1.5-1.8 Notes Packet
advertisement

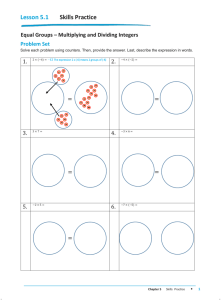
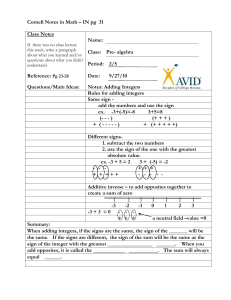
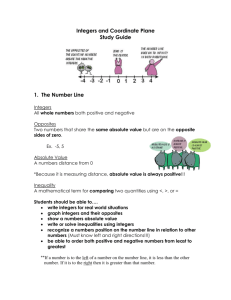
M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 1 of 16 Academic Pre-Algebra Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Variables, Expressions, & Integers Name___________Pd___ M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 2 of 16 Sections 1.5-1.6 Vocabulary Words Mean, Median, Mode, and Range Notes: Mean Median Mode Range Section 1.5 Notes: Additive inverse Whole numbers Sections 1.7-1.8 Vocabulary Words Section 1.8 Notes: Origin Scatter plot Quadrant Coordinate plane Ordered pair X-coordinate Y-coordinate X-axis Y-axis M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 3 of 16 Mean, Median, Mode, and Range Learning Goal: We will find the mean, median, mode, and range of a set of data. Mean – the sum of the data values divided by the number of data values Median – the middle value when the values are written in numerical order Mode – the data value that occurs most often (may have no mode or more than one) M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 4 of 16 Range – the difference of the greatest data value and the least data value Practice: M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Section 1.5: Adding Integers Learning Goal: We will add positive and negative integers. USING A NUMBER LINE: Example 1: Adding Integers Using a Number Line ON YOUR OWN: Page 5 of 16 M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes ADDING INTEGERS: 1. Same Signs 2. Different Signs 3. Opposites Additive Inverse Property: Additive Inverse – Example 2: Adding Two Integers Example 3: Adding More Than Two Integers Find the sum Page 6 of 16 M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes ON YOUR OWN: Example 4: Evaluating Variable Expressions ON YOUR OWN: Page 7 of 16 M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 8 of 16 Section 1.6: Subtracting Integers Learning Goal: We will subtract positive and negative integers. Relating Subtraction to Addition: Example 1: Subtracting Integers a. 3 11 ON YOUR OWN: b. 4 (7) c. 6 (14) M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 9 of 16 Example 2: Evaluating Variable Expressions ON YOUR OWN: Finding Change Using Subtraction **You can use subtraction to find the change of a variable quantity. ***Subtract the _____________________ of the quantity from the ___________________________. Example 3: Evaluating Change Eruptions have caused the volcano to grow. In 1962, the summit elevation of Kick-‘em-Jenny was -235 meters. In 2002, the summit elevation was -182 meters. By how many meters did the elevation of the volcano change? M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes ON YOUR OWN: Page 10 of 16 M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 11 of 16 Section 1.7: Multiplying Integers and Dividing Learning Goal: We will multiply and divide integers. Multiplying Two Integers: 1. Product of Same Signs 2. Product of Different Signs 3. Product of An Integer and Zero Example 1: Multiplying Integers a. 3(7) ON YOUR OWN: Find the product. b. 11(4) c. 52(0) M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Example 2: Multiplying Integers Dividing Integers 1. Quotient of Same Signs 2. Quotient of Different Signs 3. Quotient of An Integer and Zero Page 12 of 16 M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Example 3: Dividing Integers b. 30 5 a. 56 (7) ON YOUR OWN: Find the quotient. Example 4: Finding a Mean Page 13 of 16 c. 03 M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 14 of 16 Section 1.8: The Coordinate Plane Learning Goal: We identify and plot points in a coordinate plane. Vocabulary: Coordinate plane – a system formed by the intersection of a horizontal number line called the x-axis and a vertical number line called the yaxis Ordered pair – a pair of numbers (x, y) that can be used to represent a point in a coordinate plane. The first number is the x-coordinate, and the second number is the y-coordinate. Quadrant – one of four regions that a coordinate plane is divided into by the x-axis and y-axis. Origin – the point (0, 0) where the x-axis intersects the y-axis x-axis – the horizontal number line in a coordinate plane y-axis – the vertical number line in a coordinate plane Example 1: Naming Points in a Coordinate Plane M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes ON YOUR OWN: Give the coordinates o the point. 1. C 2. D 3. E Example 2: Plotting Points in a Coordinate Plane ON YOUR OWN: Page 15 of 16 M3: Sections 1.5 to 1.8 Notes Page 16 of 16 scatter plot - a graph in a coordinate plane that displays paired data. Each data pair is plotted as a point. Example 3: Making a Scatter Plot