SEMESTER 1 MODULE 1
advertisement

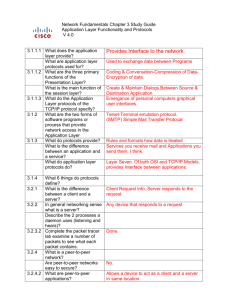
SEMESTER 1 Chapter 3 Application Layer Functionality and Protocols V 4.0 3.1.1.1 What does the application layer provide? What are application layer protocols used for? 3.1.1.2 What are the three primary functions of the Presentation Layer? What is the main function of the session layer? 3.1.1.3 What do the Application Layer protocols of the TCP/IP protocol specify? 3.1.2 What are the two forms of software programs or process that provide network access in the Application Layer 3.1.3 What do protocols provide? 3.1.4 3.2.1 3.2.2 What is the difference between an application and a service? What do application layer protocols do? What 6 things do protocols define? the interface between the applications we use to communicate and the underlying network over which our messages are transmitted to exchange data between programs running on the source and destination hosts Coding and conversion of Application layer data to ensure that data from the source device can be interpreted by the appropriate application on the destination device. Compression of the data in a manner that can be decompressed by the destination device. Encryption of the data for transmission and the decryption of data upon receipt by the destination. create and maintain dialogs between source and destination applications the format and control information necessary for many of the common Internet communication functions applications and services the rules and formats that govern how data is treated Applications interact with the user and services prepare data for the network Protocols provide the rules and formats that govern how data is treated. 1. processes on either end of the communication 2. types of messages 3. syntax of messages 4. meaning of any informational fields 5. how messages are sent and the expected response 6. interaction with the nextlower layer What is the difference the device requesting the information is called between a client and a a client and the device responding to the server? request is called a server In general networking sense any device that responds to requests from what is a server? client applications is functioning as a server Describe the 2 processes a "listening" for a request from a client, because daemon uses (listening and hears)? 3.2.3.2 Complete the packet tracer lab examine a number of packets to see what each packet contains. 3.2.4 What is a peer-to-peer network? Are peer-to-peer networks easy to secure? 3.2.4.2 What are peer-to-peer applications? 3.3.1 What do port numbers identify? What does the DNS protocol do? 3.3.1.2 What does the nslookup utility allow you to do? What does the command ipconfig /displaydns show? 3.3.1.3 What happens if a DNS server does not have a name in its stored records? If the same request is made again where does the DNS server look? 3.3.1.4 When is a server declared to be an authoritative server? 3.3.2.1 Define the three parts of a url as listed on the page? What type of request is sent to the server when retrieving a web page? 3.3.2.2 What does the POST command do? What does the PUT command do? What protocol is used for they are programmed to respond whenever the server receives a request for the service provided by the daemon "hears" a request from a client, it exchanges appropriate messages with the client, as required by its protocol, and proceeds to send the requested data to the client in the proper format two or more computers are connected via a network and can share resources (such as printers and files) without having a dedicated server No allows a device to act as both a client and a server within the same communication applications and Application layer services that are the source and destination of data defines an automated service that matches resource names with the required numeric network address. allows the user to manually query the name servers to resolve a given host name Displays all of the cached DNS entries on a Windows XP or 2000 computer system It passes the request on to another DNS server In its cache When the resource is directly held on that server http:- protocol www.cisco.com- name of server web-server.htm- name of file or page GET Sends information to the web server Sends resources or content to the web server HTTPS: 3.3.2.3 3.3.3 3.3.3.2 3.3.3.3 3.3.3.4 secure transmission across the web? Packet Tracer Lab What 2 Application Layer protocols are used in sending and receiving email? What is another name for an email application? What are the two processes that email servers perform? What happens to emails in many companies once the email reaches the internal server? List and describe some of the commands used by the SMTP protocol. 3.3.4 What is File Transfer Protocol (FTP)? What are the 2 ports used and their purpose in FTP? 3.3.5 What does Dynamic Host Confirmation Protocol (DHCP) do for a network? 3.3.5.2 What are the 4 types of messages sent and received in DHCP? 3.3.6 What is SMB (Server Message Block)? 3.3.6.2 What are the 3 message types of SMB messages? 3.3.8 What does the Telenet application provide? 3.3.8.2 What protocol is recommended alternative to Telnet when security is a concern? 3.4 We will skip these labs 3.5.1.2 This is a self scored quiz that will help prepare for the POP (Post Office Protocol) and SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) MUA Mail User Agent MTA Mail Transfer Agent MDA Mail Delivery Agent Converted to a proprietary protocol for mail delivery HELO - identifies the SMTP client process to the SMTP server process EHLO - Is a newer version of HELO, which includes services extensions MAIL FROM - Identifies the sender RCPT TO - Identifies the recipient DATA - Identifies the body of the message developed to allow for file transfers between a client and a server 21- Used for control 20- Used for actual file transfer allows a host to obtain an IP address dynamically when it connects to the network DHCP Discover DHCP Offer DHCP Request DHCP Acknowledge the structure of shared network resources, such as directories, files, printers, and serial ports Start, authenticate, and terminate sessions Control file and printer access Allow an application to send or receive messages to or from another device provides a standard method of emulating textbased terminal devices over the data network. SSH Secure Shell protocol test 3.5.1.3 Packet Tracer Lab that is relatively challenging and should help preparing for the exam. Not required, but would be helpful. 3.6.1 Quiz that also prepares you for the test. * What are the characteristics of OSI application layer? Layer seven, is the top layer of both the OSI and TCP/IP models. It is the layer that provides the interface between the applications we use to communicate and the underlying network over which our messages are transmitted. Application layer protocols are used to exchange data between programs running on the source and destination hosts. * How does the application layer handle application requests from multiple different clients at the same time? A single application may employ many different supporting Application layer services; Servers typically have multiple clients requesting information at the same time. The Application layer processes and services rely on support from lower layer functions to successfully manage the multiple conversations * What are the 2 types of the network application layer software? There are two forms of software programs or processes that provide access to the network: applications and services. * You need to know functions of the following Application Layer protocols. File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is used for interactive file transfer between systems Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is used to transfer files that make up the Web pages of the World Wide Web. For secure communication across the Internet, the HTTP Secure (HTTPS) protocol is used for accessing or posting web server information. Telnet, a terminal emulation protocol, is used to provide remote access to servers and networking devices. SSH provides stronger authentication than Telnet and supports the transport of session data using encryption Domain Name Service Protocol (DNS) is used to resolve Internet names to IP addresses. o The DNS server stores different types of resource records used to resolve names. These records contain the name, address, and type of record. o Some of these record types are: A - an end device address NS - an authoritative name server CNAME - the canonical name (or Fully Qualified Domain Name) for an alias; used when multiple services have the single network address but each service has its own entry in DNS MX - mail exchange record; maps a domain name to a list of mail exchange servers for that domain Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is used for the transfer of mail messages and attachments. o SMTP is a long established Internet protocol that is used for the delivery and receipt of e-mail. Post Office Protocol (POP): In order to receive e-mail from an e-mail server, the e-mail client can use POP. Telnet, a terminal emulation protocol, is used to provide remote access to servers and networking devices. SMB: Server Message Block (SMB) is a client/server file sharing protocol. The following are not application layer protocol (layer 7). We will discuss them in a later chapter - ARP - ICMP - PPP * What is client-server network model? What are the advantages of the client-server model? Centralized administration Security is easier to enforce the device requesting the information is called a client the device responding to the request is called a server. a client may transfer a file to the server for storage purposes (upload). Data from a server to a client as a download. * What are the characteristics of “clients” in the client-server network? A P2P application, allows a device to act as both a client and a server within the same communication Some P2P applications use a hybrid system where resource sharing is decentralized but the indexes that point to resource locations are stored in a centralized directory. Peer-to-peer applications can be used on peer-to-peer networks, client/server networks, and across the Internet A simple home network with two computers sharing a printer is an example of a peer-to-peer network. * Study the following graphic very carefully. What are the components used to forward mail between the servers? What are the purposes of MTA? o The MTA receives messages from the MUA or from another MTA on another e-mail server. o The MTA process is used to forward e-mail o The SMTP transport of e-mail between e-mail servers (MTA). What are the purposes of MDA? o If the mail is addressed to a user whose mailbox is on the local server, the mail is passed to the MDA.