Biology 2nd semester exam objectives/review DNA, RNA, Protein

Biology 2
nd
semester exam objectives/review
DNA, RNA, Protein synthesis objectives
1. Describe the structure of DNA, RNA, and proteins
2. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA
3. Identify the monomers of DNA, RNA, and protein
Protist and Fungi Objectives
Protists:
24. Describe general characteristics of Kingdom Protista.
25. List and describe the three general categories of Protists
4. Explain what happens in each of the following processes: replication, transcription, and translation
5. List the parts of a nucleotide.
6. Identify and label the structure of a nucleotide
7. Identify the two scientists credited with discovering the shape of DNA.
8. Explain base-pairing rules for both DNA and RNA
9. Explain what happens to traits when genes have codominance incomplete dominance, multiple alleles , or sex linkage.
10. On a pedigree, identify what each shape or symbol represents.
11. Interpret information given on a pedigree, including identifying whether a trait could be dominant or recessive.
Define: DNA, replication, nucleotide, mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, transcription, translation, double helix, mutation, codominance, multiple allele inheritance, polygenetic traits, sex linked traits, gene, genetic code, codon, amino acids
Objectives Taxonomy and evolution:
12. List in order the correct sequence of taxonomic classification from the most inclusive (largest) to the least inclusive (smallest) level.
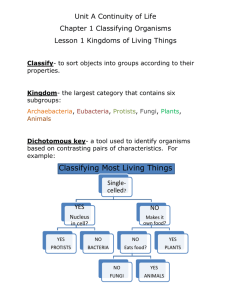
13. Classify organisms into the 6 kingdoms based on characteristics associated with that kingdom.
14. Explain the term binomial nomenclature and be able to recognize the genus and species in the scientific name.
15. Correctly write a scientific name.
16. Explain the difference between homologous and analogous structures.
17. List and discuss 5 pieces of evidence that scientist say support evolution and classification of organisms.
18. Identify who Charles Darwin was while describing his scientific work in the field of evolution.
Define: taxonomy, domain, taxon, binomial nomenclature, species, hybrid, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, natural selection, homologous structures, analogous structures
Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, and viruses objectives
19. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells regarding chromosomes, size, general structure, and general characteristics.
20. Identify what type of cell (meaning prokaryotic or eukaryotic) the two bacteria kingdoms have.
21. List the characteristics that are different between the two bacteria kingdoms.
22. Describe characteristics of the kingdom Archaebacteria.
23. Describe characteristics of the kingdom Eubacteria.
Define: Peptidoglycan, Nitrogen fixation, binary fission, conjugation, virus, vaccine, antiviral drugs, while giving examples of organisms found in each category.
26. List and describe the 4 groups of protozoa.
27. List and describe the 6 groups of algae.
28. List and describe three structures that protists use for locomotion.
29. List and describe ways that protists are beneficial and harmful to other living things.
Fungi:
30. Describe general characteristics of Kingdom Fungi.
31. List ways fungi can be helpful and harmful.
32. Explain generally how fungi get nutrition without actually consuming (eating) other organisms.
33. List common examples of fungi.
Define: binary fission, algae, Parasite, mutualistic relationship, amoeba, ciliate, flagellate, sporozoan, Conjugation, Protist,
Protozoa, Pseudopodia, dinoflagellates, red algae, brown algae, green algae, Diatom, Red tide, Budding, Chitin, Fragmentation,
Yeast, Lichen
Plants—Part 1 objectives: Basics and classification
34. Describe characteristics of all plants. (at least 4 characteristics!)
35. Correctly write the formula for photosynthesis.
36. Explain the basis for classifying plants, while giving examples of plants in each group.
37. Identify the two types of vascular tissue, while naming the materials that each transports.
38. Describe characteristics and examples of non-vascular plants, vascular seedless plants, and vascular seed plants, while giving examples of each type of plant.
39. Explain the purpose of seeds.
40. Explain the process of plant reproduction from gamete development, pollination, and fertilization.
41. Compare and contrast gymnosperms and angiosperms.
42. Compare and contrast monocots and dicots in terms of leaf structure, cotyledons, leaf and petal numbers, vascular systems, and examples.
Define: nonvascular, vascular, vascular tissues, xylem, phloem, seed, conifers, fruit, gametophyte,
Plants 2—Objectives
43. Label and explain the function of the parts of a flower. Blue bio book page: 642
44. List and explain 5 adaptations that plants have for life on land.
45. Identify and explain the function of 3 main plant organs.
46. Identify the function of guard cells, stomata, epidermis and chloroplasts.
Define: pollination, self pollination, cross pollination, pollen tube, fertilization, epidermis, stomata, guard cells, chloroplasts, transpiration
Animal Characteristics and Invertebrates Objectives
47. List general characteristics of ALL animals.
48. Explain the difference between invertebrates and vertebrates.
49. Identify areas of an animal associated with the following anatomical words: dorsal, ventral, posterior, anterior.
50. Explain the difference between an endoskeleton and exoskeleton, while giving the function of each skeleton.
51. List the three main types of arthropods while giving characteristics, numbers of legs, and examples of each.
52. Explain the difference between simple (incomplete) metamorphosis and complete metamorphosis while listing the stages of each.
53. List and describe the following phyla in terms of symmetry, body plan, circulation, examples, methods of reproduction, and general characteristics: Phylum
Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nematoda,
Annelida, Molluska, Arthropoda, and Echinodermata ( your chart)
Define: symmetry, radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry, anterior, posterior, dorsal, ventral, exoskeleton, endoskeleton, invertebrate, vertebrate, , filter feeding, sessile, molt (or molting), metamorphosis, tube feet, larva, pupa, nymph, complete metamorphosis, incomplete metamorphosis, asymmetry
Phylum Chordata Objectives
54. List characteristics of ALL chordates.
55. Give examples of vertebrate chordates.
56. List the characteristics that all vertebrates have.
57. List the general characteristics, reproduction (whether internal or external fertilization), symmetry, and any important/significant characteristics of animals in the following classes: Agnatha, Chondrichtheyes, Osteichtheyes, Amphibia,
Reptilia, Aves, and Mammalia.
58. Give examples of animals in each of the following classes:
Agnatha, Chondrichtheyes, Osteichtheyes, Amphibia, Reptilia,
Aves, and Mammalia.
59. List and give examples of three groups of mammals.
60. Explain the difference in the birth/development of young in the three mammal groups.
Define: ectotherm, lateral line system, gills, swim bladder, endotherm
Ecology basics and cycles objectives:
61. List and describe the levels of organization in the environment from most to least inclusive, carrying the organization from the biosphere to the atomic level (atoms).
62. Correctly identify the relationships between organisms in food chains/webs/pyramids using the correct terms such as: primary producer, autotrophs, secondary/tertiary consumers, 1 st order heterotrophs, decomposers.
63. Explain how nutrients are recycled in the following cycles: water, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen (focus on where nutrients are stored, how they enter/exit organisms).
Define: ecology, habitat, niche, abiotic factors, biotic factores, resources, competition, producers, consumers, herbibores, carnivores, scavengers, decomposers, food chain, food web, energy/ecologic pyramid, 10% rule
Communities, Populations, and Biomes Objectives
64. Define and identify examples of density dependent and density independent factors.
65. Define carrying capacity and explain how limiting factors affect population size as it approaches carrying capacity.
66. Define and describe the processes of primary and secondary succession, including how it occurs and why it occurs, and the pioneer species for each type.
67. Identify biomes based on: general characteristics and locations, plants, animals, soil conditions, temperatures, and precipitation characteristics.
Define: limiting factor, climax community, pioneer species, biomes
For all topics this semester:
Interpret and analyze scientific information on data tables, charts, or graphs.