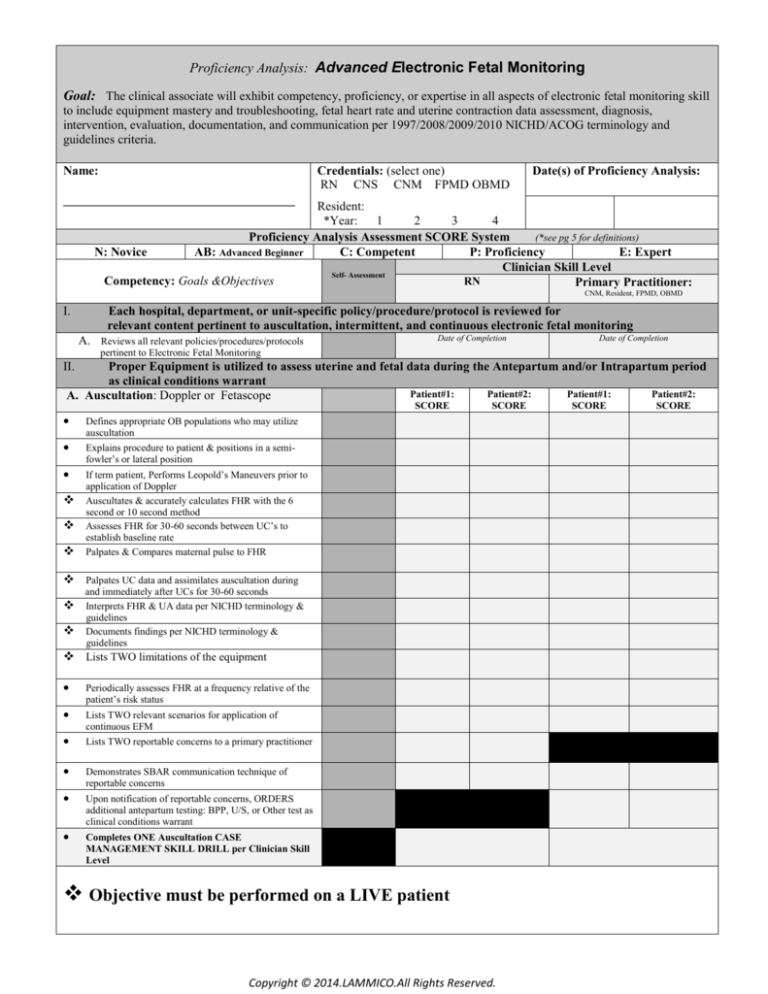
Proficiency Analysis: Advanced Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Goal: The clinical associate will exhibit competency, proficiency, or expertise in all aspects of electronic fetal monitoring skill
to include equipment mastery and troubleshooting, fetal heart rate and uterine contraction data assessment, diagnosis,
intervention, evaluation, documentation, and communication per 1997/2008/2009/2010 NICHD/ACOG terminology and
guidelines criteria.
Credentials: (select one)
RN CNS CNM FPMD OBMD
Name:
Date(s) of Proficiency Analysis:
_____________________________________
Resident:
*Year:
1
2
3
4
Proficiency Analysis Assessment SCORE System
(*see pg 5 for definitions)
N: Novice
AB: Advanced Beginner
C: Competent
P: Proficiency
E: Expert
Clinician Skill Level
Self- Assessment
RN
Competency: Goals &Objectives
Primary Practitioner:
CNM, Resident, FPMD, OBMD
I.
Each hospital, department, or unit-specific policy/procedure/protocol is reviewed for
relevant content pertinent to auscultation, intermittent, and continuous electronic fetal monitoring
A. Reviews all relevant policies/procedures/protocols
Date of Completion
Date of Completion
pertinent to Electronic Fetal Monitoring
II.
Proper Equipment is utilized to assess uterine and fetal data during the Antepartum and/or Intrapartum period
as clinical conditions warrant
Patient#1:
Patient#2:
Patient#1:
Patient#2:
A. Auscultation: Doppler or Fetascope
SCORE
SCORE
Defines appropriate OB populations who may utilize
auscultation
Explains procedure to patient & positions in a semifowler’s or lateral position
If term patient, Performs Leopold’s Maneuvers prior to
application of Doppler
Auscultates & accurately calculates FHR with the 6
second or 10 second method
Assesses FHR for 30-60 seconds between UC’s to
establish baseline rate
Palpates & Compares maternal pulse to FHR
Palpates UC data and assimilates auscultation during
and immediately after UCs for 30-60 seconds
Interprets FHR & UA data per NICHD terminology &
guidelines
Documents findings per NICHD terminology &
guidelines
Lists TWO limitations of the equipment
Periodically assesses FHR at a frequency relative of the
patient’s risk status
Lists TWO relevant scenarios for application of
continuous EFM
Lists TWO reportable concerns to a primary practitioner
Demonstrates SBAR communication technique of
reportable concerns
Upon notification of reportable concerns, ORDERS
additional antepartum testing: BPP, U/S, or Other test as
clinical conditions warrant
Completes ONE Auscultation CASE
MANAGEMENT SKILL DRILL per Clinician Skill
Level
Objective must be performed on a LIVE patient
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
SCORE
SCORE
2
Clinical Competency Analysis: Advanced Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Clinician Skill Level
Competency: Goals &Objectives
Self- Assessment
RN
Primary Practitioner:
CNM, Resident, FPMD, OBMD
B. Electronic Fetal Monitor:
(Make & Model: ________________________________________________________________________)
1. Test Button
Locates & Explains implications for use
Runs a TEST & Interprets results correctly
Outlines proper procedure for abnormal TEST
results
2.
Mark Button
Locates & Explains implications for use
3. Time/Date/Clock
Locate & Demonstrates how to adjust settings
4. Logic/Artifact Eliminator/ECG Disabled
Locates & Demonstrates how to adjust settings
List TWO Fetal clinical conditions necessitating
disabling the button (extreme rate abnormalities
or dysrhythmias)
5.
Tocodynamometer
Explains how equipment collects & interprets
data
Locates point of maximum intensity & Palpates UC’s &
resting tone prior to placement
6.
Demonstrates how to adjust & reset baseline
Identifies proper cleaning and storage
External Ultrasound
Explains how equipment collects & interprets
data
Demonstrates proper connection to monitor &
placement on patient for quality data collection
If term patient, Performs Leopold’s Maneuvers prior to
application & places device over point of maximum
intensity
Demonstrates how to improve channel quality
Palpates & Compares maternal pulse to FHR
7.
Identifies proper cleaning and storage
Fetal Electrocardiogram (FECG)
Explains how equipment collects & interprets
data
Identifies indications/contraindications to placing
the FECG
Demonstrates proper application of the FECG
8.
Demonstrates proper connection to monitor
LISTS TWO troubleshooting techniques to
improve data collection & quality
Intrauterine Pressure Catheter (IUPC)
Explains how equipment collects & interprets
data
Identifies indications/contraindications to placing
the IUPC
Demonstrates proper application of the IUPC
(*RN Approval for application varies per State Licensure guidelines)
Demonstrates proper connection to monitor
Demonstrates how to zero transducer
Performs periodic palpation to validate data
collected
LISTS TWO troubleshooting techniques to
improve data collection & quality
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
3
Clinical Competency Analysis: Advanced Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Clinician Skill Level
Competency: Goals &Objectives
Self- Assessment
RN
Primary Practitioner:
CNM, Resident, FPMD, OBMD
III.
Each clinician will identify, intervene, evaluate, categorize, document, and communicate all reassuring and
nonreassuring FHR and UA data per NICHD guidelines and terminology
A. RISK Assessment & Interpretation
Defines AWHONN/ACOG standards for evaluation of FHR & UA data
during latent phase, active phase, and second stage of the LOW & HIGH
RISK PATIENT
B. Uterine Contraction Analysis
Identifies UA data for frequency, intensity, duration, & resting tone at fundal
point of maximum intensity & at appropriate intervals per patient risk status
Promptly Identifies causation of nonreassuring/abnormal findings (ie:
tachysystole, hypertonus, polysystole, tentanic etc)
Intervenes initially with the least invasive methods to improve maternal,
fetal, and uterine conditions if nonreassuring findings persist
Evaluates resolution of nonreassuring findings & alters plan of care
accordingly
C. FHR Analysis(Baseline: FHRB & Variability: FHRV)
Identifies ALL FOUR Characteristics of a Normal/Healthy FHR pattern
Identifies FHR data for FHRB, normal range, exclusion criteria, and
segment criteria per NICHD guidelines
Promptly Identifies causation of nonreassuring/abnormal FHRB findings (ie:
tachycardia, bradycardia, dysrhythmias, or sinusoidal pattern)
Identifies FHR data for FHRV per NICHD guidelines (absent, minimal,
moderate, marked)
Promptly Identifies causation of nonreassuring/abnormal FHRV findings (ie:
absent, minimal, or marked)
Intervenes initially with the least invasive methods to improve maternal,
fetal, and uterine conditions if nonreassuring findings persist
Evaluates resolution of nonreassuring findings & alters plan of care
accordingly
D. Periodic or Episodic Pattern Analysis
Define the term Periodic, Episodic, Abrupt, Gradual, intermittent, &
recurrent per NICHD criteria
Identifies FHR data for ACCELERATIONS per gestational age
requirements as outlined in NICHD guidelines
Identifies FHR data for EACH DECELERATION per NICHD guidelines
Promptly Identifies causation of nonreassuring/abnormal PERIODIC OR
E.
F.
EPISODIC findings (ie: recurrent late, variable, or prolonged decelerations,
intermittent or recurrent severe late or variable decelerations)
Intervenes initially with the least invasive methods to improve maternal,
fetal, and uterine conditions if nonreassuring findings persist
Evaluates resolution of nonreassuring findings & alters plan of care
accordingly
NICHD Three Tier FHR Interpretation System
Categorize FHR Patterns according to new NICHD System
EVOLUTION
Evaluates Evolution of the FHR/UA Data Periodically at Patient Hand-off,
Rounds, or Shift Report
G. COMMUNICATION
Demonstrates SBAR communication technique of reportable concerns
If Delay or NO Response from Clinician, communicates reportable concerns
to administrative leadership in a timely manner
DOCUMENTATION
Documents FHR/UA data in an objective & concise format via electronic or
H.
paper technique
Documents FHR/ UA data periodically per protocol using NICHD
terminology & categorization with supplemental terminology as outlined in
additional references as indicated
Completes TWO EFM SKILLS ANALYSIS ALGORITHMS per
Clinician Skill Level
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
4
Clinical Competency Analysis: Advanced Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Goal: The clinical associate will exhibit competency, proficiency, or expertise in all aspects of electronic fetal monitoring skill
to include equipment mastery and troubleshooting, fetal heart rate and uterine contraction data assessment, diagnosis,
intervention, evaluation, documentation, and communication per 1997/2008/2009/2010 NICHD/ACOG terminology and
guidelines criteria.
Clinical Skill Level
Competency: Goals &Objectives
Primary
RN
Practitioner
CNM, Resident, FPMD,
OBMD
IV.
Each clinician will perform non-electronic & electronic fetal monitoring skill at a level of competency,
proficiency, or expert prior to independent patient care
Final Cumulative Score:
N
AB
C
P
E
Recommended for Remediation
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o NO
o NO
o YES
o YES
If YES, Remediation Action Plan for Improved Performance includes: (select all that apply)
Instructional Methods:
Methods of Evaluation:
(DT) Didactic Teaching w/ resources
o (SA) Self Assessment
(PP) Policy/Procedure/Protocol Review
o (PO) Preceptor Observation
(SLM) Self-Learning Module
o
(AP0) Advanced Practice Observation (NP, CNM, MD)
(T/P) Textbooks or Periodicals
o (SC) Skills Checklist
(PCL) Patient Care Literature
o (RD) Return Demonstration
(CS) Case Study Analysis/Presentation
o (CA) Chart Audit
(CT) Computer Tutorials
o (PR) Peer Review
(VID) Video Tapes
o (PT) Post Testing
(AUD) Audio Tapes
(DEM) Demonstration
IF YES, Date for Reassessment of Skills
Recommended for Annual Reassessment
I am qualified clinician with PROFICIENT skill & knowledge regarding non-electronic &
electronic fetal monitoring assessment techniques, NICHD terminology & guidelines, and
current evidence-based literature supporting additional terminology and management
options regarding nonreassuring findings. To the best of my ability and without assistance
to the clinician, I have evaluated their skill in advanced EFM.
o NO
o NO
o YES
o YES
Instructor Credentials: (select one)
RN CNS CNM FPMD OBMD
Resident:
*Year:
1
2
3
4
Proficiency Analysis Instructor: ____________________________________
Clinician Electronic Signature: _________________________________________________________________________
Final Competency Assessment Score: This area will be an ongoing assessment until the clinical associate demonstrates a level of “C for Competent”
or greater. All clinical associates must meet a level of “C for competent” or greater to perform as an unsupervised individual practitioner within the unit.
Novice: A beginner (New graduate or New skill) with minimal practical skills & the inability to apply theory into practice; dependent on constant direct
supervision. Independent patient care inappropriate & unsafe.
Advanced Beginner: Exhibits a basic knowledge with practical experience regarding routine or stable patients; lacks organization and needs support in
priority setting; independent with routine care but dependent with advanced EFM skills and/or techniques. Needs supervision until consistent.
Competent: Functions completely independent with stable or routine EFM patients yet continues to expend excess energy when making decisions in
complex patient situations; independent yet seeks unit expert with complex EFM scenarios.
Proficient: Functions independently in both routine and complex EFM clinical situations. May act as a preceptor and/or instructor for EFM skills.
Expert: Exhibits a highly evolved understanding of EFM theory and knowledge and offers exceptional clinical expertise in all complex clinical situations.
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.
5
Resources:
1. American Academy of Pediatrics and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
(2007).Guidelines for Perinatal Care, 6th ed.): Elk Grove Village, IL: Author.
2. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). (2010/2013). Management of
Intrapartum Fetal Heart Rate Tracings Surveillance (Practice Bulletin #116). Washington, DC: Author.
3.
ACOG. (2009/2013). Intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring: Nomenclature, interpretation, and
general management principles (Practice Bulletin #106). Washington DC: Author.
4. AWHONN. (2008). Fetal Heart Monitoring (Position Statement). Washington, DC: Author.
5. AWHONN. (2004). Amniotomy and Placement of Internal Fetal Spiral Electrode through Intact
Membranes (Clinical Position Statement). Washington, DC: Author.
6. AWHONN. (1998). Competence Validation for Perinatal Care Providers: Orientation, Continuing
Education, and Evaluation. Philadelphia PA: Lippincott.
7. Curran, C., & Torgersen, K. (2006). abcdEFM: The TEXTBook, Electronic Fetal Monitoring. Virginia
Beach, VA: Clinical Specialists Consulting, Inc.
8. Feinstein, N.F., Sprague, A. & Trepanier, M.J. (2008). Fetal Heart Rate Auscultation (2nd ed.).
Washington DC: Author.
9. Freeman, R, Garite, T, & Nageotte, M. (2003). Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring (3rd Ed). Philadelphia, PA:
Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins.
10. Lyndon, A., & Ali, L. U. (Eds.). (2009). Fetal Heart Monitoring: Principles and Practices (4th Ed.).
Dubuque, IA: Kendall Hunt Publishing.
11. Macones, G. A., Hankins, G. D., Spong, C. Y., Hauth, J., & Moore, T. (2008). The 2008 National
Institute of Child Health and Human Development Workshop Report on Electronic Fetal Monitoring:
Update on definitions, interpretation, and research guidelines. Obstet & Gynecol ; 112(3):pp. 661-666.
12. Menihan, CA, & Zottoli, EK. (2007). Electronic Fetal Monitoring: Concepts and Applications (2nd
Ed). Philadelphia PA: Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins.
13. National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) Research Planning Workshop.
(1997). Electronic fetal heart rate monitoring: Research guidelines for interpretation. Am J Obstet
Gynecol, 177(6):1385-1390, and J Obstet Gynecol Neonat Nurs, 26(6): 635-640.
Copyright © 2014.LAMMICO.All Rights Reserved.







