Supplemental Methods: Genomic Instability Assays
advertisement

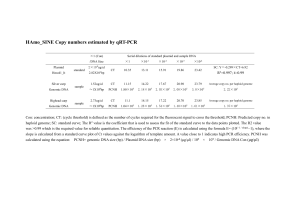
Supplemental Methods: Genomic Instability Assays The PALA assay was performed essentially as previously described 24,25. PALA, an inhibitor of the aspartate transcarbamylase activity of the multifunctional CAD enzyme, was obtained from the Drug Synthesis and Chemistry Branch, Developmental Therapeutics Program, Division of Cancer Treatment, National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD. SCp2 were exposed to MMP-3 or induced to express MMP-3, then MMP-3 was removed or repressed for 24-48 hours before cells were trypsinized, counted, and allowed to adhere to new dishes before being exposed to 200 M PALA (the LC50 of PALA for SCp2 cells was determined to be 25 M). Acquisition of resistance to PALA was assessed by counting the number of surviving colonies relative to the total cells plated. Unless otherwise indicated, PALA assays were performed on cells that had been treated for 14 days. For FISH analysis of the CAD locus, BAC probes (BACPAC, Oakland, CA) rp23-73H2O (mouse chromosome 9) and rp23-154k6 (mouse chromosome 5, containing CAD locus) were labeled using Bioprime DNA Labeling System (Invitrogen) using FITC-dUTP (NEN) for rp23-73H2O or Cy3dUTP (Amersham) for rp23-154k6, and then hybridized to SCp2 cells that had been treated with MMP-3 or MMP-3 and PALA; the number of copies per cell was quantified using fluorescence microscopy. Genomic alterations were assayed using array-based comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) as previously described30, except that mouse BAC arrays and mouse Cot-1 DNA (Invitrogen) were used instead of human Cot-1 DNA. Clonal populations were derived from SCp2 cells grown in the presence (clones N2, N11, N12, N13) or absence (clones D, F, I) of MMP-3 for 14 days, then selected for resistance to PALA in the absence of MMP-3. The reference DNA used for all CGH samples was derived from parental SCp2 cells (not treated with PALA or MMP-3), and all DNA was isolated using DNeasy Tissue Kit (Qiagen).