cm2) =(cps-BG)/(Ec*Ew*A) (gamma counter) contamination (Bq/cm2)= Am/( Ew*A) (activity meter) cps: BG: Ec: Ew: A: Am: counts per second for sample instrument background counter efficiency (cps/Bq) wipe efficiency (assumed to be 0.1) wiped area (cm2) measured activity (Bq) CONCLUSIONS 2 Radiation Protection in Nuclear Medicine PRACTICAL SESSION 3 Workplace monitoring Dose rate monitor: Background: Contamination monitor: Background: Wipe measurement devce: Place of measurement Dose rate (μSv/h) Contamination (cps) Wipe test (Bq/cm2) Comment 3