Wind Power Point
advertisement

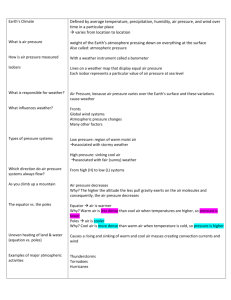
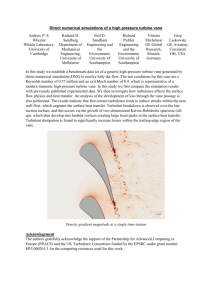
Wind Power Point Teacher Script Slide 1 Wind comes in many forms – a hurricane on the coast, an arctic front, a summer breeze… Wind energy does not pollute and thus, wind energy reduces carbon dioxide omissions that cause global warming. As long as the wind blows, energy from the wind is created. Wind is considered an inexhaustible (renewable) resource. Slide 2 The entire Earth experiences winds, but some places have stronger and more consistent wind than others. How Does Wind Form… • The rotation of the Earth (Coriolis effect): – The Earth spins about 1000 mph at the equator – The spinning of the Earth causes the atmosphere to spin along with it in a curved path Slide 3 The Coriolis effect is caused by the rotation of the Earth. Because the earth is solid and the atmosphere is gas, the atmosphere spins at a different speed and along curved paths. www.mhhe.com …How Does Wind Form? • Differences in temperature: – Angle of sun rays are greater towards poles (less heat at high latitudes) – Warm air from the equator moves towards the poles and cool air from the poles moves towards the equator – Mountains day: cool air on top, warm air below night: cool air drops, warm air rises – Large bodies of water (cooler than land in day) ( ) easyweb.easynet.co.uk Slide 4 In warm areas, air molecules spread apart. The separation of air molecules is called a low pressure system. Cooler (denser) air rushes towards the mass of warmer air. Once the cool air molecules fill the spaces between the warm air molecules the 1 temperature stabilizes and it becomes a high pressure system. This cycle occurs on a large scale with cool air from the poles moving towards the equator and heating, and then the air moves back toward the poles. The air is cooler at the poles because the angle that the sun’s rays strike the Earth is greater (less heat per area). Sun rays are more direct at the equator (more heat per area). The same cycle occurs on a smaller scale in areas with mountains or large bodies of water. The air on top of a mountain is cooler in the day than the air in the valley below. At night, the cool air on top of the mountain drops while the warm air rises and cools – the cycle repeats. During the day, the air above the water is cooler than the air over the land causing the winds to blow towards the water. At night, the land and air cools causing the wind to blow from the water to the land. Slide 5 A wind vane measures the direction wind blows. One example is the common “rooster” wind vane sometimes found on country barns. Wind Instruments www.sendweathervanes.com Wind Vane www.process-controls.com Cup Anemometer www.process-controls.com Ultrasonic Anemometer A cup anemometer measures the wind velocity. The cups capture pockets of air thus rotating in a circular motion. The number of revolutions per minute (rpm) relates directly to the wind velocity. An ultrasonic anemometer measures the wind velocity in a three-coordinate system (U-V-W). The ultrasonic anemometer makes measurements almost instantaneously. The approximate cost is $5,000. Slide 6 When scientists are looking for a good place to build a wind farm, there are a few general principles they go by. Windy Site Locations • Wind speeds increase with altitude: – Hills are better than depressions – Tall towers are better than short towers – Flat coastlines are better than steep cliffs (turbulence) www.me3.org • Large bodies of water cause wind changes: – Offshore turbines are popular due to stronger winds – The cooling and heating effect of water and land creates wind www.windpower.org Wind speeds increase with altitude. Wind turbines with tall towers are generally better powered than 2 turbines with short towers, although a short tower with more wind can produce a larger amount of energy than a tall tower with less wind. Hills are typically better than flat land. When a hill is too steep or there are steep cliffs in an area, the wind’s directional flow gets interrupted and turbulence (rough air) is created (i.e. turbulence on an airplane). Wind turbines do not work well in areas with high turbulence because it can cause wear-and-tear and damage turbine parts. Wind turbines are being placed off the coastline in European countries. Coasts provide a reliable source of strong winds due to the cooling and heating effect of water and land. Flat coastlines are better suited to wind farming than coasts with cliffs or hills because of turbulence. Slide 7 Turbulence Causes of Turbulence: Buildings, Steep Cliffs, Trees … Turbulence is created by objects disrupting the flow of wind. In the picture above, the building and vegetation block the flow of wind causing air eddies to form. The magnitude (strength) and direction of the eddies vary thus creating wind turbulence. www.u.arizona.edu 3