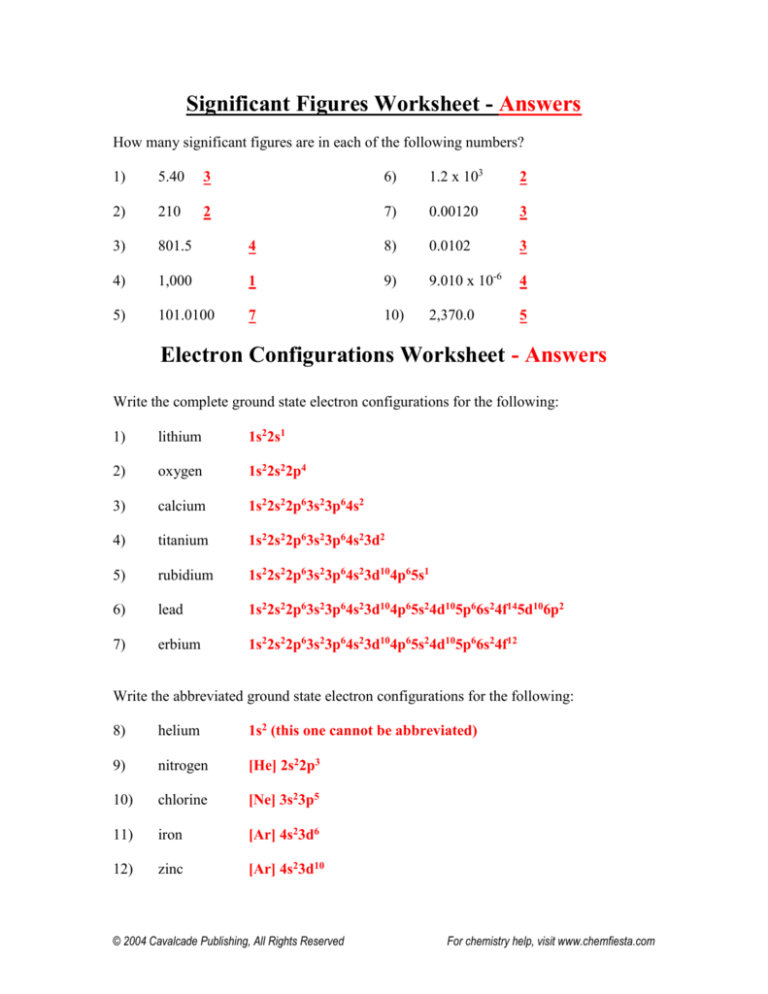
Significant Figures Worksheet - Answers
How many significant figures are in each of the following numbers?
1)
5.40
3
6)
1.2 x 103
2
2)
210
2
7)
0.00120
3
3)
801.5
4
8)
0.0102
3
4)
1,000
1
9)
9.010 x 10-6
4
5)
101.0100
7
10)
2,370.0
5
Electron Configurations Worksheet - Answers
Write the complete ground state electron configurations for the following:
1)
lithium
1s22s1
2)
oxygen
1s22s22p4
3)
calcium
1s22s22p63s23p64s2
4)
titanium
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d2
5)
rubidium
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s1
6)
lead
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s24f145d106p2
7)
erbium
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s24f12
Write the abbreviated ground state electron configurations for the following:
8)
helium
1s2 (this one cannot be abbreviated)
9)
nitrogen
[He] 2s22p3
10)
chlorine
[Ne] 3s23p5
11)
iron
[Ar] 4s23d6
12)
zinc
[Ar] 4s23d10
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
13)
barium
[Xe] 6s2
14)
polonium
[Xe] 6s24f145d106p4
Periodic Trends Worksheet - Solutions
1)
Rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius: carbon, aluminum,
oxygen, potassium.
From smallest to largest:
oxygen < carbon < aluminum < potassium
2)
Rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity: sulfur, oxygen,
neon, aluminum.
From smallest to largest:
neon < aluminum < sulfur < oxygen
4)
Why does fluorine have a higher ionization energy than iodine?
It is harder to pull electrons off of fluorine because fluorine has a higher
electronegativity than iodine. Iodine has a much lower electronegativity than
fluorine because of the shielding effect, which states that the electrons in
inner energy levels tend to push electrons in outer energy levels away from
the nucleus. This pushing makes it harder for iodine to grab electrons.
5)
Why do elements in the same family generally have similar properties?
Because they have similar electron configurations and the same number of
valence electrons. Because valence electrons are responsible for most of the
chemistry we observe, this similarity causes the properties of the elements to
also be similar.
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
Answers – Naming Chemical Compounds
Name the following chemical compounds:
1)
NaBr
sodium bromide
2)
Ca(C2H3O2)2
calcium acetate
3)
LiCN
4)
Ti(SO4)2
titanium(IV) sulfate
5)
FePO4
iron(III) phosphate
6)
K3N
potassium nitride
7)
HC2H3O2
8)
Sr(ClO)2
9)
Zn(NO2)2
zinc nitrite
10)
V2S3
vanadium(III) sulfide
11)
Mo(HSO4)2
12)
nickel (III) sulfide
Ni2S3
13)
manganese (II) phosphate
Mn3(PO4)2
14)
silver acetate
AgC2H3O2
15)
Co2(C2O4)3
16)
magnesium sulfate
17)
potassium carbonate
K2CO3
18)
ammonium oxide
(NH4)2O
19)
tin (IV) selenide
SnSe2
20)
HI
MgSO4
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
Ionic Naming Practice Problems - Solutions
Name the following ionic compounds:
1)
NaBr
sodium bromide
2)
Sc(OH)3
scandium hydroxide
3)
V2(SO4)3
vanadium (III) sulfate
4)
NH4F
ammonium fluoride
5)
CaCO3
calcium carbonate
6)
NiPO4 nickel (III) phosphate
7)
Li2SO3
lithium sulfite
8)
Zn3P2
zinc phosphide
9)
Sr(C2H3O2)2 strontium acetate
10)
Cu2O
copper (I) oxide
11)
Ag3PO4
silver phosphate
12)
YClO3 yttrium chlorate
13)
SnS2
tin (IV) sulfide
14)
Ti(CN)4
titanium (IV) cyanide
15)
KMnO4
potassium permanganate
16)
Pb3N2
lead (II) nitride
17)
CoCO3
cobalt (II) carbonate
18)
CdSO3
cadmium sulfite
19)
Cu(NO2)2
copper (I) nitrite
20)
Fe(HCO3)2
iron (II) bicarbonate
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
Write the formulas for the following ionic compounds:
21)
lithium acetate
LiC2H3O2
22)
iron (II) phosphate
Fe3(PO4)2
23)
titanium (II) selenide TiSe
24)
calcium bromide
CaBr2
25)
gallium chloride
GaCl3
26)
sodium hydride
NaH
27)
beryllium hydroxide
Be(OH)2
28)
zinc carbonate
ZnCO3
29)
manganese (VII) arsenide
Mn3As7
30)
copper (II) chlorate
Cu(ClO3)2
31)
cobalt (III) chromate Co2(CrO4)3
32)
ammonium oxide
33)
potassium hydroxide KOH
34)
lead (IV) sulfate
35)
silver cyanide
36)
vanadium (V) nitride V3N5
37)
strontium acetate
38)
molybdenum sulfate Mo(SO4)3
39)
platinum (II) sulfide
PtS
40)
ammonium sulfate
(NH4)2SO4
(NH4)2O
Pb(SO4)2
AgCN
Sr(C2H3O2)2
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
Solutions for the Naming Ionic Compounds Practice Worksheet
If you need help naming ionic compounds, you should check the helpdesk
section of my webpage (http://www.chemfiesta.com) for a method that might help
you out.
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
10)
ammonium chloride
iron (III) nitrate
titanium (III) bromide
copper (I) phosphide
tin (IV) selenide
gallium arsenide
lead (IV) sulfate
beryllium bicarbonate
manganese (III) sulfite
aluminum cyanide
11)
12)
13)
14)
15)
16)
17)
18)
19)
20)
Cr(PO4)2
V(CO3)2
Sn(NO2)2
Co2O3
Ti(C2H3O2)2
V2S5
Cr(OH)3
LiI
Pb3N2
AgBr
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
Solutions for the Balancing Equations Practice Worksheet
1)
2 NaNO3 + PbO Pb(NO3)2 + Na2O
2)
6 AgI + Fe2(CO3)3 2 FeI3 + 3 Ag2CO3
3)
C2H4O2 + 2 O2 2 CO2 + 2 H2O
4)
ZnSO4 + Li2CO3 ZnCO3 + Li2SO4
5)
V2O5 + 5 CaS 5 CaO + V2S5
6)
Mn(NO2)2 + BeCl2 Be(NO2)2 + MnCl2
7)
3 AgBr + GaPO4 Ag3PO4 + GaBr3
8)
3 H2SO4 + 2 B(OH)3 B2(SO4)3 + 6 H2O
9)
S8 + 8 O2 8 SO2
10)
Fe + 2 AgNO3 Fe(NO3)2 + 2 Ag
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
Types of Reactions Worksheet – Solutions
Balance the following equations and indicate the type of reaction taking place:
1)
3 NaBr + 1 H3PO4 1 Na3PO4 + 3 HBr
Type of reaction: double displacement
2)
3 Ca(OH)2 + 1 Al2(SO4)3 3 CaSO4 + 2 Al(OH)3
Type of reaction: double displacement
3)
3 Mg + 1 Fe2O3 2 Fe + 3 MgO
Type of reaction: single displacement
4)
1 C2H4 + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 2 H2O
Type of reaction: combustion
5)
2 PbSO4 2 PbSO3 + 1 O2
Type of reaction: decomposition
6)
2 NH3 + 3 I2 1 N2I6 + 3 H2
Type of reaction: double displacement
7)
1 H2O + 1 SO3 1 H2SO4
Type of reaction: decomposition
8)
1 H2SO4 + 2 NH4OH 2 H2O + 1 (NH4)2SO4
Type of reaction: acid-base
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
1)
____ Ag2SO4 + ____ NaNO3 no reaction!
Examining this reaction, it appears that a double displacement reaction will
occur. This would lead to the conclusion that the products would be
AgNO3 and Na2SO4. However, for this reaction to occur, both reactants and
only one of the products must be soluble in water. If you look up the
solubilities on a chart, you’ll find that Ag2SO3 is partly soluble in water, and
all of the other compounds are totally soluble in water. This tells us that
this reaction will not occur.
2)
____ NaI + ____ CaSO4 no reaction!
Another double displacement reaction, this time with Na2SO4 and CaI2 as
products. Because both products are soluble in water and CaSO4 is only
partially soluble in water, the conditions for a successful double
displacement reaction are not met.
3)
2 HNO3 + 1 Ca(OH)2 1 Ca(NO3)2 + 2 H2O
It’s an acid-base reaction, and acid-base reactions occur readily whether or
not the reactants are both soluble in water.
4)
1 CaCO3 1 CaO + 1 CO2
It’s a decomposition reaction. If you didn’t guess that these were the
products, you should have at least known that it was a decomposition
reaction and predicted that this would have broken into its constituent
elements, Ca, C, and O2.
5)
1 AlCl3(aq) + 1 (NH4)3PO4(aq) AlPO4(s) + 3 NH4Cl(aq)
This is a double displacement reaction, except in this case both of the
reactants and only one product are soluble in water. Because the
conditions for a successful reaction are met, the reaction does occur!
6)
____ Pb + ____ Fe(NO3)3 no reaction!
Though this is a single displacement reaction, lead is lower on the activity
series than the iron it would replace. As a result, this reaction does not
occur.
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com
7)
2 C3H6 + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O
The reactants suggest that this is a combustion reaction, meaning that the
products must be carbon dioxide and water. Once you figure this out, the
only thing left to do is balance it, as shown.
8)
2 Na + 1 CaSO4 1 Na2SO4 + 1 Ca
This should clearly be a single displacement reaction. Because sodium is
higher on the activity series than calcium, this reaction does occur.
© 2004 Cavalcade Publishing, All Rights Reserved
For chemistry help, visit www.chemfiesta.com






