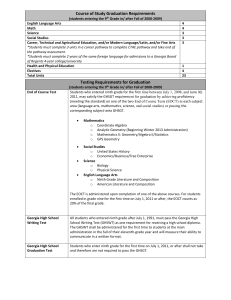
Content Review Guide
advertisement

KEY Content Review Guide for the Georgia High School Graduation Test in Science Carrollton High School TABLE OF CONTENTS Description of Graduation Test & Review Guide………………………………... 3 Test Taking Tips……………………………………………………………………. 4 Characteristics of Science Experimental Design………………………………….…………………………. Reading & Interpreting Data…………………………..………………………… Research Sources………………………………………………………………… 6 8 12 Domain 1: Cells and Heredity Cells……….…………………………………………………………………….. Heredity…………………………………………………………………………. Kingdoms………………………………………………………………….……. 14 21 28 Domain 2: Ecology……………………………………………….……………….… 30 Domain 3: Structure and Properties of Matter Matter…………………………………………………………………………….. Acids & Bases……………………………………………………………………. 38 49 Domain 4: Energy Transformations…….……………………….………………… 51 Domain 5: Forces, Waves, and Electricity Forces………………………………………...………………….………………. Waves…………………………………………………………….……………… Electricity & Magnetism..……………………………………….…………..…... 55 63 70 Resources Science Facts and Formulas……………………………………………………… Periodic Table……………………………………………………………………. Practice Test……………………………………………………………………… Answer Key………………………………………………………………………. 74 75 76 83 Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 2 of 84 The Georgia High School Graduation Test The Georgia High School Graduation Test (GHSGT) is a requirement for all students wishing to receive a Georgia diploma. It tests two main content areas: Ecology Domain 25% of test Cells and Heredity Domain 17% of test Biology 26% of test Structure and Properties of Matter Domain Physical Science Energy Transformations Domain Forces, Waves, and Electricity Domain 16% of test 16% of test Additionally, questions about the characteristics of science are integrated across the five domains. Two reference sheets accompany the questions on the GHSGT. These reference sheets are given to each student when testing. The two reference sheets have been included in the back of this Review Guide in the Resources section. How to Use this Review Guide This guide has been set up by domain area. The concept descriptions review the basic concepts that are likely to be tested on the GHSGT. Read through the concepts and examples and then try to answer the Practice Questions on your own. Use the reference sheets provided to you in the Resources Section. You may check your answers to the Practice Questions using the Key in the Resources Section. Carefully read the Test Taking Tips section of this Guide. the GHSGT. It gives you hints to help you do your best on Good luck! Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 3 of 84 Test-Taking Tips Before the test o o o o Make sure you know the date, time, and location of your test. Set up a flexible study schedule before the test to focus on your weakest areas. Make sure you have two #2 pencils with erasers with you. Have a good breakfast, drink plenty of water, and stop by the restroom before the test begins. o Stay positive! Reading the Question o Read the entire question and all the choices before answering the question. o If there is a reading passage associated with the question, it may help to read the question first but not the answer choices (you don’t want them to bias you), then the passage, then the question again. Finally read all answer choices. o If you don’t know a word, cover it up and read the question without the confusing word, or use context clues to help you determine the meaning of the word. o Use root words that you already know to help you determine words you don’t know. o There are no trick questions. Don’t make a question harder than it should be. Answering the Question o Take your time and read all answer choices before choosing. o If you are sure of the answer, pick it. o If you are not sure, but can eliminate some wrong answer choices, then make an educated guess. o Look for words in the answer choices that restrict the realm of the answer or are all encompassing such as all, none, never, always. Be aware that these are usually not the right choices because they do not leave room for exceptions. o If you have absolutely no idea, skip the question. At the end of the test, guess randomly on any questions you did not answer. o Answer every question and do not leave any blank! There is no penalty for guessing! After You Finish o If you left any questions blank, go back and see if you can answer them. If you have no idea, randomly choose an answer. o Check your answers. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 4 of 84 Practice Questions: Use the suggestions on the previous page to help you determine the best answer. 1. An endoscopic surgery requires a camera to ___________. A. take a picture of your brain B. map the beating of your heart C. enter inside your body to view inside D. take pictures of the surgeon who is working on the patient (Hint: Break the word “endoscopic” into root words in order to help you choose the best answer.) 2. Which of the following does not describe DNA? A. Deoxyribose is the sugar found in DNA. B. Proteins are found in DNA. C. DNA is a type of nucleic acid. D. Phosphate groups make up DNA. (Hint: Use the letters in “DNA” to eliminate 2 of the choices.) 3. Pick the statement that is most correct about global warming. A. Global warming will definitely cause the polar ice caps to melt. B. Records indicate that global warming has caused the Earth’s temperature to increase by a few degrees every single year. C. Global warming is a natural process of trapping heat on Earth. D. Pollutants like CFC’s and hydrocarbons are the only causes of global warming. (Hint: Look for words that restrict the answer such as “always, never, only, every.” Often these choices are incorrect.) Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 5 of 84 Characteristics of Science Experimental Design When scientists investigate a problem, they use a logical approach called the scientific method. There are steps to this method of problem solving: Problem Hypothesis Experiment Conclusion question that is being investigated educated guess (usually an “if…then” statement) testing of the problem summary statement that is based on data collected After the problem is identified and initial observations are made, a hypothesis is stated. It is usually stated as an “if… then” statement. An experiment is designed to test the hypothesis. The purpose of an experiment is to collect data that can be used to reach a conclusion. It must be possible to repeat the experiment over and over, with the same results every time. In order to do this, only one thing is changed in the experiment (the manipulated or independent variable) and its effect on something else (the responding or dependent variable) is observed. All other factors must remain the same throughout the experiment (controlled variables) to be sure the change seen in the responding variable is a result of the change made in the manipulated variable. Observations and measurements are made and recorded during the experiment. These are known as data. Many trials are done and a conclusion is drawn which will either support or not support the hypothesis. The hypothesis may be revised and the process repeated. A supported hypothesis may become part of a theory. A theory is the best-known explanation for what has been observed. Theories can be changed as new information becomes available. A theory will never be proven since it is not a fact, but rather, an explanation. There are many theories in science including the Atomic Theory, the Theory of Plate Tectonics, and the Theory of Evolution. A scientific law is a statement of a relationship that is observed in the natural world without exception. Among these are Newton’s Laws of Motion, the Law of Conservation of Mass/Energy, and the Gas Laws. Unlike a theory, a scientific law is not an explanation; rather, it is a statement of fact. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 6 of 84 Practice Questions: Read the following and answer the questions that follow. Joe likes sugar in his iced tea; however, he forgot to put sugar in his tea today. Joe tried adding the sugar to the glass of iced tea. It didn’t dissolve very well, so he decided to try an experiment. He took 5 glasses each with 200 mL of unsweetened tea. He made each glass of tea a different temperature and then added 15 grams of sugar to each. He recorded the results after stirring each glass for 2 minutes. 1. What statement best represents the problem being investigated? A. The effect of tea on the dissolving rate of sugar B. The effect of amount of sugar in making an iced tea solution C. The effect of temperature on the amount of tea that dissolved D. The effect of temperature on the solubility of sugar 4.Which variable was the responding/ dependent variable? A. Temperature of tea B. Amount of sugar used C. Amount of tea made D. Amount of dissolved sugar 5.In a line graph, the manipulated variable is placed on the x-axis. Which variable would be graphed on the x-axis? A. Temperature of tea B. Amount of sugar dissolved C. Amount of sugar used Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 7 of 84 Characteristics of Science Reading and Interpreting Data Concept #1: In any experiment, scientists must observe and record data, which are observations and measurements made during an experiment. To best record this data, scientists set up tables in order to be organized in their observation and measurement collection. Graphs can then be constructed from gathered data in order to make a visual comparison of the data and better share information with other scientists, especially when scientists suspect a proportional relationship between the variables. A scientific graph must have a title. The purpose of a graph is to share information in a concise way. A good title must be descriptive of the information being conveyed. The graph will have two axes, a horizontal axis (x axis) which represents the independent/ manipulated variable (the factor the scientist altered) and a vertical axis (y axis) which represents the dependent/ responding variable (the factor that changed based on the independent variable). Each axis must be labeled or titled with the variable (the factor being tested) it represents as well as the unit used to measure the variable. An appropriate scale must be chosen that will allow all the data to be graphed. Each pair of data points must be plotted and a best-fit line or curve (smooth, not dot-to-dot) drawn to represent the general tendency of the data points. After graphing the data, scientists look for a proportional relationship. Often, the relationship will be a direct proportion, in which the two quantities being compared change in the same way. In other words, when one variable is doubled, the other variable is doubled as well. This relationship, when graphed, will produce a straight line. Another relationship is an inverse proportion, in which the two quantities being compared change in an opposite way. In other words, when one variable is doubled, the other variable is halved. When graphed, an inverse proportion produces a hyperbolic curve. Direct proportion Inverse proportion Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 8 of 84 Practice Questions: Use the information and the table to answer the questions that follow. Area, A (cm2) Pressure, P (N/cm2) Pressure is calculated by dividing an exerted force by the area over which the force is exerted. In other words, 1.0 25.0 2.0 12.5 3.0 8.5 4.0 6.4 5.0 5.0 Pressure = force ÷ area In a particular experiment, a student calculated the pressure resulting when she changed the surface area over which an unchanging force was applied. She recorded her data in the table to the right. 1. In this experiment, which variable is the independent/manipulated variable? _Surface area__ Which variable is the dependent/responding variable? ___Pressure___ 2. Which variable will be placed along the x-axis? ____Surface area____ Which variable will be placed along the y-axis? ____Pressure____ 3. Graph the data from the table, being sure to follow all of the guidelines for scientific graphing listed on the previous page. Pressure vs. Area Pressure (N/cm2) 30.0 25.0 20.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 0.0 1 2 3 4 5 Area (cm2) 4. According to the shape of the best-fit curve, the proportion existing between the two variables is (inverse, direct). Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 9 of 84 Concept #2: A bar graph is used to show comparisons among data that do not continuously change. Thick bars rather than data points are used to show the relationships among data. Follow the steps below to construct a bar graph. Place the independent/manipulated variable on the x-axis. Place the dependent/responding variable on the y-axis. Plot the data by drawing thick bars from the x-axis up to an imaginary point where the y axis would intersect the bar. Make sure to title the graph. Practice Questions: Use the graph to answer the questions that follow. Vibrations per Second os qu it o M Ho ne yb ee Vibrations per Second Ho us ef ly Be et le 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 1. Which insect has the greatest wing vibration per second? A. Honeybee B. Housefly C. Mosquito 2. Which insect has the least wing vibration per second? A. Honeybee B. Housefly C. Beetle 3. Which is the independent variable? A. Wing vibrations per second B. Insect type Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 10 of 84 Concept #3: Pie graphs are a good way to show the relationship between relative amounts of materials or percentages of materials. They can also be used to show the actual amount that is represented. The relative sizes of the wedges would still give you a good picture of how each subdivision is related to the total amount represented. A pie graph clearly shows how the whole is made up of its parts. To make a pie graph you must have a compass. You will also need a protractor and a ruler. Construct the circle with the compass. Draw a line from the center of the circle to the edge of the circle at the 12:00 position. Use the top center of the circle as your starting point (12:00 position). Remember that a circle is made of 360 degrees, and divide each segment appropriately. Think of a circle as divided into 100 parts, so each part is 3.6 degrees. To determine the angle for each segment simply multiply the percentage by 3.6. Complete the graph by labeling the sections and giving the graph a title. Practice Questions: Amount of Time Spent on Daily Activities Use the table and graph to answer the questions that follow. Activity school sleep job leisure meals homework # of Hours 6 6 4 4 2 2 % of Day 25% 25% 17% 17% 8% 8% homework 8% meals 8% school 25% leisure 17% job 17% 1. Which two activities together took up half of the day? A. Leisure and School B. Meals and School C. Sleep and School 2. Which two activities took up the least amount of time? A. Meals and Homework B. Sleep and Job C. Sleep and School 3. Which activity takes up the same amount of time as meals and leisure together? A. Job B. School C. Homework 4. Which activity took up one fourth of the day? A. Leisure B. Sleep C. Homework Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 11 of 84 sleep 25% Characteristics of Science Research Sources Concept #1: There are many different sources you can use to do scientific research. Some sources you might use are an Internet search engine (like Google), encyclopedias, books, or journal articles. Many encyclopedias, books, and journal articles are now available online. Match the resource with its description. 1. Card catalog A. Magazines or books containing papers from scientists on their experimental findings 2. Internet B. Atlas, dictionary, encyclopedia, and other generic sources 3. Reference materials C. A catalog of books and reference materials available at the 4. Science journals library and arranged in order for easy use D. Electronic network that connects computers across the world and that is often used to share information Answers: 1 C, 2 D, 3 B, 4 A Using an Internet search engine: Make the search criteria as specific as possible. For example, if you are researching how salt added to soil influences rose plant growth, you would not want to look up “roses” or “salt” or “soil” but a combination of all 3 words. This will help you avoid information that is useless to you like how humans should reduce salt intake from their food. Using books: There are many helpful resources in a book. Match the book resource with its description. 1. Glossary A. Lists the order of information found in the book 2. Index B. A collection of terms with their meanings 3. Table of Contents C. Lists alphabetically the subjects of the book and the page numbers where you can find the subject Answers: 1 B, 2 C, 3 A Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 12 of 84 Concept #2: The sources you use should be valid. This means that the source comes from a reputable location. If you are using an Internet source, it is best to use a webpage with the site suffix of .gov (a government website), .edu (an educational website), or .org (a non-profit organizational website). Usually a website with a site suffix of .com is not considered to be the most reliable. Critically look at websites and see if they have an agenda for selling a product. Some .com sites might have biased information because they are trying to persuade you to purchase something. Remember, anyone can put anything on the Internet - it doesn’t make it factual information! Concept #3: Any sources you use have to be properly documented. If you use a source, you need to paraphrase the document (not just copy and paste). You must write things in your own words. You need to include a works cited/ bibliography of the sources you used. This way the reader will know where your information came from. Practice Questions: 1. Larry needs to find current information on any SARS outbreaks in China. Which source would give him the best information? A. Library book B. Reference material C. Internet 2. Danielle was assigned to draw a picture of an Amoeba from her textbook and she doesn’t remember what page her teacher told her to use as a reference. Where could she look to figure out exactly which page the Amoeba information is on? A. Reference material B. Index C. Table of contents For questions 3 & 4, describe how the students could better use sources for their research. 3. George is trying to research the President’s new environmental policy. He has to prepare a debate in class to show the pros and cons of the policy. He has decided to use only .gov sites to research, mainly using the President’s policy page to gather most of his information. .gov sites might be biased since the President is the head of the government. George should use other types of sites such as .org that might not be biased. 4. Katrina is searching for information for her project on bacteria. She searches several .com sites and notices that they are all trying to sell anti-bacterial soap. The one .org site she goes to for extra information is for an organization that helps fight bacterial meningitis. .com sites might exaggerate the harmful effects of bacteria to get you to buy a product. Katrina should search .org or other .com sites that are not trying to sell a product. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 13 of 84 Domain 1: Cells and Heredity Cells Concept #1: All living things are made up of at least one cell. Cells are the basic unit of structure (since they make up the parts of living things) and function (since they help living things work properly). Organisms that are made of only one cell are called unicellular organisms; those that are made of two or more cells are called multicellular organisms. Multicellular organisms are believed to have evolved (or changed over time) from unicellular organisms. Concept #2: Cells are made up of many organelles, each with a specific function. Cells that have membranes around their organelles and a true nucleus are called eukaryotic cells. All plants, animals, fungi, and protists are eukaryotes. Cells that do not have a true nucleus are called prokaryotic cells. Examples of prokaryotes are bacteria. www.cod.edu Match the cell organelle to its function. 1. nucleus 2. nucleolus 3. endoplasmic reticulum 4. golgi apparatus 5. cell membrane 6. ribosome 7. cell wall 8. chloroplast 9. mitochondria 10. lysosomes 11. microfilaments and microtubules 12. cilia and flagella www.cod.edu A. contain digestive enzymes to break down parts of the cell and dispose of wastes B. the brain or control center of the cell C. outer structure in plant and fungi cells; used for support and protection D. produce energy for the cell E. where proteins are made F. site of photosynthesis in plant and algae cells G. form the cytoskeleton, or backbone, of the cell H. packages proteins I. transportation system for moving proteins around the cell J. gatekeeper for the cell; allows some materials to enter and leave the cell K. where ribosomes are produced L. membrane bound sac that stores nutrients or water M. help the entire cell move; projections off the cell’s surface 13. vacuole Answers: 1 B, 2 K, 3 I, 4 H, 5 J, 6 E, 7 C, 8 F, 9 D, 10 A, 11 G, 12 M, 13 L Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 14 of 84 blogs.ign.com Concept #3: The Cell Theory 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit or structure and function in organisms 3. All cells are produced from other cells. Concept #4: Homeostasis is a self-adjusting mechanism that helps organisms maintain a stable internal environment in the face of a changing external environment. An example includes a body sweating in response to an increase in body temperature. Organisms also need to move materials into and out of their cells. To do this, cells use passive and active transport. In passive transport, molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This does not require energy. Examples of passive transport are simple diffusion and osmosis (where only water moves through a membrane). In active transport, molecules move from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This does require energy (usually in the form of ATP), and includes examples like endocytosis (bringing things into the cell) and exocytosis (making things exit the cell). www.uic.edu www.uic.edu Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 15 of 84 www.uic.edu Practice Activity: Label the plant and animal cells and their parts. www.ndpteachers.org Diagram A is a(n) _ plant____ cell. Diagram B is a (n) ____animal___ cell. 1. ____cell wall________________ 2. ___mitochondria_____________ 3. ____vacuole_________________ 4. ____Golgi apparatus__________ 5. _____cytoplasm_____________ 6. _____nuclear membrane_______ 7. _____nucleolus______________ 8. ______nucleus_________________ 9. ______chromosome_____________ 10. ____endoplasmic reticulum______ 11. ______chloroplast_____________ 12. ______centriole_______________ 13. ______lysosome______________ cell wall centriole chloroplast chromosome cytoplasm endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus lysosome mitochondria nucleus nucleolus nuclear membrane vacuole Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 16 of 84 Concept #5: Cells need energy to function. To create energy, cells use their mitochondria to do a process called cellular respiration. In cellular respiration, glucose is broken down into energy, or ATP. Every organism (plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and protists) does cellular respiration, which is displayed in the following formula: C6H1206 + 6 O2 glucose oxygen 6 H2O + 6 CO2 + ATP water carbon dioxide energy Where do the cells get the glucose from? o Consumers or heterotrophs (organisms that cannot make their own food) eat food which is broken down into glucose, a special type of sugar. The glucose is combined with oxygen from the atmosphere in order to make energy. Water and carbon dioxide are wastes produced from respiration. o Producers or autotrophs (organisms that can make their own food) make their own glucose in a process known as photosynthesis. This occurs in the chloroplasts of producers. During this process, the producer gathers light, water, and carbon dioxide, and produces glucose and the waste product oxygen. The producer can then use the glucose during respiration to make energy. Photosynthesis is displayed in the following formula: 6 H20 water Reaction Type Energy Source Form of Energy produced Reactants Products + 6 CO2 carbon dioxide C6H1206 + light glucose Respiration Exothermic Glucose ATP O2, glucose (C6H12O6) CO2 , H2O, energy 6 O2 oxygen Photosynthesis Endothermic Light Glucose CO2, H2O, energy O2. glucose (C6H12O6) www.cwanswers.com Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 17 of 84 Concept #6: Somatic cells (body cells) divide during a process known as mitosis. Cells may need to divide because of damage, injury, or growth. During this process, one cell doubles all of its contents, and then splits into two daughter cells. The two daughter cells are identical to each other and to the parent cell they came from. Phase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Major Events of Mitosis Events Stringy chromatin condenses into chromosomes (x-shaped structures) Nucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear Spindle begins to form Chromosomes line up along the middle (equator) of the cell Chromosomes split Nucleolus and nuclear membrane reform During cytokinesis, the two cells completely split. When cells are not actively dividing, they are in a phase known as interphase. During this phase, cells grow, get ready for mitosis (by copying their DNA in a process called replication), and do normal cell functions. Together, interphase and mitosis are known as the cell cycle. Plant Mitosis Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase www.life.illinois.edu Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 18 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. Which of the following terms is the most inclusive? A. Cells B. Organs C. Organ systems D. Tissues 2. Which statement is NOT true about cellular transport? A. Cell transport may or may not require energy. B. Materials can move into and out of cells. C. All materials move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. D. The cell membrane helps to control which items enter and leave the cell. 3. An old organelle in a cell needs to be broken down before it can be disposed. Which organelle would be most likely to perform the function of breaking down the old organelle? A. Nucleus B. Lysosome C. Endoplasmic reticulum D. Cell membrane 4. Which statement is NOT true about cellular respiration? A. All organisms undergo cellular respiration. B. Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria of cells. C. Cellular respiration is responsible for making energy in the form of ATP. D. Cellular respiration only occurs in animals. 5. Mitosis is the process of duplicating cells. Following are steps involved in mitosis, but they are out of order. i. One cell splits into two cells. ii. Cell contents, including DNA, are duplicated. iii. The chromosomes, or DNA material, line up at the middle of the cell. What is the proper order of the steps? A. i.,ii., iii. B. ii., iii., i. C. ii., i., iii. D. iii., ii., i. 6. Read the following and answer the question that follows. Volvox is a colonial protist that lives in freshwater. It is composed of many individual organisms that use the sun’s light to make their own food. Based on the reading, which of the following statements must be true about Volvox? A. It contains chloroplasts in order to do photosynthesis. B. It is a unicellular organism. C. Volvox must be really neat to look at. D. Since Volvox makes its own food, it must not ever need to do cellular respiration. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 19 of 84 7. Which of the following processes involves the chloroplast? A. cell division B. conversion of light energy to chemical energy C. formation of reproductive cells D. stringing amino acids together 8. What is the basic unit of structure and function of living things? A. cell B. organ C. molecule D. organelle 9. Which organelle helps to maintain homeostasis within a multicellular organism through exchange of materials with other nearby cells? A. cell membrane B. mitochondrion C. nucleus D. vacuole 10. Which statement best describes active transport? A. Molecules move very quickly across the membrane. B. Energy is expended to move molecules across a membrane. C. More molecules move across a membrane than in diffusion. D. Water molecules stream across a membrane into a concentrated solution. 11. An animal cell is placed in a solution of distilled water. If left overnight, this cell will A. shrivel and die B. swell and burst C. undergo plasmolysis D. remain the same since it has a cell wall to protect it 12. Which is the best example of a multicellular organism maintaining homeostasis? A. a dog salivating at the sound of a bell B. a moth flashing eye spots on its wings C. a wolf remaining with a pack of other wolves D. a kangaroo rat producing concentrated urine 13. In order to measure the rate of photosynthesis by a plant, a researcher should measure the amount of A. oxygen produced B. sunlight absorbed C. carbon dioxide produced D. glucose used Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 20 of 84 Heredity Domain 1: Cells and Heredity Concept #1: Traits are passed from generation to generation. This is called heredity. The study of heredity is known as genetics. Traits are passed through genes, which are composed of DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is found in the nucleus of every cell of every organism and is made up of phosphate groups, deoxyribose sugars and nucleotides called adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. The shape of DNA is a double helix (twisted ladder). It controls the cell’s activity. DNA is a type of nucleic acid, which is one of the 4 major biological, or organic, compounds. cnx.org www.cs.bham.ac.uk The four biological compounds all contain carbon and hydrogen. They make up all living things. Name Examples Made up of Function Carbohydrates Sugars & Starches Monosaccharides Energy Lipids Fats, Oils, & Waxes Glycerols and Stored energy fatty acids Cell membrane formation Insulation and protection Proteins Enzymes Amino acids Build structures of body Muscles Help parts function Speed up reactions Nucleic Acids DNA & RNA Nucleotides Transmit heredity information Make proteins Concept #2: DNA controls the cell’s activities by helping to manufacture proteins. Proteins are important because they make up the body’s structure and help it to function. For example, all muscles are made of protein. DNA contains the recipe for making proteins, but since it never leaves the nucleus, another nucleic acid known as RNA, or ribonucleic acid, actually makes the proteins. This is how proteins are made: Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 21 of 84 1. DNA is the recipe for proteins and it is always found in a cell’s nucleus. 2. DNA’s protein recipe is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) during a process called transcription. This also occurs in the nucleus. 3. mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome, where all proteins are assembled. 4. Transfer RNA (tRNA) comes to the ribosome with amino acids (what proteins are made of) where it reads the recipe and assembles the proteins in a process called translation. 5. The amino acids are bonded together to make a protein. 6. A mutation is a sudden change in the code. www.mysciencebox.org How are DNA and RNA alike and different? Double-stranded Found in nucleus Contain heredity information Thymine pairs with adenine DNA Single-stranded Moves around the cell Uracil pairs with adenine Help to make proteins Nucleic acids Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 22 of 84 RNA Concept #3: In order to pass genes from parent to offspring, sex cells (or gametes) containing the DNA must be made. Male gametes are known as sperm and are produced in the testes. Female gametes are known as eggs (or ova) and are made in the ovaries. The process of producing gametes is known as meiosis. During meiosis, the number of chromosomes is halved. In humans, the number of chromosomes in a sperm is 23 and the number of chromosomes in an egg is 23. When the two gametes fuse, they make a zygote (the beginning stage of a baby) with 46 chromosomes. Since the zygote has two sets of DNA (one from mom and one from dad), it is known as diploid. If it only had ½ that amount of DNA, it would be called haploid. Sperm and egg are haploid. Phases of Meiosis: o Meiosis I- Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I o Meiosis II- Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II Events of Meiosis: o Prophase I- homologous (or matching) chromosomes join to form a tetrad. o Metaphase I- Homologous chromosomes line up at the middle of the cell. o Anaphase I- Homologous chromosomes split. o Telophase I/ Cytokinesis- The one cell splits into two cells. Each cell is different. o Metaphase II- The individual chromosomes line up at the middle of each of the two cells. o Anaphase II- The chromosomes split. o Telophase II/ Cytokinesis- The two cells each split, forming a total of four cells. Results of Meiosis: o Males- 4 haploid sperm are produced. o Females- 1 large haploid egg and 3 small polar bodies (which are not used) are produced. www.reviewsheetscentral.com Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 23 of 84 Practice Activity: Determine if the following statements describe the processes of mitosis and/or meiosis. Place a check mark in the correct column. 1. produces two identical daughter cells 2. produces four cells 3. chromosome number is halved 4. chromosome number is maintained 5. one division is involved 6. two divisions are involved 7. associated with sexual reproduction 8. associated with asexual reproduction 9. genetic variation is more likely 10. daughter cells are identical to parent 11. takes place in somatic cells 12. duplication of chromosomes occurs 13. necessary for growth and maintenance 14. produces gametes Mitosis √ Meiosis √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ Concept #4: Gregor Mendel is known as the father of genetics. He studied heredity in pea plants and determined many of the genetic principles we still use today. Before we look at Mendel’s Laws of Genetics, let’s review some of the basic genetic terms. Terms Definitions Allele the different forms of a gene; one allele for each trait comes from each parent Dominant the allele that masks a recessive allele; represented by a capital letter Recessive the allele that is masked by a dominant allele; represented by a lowercase letter Homozygous when the two alleles in a gene pair are the same; can be homozygous dominant (like AA) or homozygous recessive (like aa) Heterozygous when the two alleles in a gene pair are different (like Aa); also known as hybrid Gene a segment of DNA that codes for a particular trait Genotype the gene combination of an organism (like Tt) Phenotype the physical appearance of an organism (like tall or short) Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 24 of 84 Mendel’s Laws tell us about genetics: His first law states that each gene has two alleles. One allele came from the offspring’s mom and one came from dad. During meiosis, the two alleles separate (or segregate) from each other. Because of this, an offspring will only get one allele from each parent. This law is known as the Law of Segregation. Mendel’s second law is known as the Law of Independent Assortment. This tells us that during meiosis, genes for different traits assort independently from each other. This means, for example, that the gene for a big nose is completely separate from the genes for tallness. We know this makes sense because not everyone who has a big nose is incredibly tall. We can use what we know about genetics to predict the offspring of two parents reproducing. The way we do this is with a Punnett square. Example: Martians have 2 different skin tones- green (which is dominant) and gray (which is recessive). Let’s say a mom Martian has homozygous gray skin (so she is gg) and dad Martian has heterozygous green skin (so he is Gg). If these two were to produce offspring, what is the likelihood that the baby will be gray like its mom? Dad Mom G g g g Gg gg Gg gg Potential offspring According to this Punnett square, there is a 2/4, or 50%, chance the baby will be gray (gg) like its mom. Practice Activity: In a certain plant species, rough seeds (R) are dominant over smooth seeds (r). Using the following Punnett square, predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring whose parents are both heterozygous (Rr). R r R RR Rr r Rr rr Genotypes: _25_% homozygous rough seeds (RR) _50_% heterozygous rough seeds (Rr) _25_% homozygous smooth seeds (rr) Phenotypes _75_% rough seeds _25_% smooth seeds Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 25 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. Where in the cell and during what process are amino acids linked to make a protein? A. Ribosome; transcription B. Ribosome; translation C. Nucleus; transcription D. Nucleus; translation 2. Which of the following displays a homozygous dominant genotype? A. BB B. Bb C. bb D. Brown 3. One of Joe and Sue’s kids has blond hair and blue eyes but the other has blond hair and brown eyes. Which of Mendel’s laws best explains this? A. Law of Segregation B. Law of Independent Assortment C. Neither since that should never happen. 4. You performed a test where you added food samples to water, shook them up, and determined whether they mixed. Which of the following biological compounds were you most likely testing for? A. Carbohydrates since they always mix with water, and with no other liquids. B. Lipids since they do not mix with water. C. Nucleic acids because DNA is found in food samples. 5. A Martian with horns (HH) marries a Martian with no horns (hh). What is the likelihood that their firstborn child will not have horns? A. 100% since all their offspring will be hh. B. 0% since all of their offspring will be HH. C. 0% since all of their offspring will be Hh. D. Cannot be determined from the information given. 6. Which of the following is NOT a reason why meiosis is important? A. It reduces the number of chromosome by half. B. It makes gametes or sex cells. C. It makes identical copies of cells in order to replace damaged cells. D. It produces genetically different daughter cells. 7. Which word describes a gamete? A. diploid B. haploid C. somatic D. body Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 26 of 84 8. If a cell has 12 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after the cell undergoes mitosis? A. 4 B. 6 C. 12 D. 24 9. The daughter cells produced in mitosis A. become gametes B. have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell C. are the result of 2 processes of division D. have the same DNA as the parent cell 10. The process of copying DNA to make new identical DNA molecules is called A. replication B. transcription C. transformation D. translation 11. Using a strand of DNA to synthesize a molecule of mRNA is called A. replication B. transcription C. transformation D. translation 12. Which of the following is NOT found in DNA? A. adenine B. guanine C. thymine D. uracil 13. When tRNA molecules carry amino acids to mRNA codons in the ribosome of a cell, the tRNA and mRNA work together to create an amino acid chain. This process is called A. replication B. transcription C. transformation D. translation 14. DNA differs from RNA because: A. DNA is always single-stranded whereas RNA is always double-stranded B. DNA contains deoxyribose, whereas RNA contains ribose. C. DNA contains uracil, whereas RNA contains thymine D. DNA contains information whereas RNA doesn't Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 27 of 84 Domain 1: Cells and Heredity Kingdoms The 6 kingdoms have differences and similarities. All living things need to obtain energy, grow, reproduce, respond to their environment, and have some organization within their bodies or cells. Archaebacteria Eubacteria “ancient “new bacteria” bacteria” Protists Thermophiles, halophiles, methanogens Green algae, E. coli, Streptococcus diatoms, Cell Level Cell Type Prokaryote Unicellular Prokaryote Unicellular Movement Flagella or cilia Flagella or cilia Habitat Extreme environments Anywhere that is warm, dark, and moist Nutrition Autotrophs Transport Simple diffusion Heterotrophs, decomposers, autotrophs Simple diffusion Heterotrophs (algae are autotrophs) Diffusion (specialized organelles move materials) Binary fission Mitosis Examples Reproduction Binary fission Amoeba, Paramecium Eukaryote Unicellular (some algae are multicellular) Flagella, cilia, or pseudopodia Water and soil Fungi Plants Molds, mushrooms, yeasts Grasses, pine trees, rose bushes, mosses Eukaryote Multicellular (yeasts are unicellular) Eukaryote Multicellular Stationary Stationary Soil, in dead organisms, and in foods like bread and wine Heterotrophs, decomposers Mainly soil but some live in water, air, or on other plants Autotrophs Heterotrophs Connected cells called hyphae move materials Most have vascular system (xylem moves water and phloem moves food) Asexual: spores (ferns and mosses), runners, and tubers Sexual: Flowers (angiosperms), fruits, seeds, and cones (gymnosperms) Vascular systems (vertebrates) Asexual and sexual spores Divisions of Classification (from most general to most specific) Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species “King Phillip Came Over For Great Spaghetti” Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 28 of 84 Animals (invertebrates and vertebrates) Insects, sponges, mammals, worms Eukaryote Multicellular Most move at some point in life Varies Asexual: budding Sexual: laying eggs or giving birth Kingdom Terms: o Binary fission- some simple organisms go through this process to divide one organism into two o Prokaryote- cell without a nucleus nor other membrane-bound organelles o Eukaryote- cell with a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles o Thermophiles, Halophiles, Methanogens- bacteria that live in extreme conditions such as no oxygen, high temperatures, and extreme salt o Organelles- tiny organ-like parts that perform functions inside cells o Unicellular - whole organism is made up of only one cell o Multicellular- organism is made of many cells that are usually organized into tissues, organs, or organ systems o Reproduction- how an organism produces offspring o Chemosynthesis- using chemicals to produce food o Photosynthesis- using light to produce food o Decomposers- using enzymes to digest food outside the body and taking in the nutrients Practice Questions: 1. The main difference between bacteria and protists is _____________. A. bacteria are unicellular and protists are multicellular B. bacteria are consumers and protists make their own food C. bacteria are found in water and protists are not D. bacteria do not have a nucleus and protists do have a nucleus 2. An organism in the Kingdom Archaebacteria would probably live everywhere except ______________. A. the Great Salt Lakes B. Old Faithful in Yellowstone National Park C. on a kitchen counter top 3. The process of chemosynthesis creates food from ___________. A. chemicals B. sunlight C. decomposition 4. Which organism is NOT a heterotroph? A. Mushroom B. Algae C. E. coli bacteria D. Spider 5. All kingdoms have some form of asexual reproduction. A. True B. False 6. Most plants and animals have _____________ to move nutrients around their bodies. A. Xylem B. Vascular tissue C. Organs called hearts Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 29 of 84 D. Phloem Domain 2: Ecology Concept #1: Levels of Ecological Organization: BIOSPHERE/BIOME (Parts of the earth and atmosphere that can support life) ECOSYSTEMS (Biotic [living] and Abiotic [nonliving] sections) COMMUNITIES (Different populations of living organisms interacting) POPULATON (A group of organisms of the same species that can interbreed to produce fertile offspring) INDIVIDUAL ORGANISM Biomes: areas with similar abiotic factors (temperature, rain, soil), plant, and animal species Terrestrial Biomes: 1. Grassland- grass is the main producer; long periods of drought; zebra, lions, and prairie dogs; prairies or steppes 2. Tundra- permafrost soil; dry, short growing season; few animals; main producers are moss and lichens; located at the northernmost part of Northern Hemisphere 3. Tropical Rain Forest- most biodiversity; lots of rainfall; constant warm temperature year round; orchids, sloths, and birds 4. Taiga- coniferous forest (pine, spruce, fir trees); snow; consumers like caribou, oxen, and snowy owls 5. Desert: hot days, cold nights; very little rainfall; reptiles, nocturnal mammals, and cacti; sandy soil 6. Temperate (Deciduous) Forest: 4 distinct seasons; deciduous trees (oak and maple); moderate rain; squirrels and deer; covers much of the U.S. and Europe Aquatic Biomes: 1. Marine-salt water environment and the organisms found there 2. Freshwater-lakes, rivers, or stream environments and the organisms found there Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 30 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. Individual organisms of the same species make up a _________. A. community B. biosphere C. population D. ecosystem 2. What main factor makes Death Valley a desert? A. It is always hot. B. It is dry. C. It doesn’t have many plants. D. It is in the Midwest. 3. Which biome is dry, has few plants, and frozen soil? A. Tundra B. Taiga C. Temperate forest D. Desert 4. Which term refers to all the living and nonliving things in an area? A. Community B. Ecosystem C. Population D. Species 5. Which biome is found in the southeast United States? A. Grassland B. Taiga C. Temperate forest D. Desert 6. Which is NOT an abiotic factor? A. Predators B. Sunlight C. Water D. Temperature Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 31 of 84 Concept #2: Organisms have different needs within their ecosystem. Habitat- where an organism lives o Example- The habitat of a bird is a nest in a tree. Niche- role or job an organism has in the ecosystem o Example- The niche of a tree is a habitat for birds and food for beetles. Abiotic factors- nonliving parts of the ecosystem o Examples- temperature, water, sunlight, soil, altitude o Nonliving things determine what plant life can live in an area and therefore what animal life will be there too (since all animals depend on plants at some level). All living things are connected by their need for energy. o A food chain shows a single set of feeding relationships from producer to consumer to decomposer. Seeds Squirrel Snake Vulture Mushrooms o A food web shows all the feeding relationships in an ecosystem. Seeds Squirrel Snake Vulture Mushrooms Mouse o Energy originally comes from the sun and is transformed into chemical energy by plants (during photosynthesis) and transferred from producer to consumers through the food web. Autotrophs (Producers) Plants and algae Heterotrophs (Consumers) Decomposers (Nutrient Recyclers) Herbivores/Primary Consumer (such as insects) eat plants Carnivores/Secondary Consumer (such as tigers) eat animals Omnivores (such as birds) eat plants and animals Scavengers (such as vultures) eat dead organisms Fungi and bacteria o Energy flows through an ecosystem, but nutrients and materials must be recycled. Decomposers help with the recycling of materials. Some materials that are recycled are nitrogen, carbon, water, and phosphorus. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 32 of 84 Relationships that some living things might have with other living things: 1. Mutualism: Both organisms benefit. Example: Ants living in trees (ants get home and tree gets protection) 2. Parasitism: One benefits and the other is harmed. Example: Tapeworm living inside a human host (human is harmed) 3. Commensalism: One benefits and the other is unaffected. Example: An epiphyte (orchid) living on a tree branch to reach sunlight (tree is not harmed) Pyramids An energy pyramid shows the flow of energy through the ecosystem as producers are eaten by primary consumers which are then eaten by secondary consumers. Each time an organism eats another only about 10% of the energy of a producer is transferred to the consumer that eats it. Therefore, there is a loss of energy available for transfer at each level of a food chain because the organisms at that level use some of the energy for their life processes. We can represent the amount of energy at each level as a part of a pyramid. www.learner.org A biomass pyramid shows that the mass of producers is greater than the mass of the consumers. www.learner.org A number pyramid shows the decrease in the number of organisms from producers to consumers. This decrease in number occurs because of the energy losses when one organism feeds on another. www.learner.org Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 33 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. An organism that feeds only on other consumers is a(n) ______________. A. herbivore B. omnivore C. carnivore D. decomposer 2. Organisms that can make their own food from sunlight are called _____________. A. heterotrophs B. omnivores C. herbivores D. autotrophs 3. Which organisms are essential for the recycling of nutrients? A. Consumers B. Producers C. Decomposers D. Scavengers 4. In the food chain below, which is an herbivore? Grass Grasshopper Frog Mushroom A. B. C. D. Grass Grasshopper Frog Mushroom 5. Which level of this food pyramid represents the largest biomass? A. Bass B. Minnows C. Copepods D. Algae Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 34 of 84 6. Fleas living on a dog are an example of A. parasitism B. mutualism C. commensalism D. predator-prey relationship 7. Base your answer on the diagram below and on your knowledge of ecology. The diagram illustrates the relationships between the organisms in a certain pond. In this pond community, which organisms are secondary consumers? A. B. C. D. aquatic crustaceans and raccoons carnivorous fish and aquatic crustaceans ducks and minnows ducks and carnivorous fish 8. Food webs are models used to show energy flow in ecosystems. In the food web shown below, what is the main source of energy for the copepods? A. Parrotfish B. Corals C. Algae D. Shrimp 9. In the food relationship where the lion eats the giraffe, and the giraffe eats plants ... 1. The lion is the prey and the giraffe is the predator. 2. The lion is the predator and the giraffe is the prey. 3. The lion is the primary consumer and the giraffe is the secondary consumer. 4. The lion is the secondary consumer and the giraffe is the primary consumer. A. 1 and 3 only B. 1 and 4 only C. 2 and 3 only D. 2 and 4 only Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 35 of 84 Concept #3: Succession is the change in a community over time to establish a “final” climax community of organisms. For example, the climax community in a temperate forest biome would be a deciduous forest with oak and maple trees, other plants, consumers, and decomposers. There are two different types of succession: o Primary succession occurs in an area where there has been no living things before. This takes time since the pioneer species (such as lichens and mosses) must create soil from rock before the plants can start to grow. o Secondary succession occurs after an established community has been destroyed (clear cutting an area or a natural disaster) and starts to regrow. This happens more quickly than primary succession because the soil is already there, as are seeds, from the previous community. In any case, the plants in the area dictate which animals will be there. Example: Small plants bring small herbivores and then carnivores come to the area to eat the herbivores. Concept #4: Humans cause the greatest amount of change to the planet. Most changes we make in nature have a negative effect. Habitat destruction (or degradation) is the biggest threat to nature and living organisms. It can be caused by clear-cutting forests; polluting the land, water and air; spraying insecticides/herbicides; or introducing non-native species into ecosystems. The effects are also extensive, such as extinction or endangerment of organisms, erosion of soil, killing areas of land/water, acid precipitation, and altering the natural food webs. Humans also try to have positive effects on the ecosystem. Zoos and conservation programs help educate people about nature, reintroduction programs try to help save endangered species, recycling helps reduce waste in landfills, and national parks protect land and animals. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 36 of 84 Concept #5: Populations increase in number over time until factors limit the population size. Examples of these limiting factors are a lack of sunlight, competition for food or resources, predators, lack of space, or disease. Limiting factors create a carrying capacity for populations so that the population does not grow bigger than the environment can support. Presently, humans have overcome all factors and due to decreased death rates and increased life expectancy, our population is growing exponentially. Population growth curves either look J-shaped if they grow exponentially or S-shaped if they have a carrying capacity. Population Population Time J-shaped growth curve Time S-shaped growth curve Practice Questions: 1. In which situation would succession occur most slowly? A. A forest growing back after being clear-cut for a neighborhood development B. A mountain rock eroding into soil and a forest growing on top C. A flood washing away all the plants and animals of a grassland D. A forest fire destroying the ecosystem 2. Which are limiting factors to human population growth? A. Amount of resources B. Food C. Predators D. We currently don’t have any limiting factors. 3. The number of organisms of a population that the ecosystem can comfortably sustain is called __________. A. the limiting factor B. carrying capacity C. an abiotic factor D. density-dependent capacity 4. Which is a positive effect of human population growth? A. Conservation programs B. Habitat destruction C. Pollution D. Extinction Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 37 of 84 Matter Domain 3: Structure and Properties of Matter Concept #1: States of Matter There are 3 states of matter present in everyday life: Solids – fixed volume and shape o Lowest energy phase o Usually the most dense state of matter (H2O is the exception) o Atoms in a solid are in fixed positions. Liquids – fixed volume but take the shape of their container Gases – take the shape and volume of their container o Highest energy phase o Least dense state of matter o Atoms in the gaseous state have freedom of movement and fill their container. Practice Questions: 1. Which of these samples could be compressed into a smaller space? A. 10 cm3 oil B. 10 cm3 helium C. 10 cm3 mercury D. All of the above 2. Which would have the greatest mass? A. 5 cm3 solid oxygen B. 5 cm3 liquid oxygen C. 5 cm3 gaseous oxygen D. All would have the same mass. 3. Which phase of matter has the most kinetic energy? A. solid B. liquid C. gas D. telophase Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 38 of 84 Concept #2: Classification of Matter Elements are composed of all the same atoms and are represented by a symbol. o Examples: Sodium (Na), Iron (Fe), Helium (He), Hydrogen (H) Compounds are composed of two or more atoms chemically combined to form a molecule or formula unit. o Properties of a compound are different from those of the elements it contains. o Compounds have chemical formulas. o Examples: NaOH, H2O, MgCl2 o Compounds can be separated only by a chemical reaction. o There are two types of compounds Ionic-formed by the attraction between two or more elements that transfer electrons (ions) Example: NaCl (one metal ion and one nonmetal ion) Covalent-formed when two or more elements share electrons Example: H2O (two nonmetals) Elements and compounds together are known as substances. Mixtures are composed of two or more elements and/or compounds that are mixed but not chemically combined. The properties of a mixture are the same as the properties of the substances it contains. Mixtures can be separated by physical means such as filtration, distillation, and chromatography. o In a homogeneous mixture, the components are mixed so thoroughly that they cannot be individually observed and the mixture appears to be one material. These are also called solutions. Solutions can be in any state. Metal alloys that are mixtures of metals are examples of solid solutions. In a solution the solvent will dissolve the solute. (Example: in a saltwater solution, water (the solvent) dissolves salt (the solute). Water is called the universal solvent since it is able to dissolve so many different things. A solvent is able to dissolve different amounts of solute depending on the amount of solvent present and the type of solute. The following terms are used to describe solutions: Saturated solutions contain the maximum amount of solute in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature and pressure. Unsaturated solutions contain less than the maximum amount of solute in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature and pressure. Supersaturated solutions contain more than the maximum amount of solute in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature and pressure. Increasing the temperature will generally increase the amount of solid solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent. Decreasing the temperature will generally increase the amount of gaseous solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 39 of 84 o In a heterogeneous mixture, the different components of the mixture can be observed. Examples are colloids such as milk and suspensions such as muddy water. Practice Questions: 1. Which of these samples of matter is NOT a pure substance? A. Water B. Brass C. Nickel D. Baking soda (NaHCO3) 2. Which of these samples of matter is heterogeneous? A. Magnesium B. Soil C. Steel D. Air 3. Identify the solution among the following. A. Copper B. Bronze C. Glucose (C6H12O6) D. Blood 4. Sugar, flavoring, and water are mixed together to make a child’s drink. Sugar is a A. Solute B. Solvent C. Heterogeneous mixture D. Element 5. Which of the following is always produced with the exact same proportions? A. Compound B. Solution C. Suspension D. Colloid Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 40 of 84 Concept #3: Atomic Structure Atoms are composed of protons (positive charge) and neutrons (neutral charge). Protons and neutrons compose the nucleus of an atom. Surrounding the nucleus are electrons (negative charge). Electrons are in clouds at different energy levels. Each energy level can accommodate up to a given number of electrons. Some periodic charts will give the number of electrons in each energy level of that atom. (1st level holds 2 electrons and 2nd level holds 8 electrons) The atomic number is the number of protons in the atom (and the number of electrons if the atom is neutral). This is the whole number on the periodic chart that identifies the element. o Atoms with fewer electrons than protons are positive ions (example: Na+1). Metallic atoms lose electrons to form positive ions. o Atoms with more electrons than protons are negative ions (example: O-2). Nonmetallic atoms gain electrons to form negative ions. The atomic mass is the number of protons plus the average number of neutrons in atoms of a given type. It is represented by the decimal number on the chart. To determine the number of neutrons in an atom, simply subtract the atom’s atomic number from its atomic mass. Atoms of a given element can have different numbers of neutrons and, therefore, different masses. These are called isotopes. The mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in a single atom. It is a whole number. Rounding the atomic mass to a whole number gives the mass number for the most common isotope of an element. Which element is this? Oxygen Comparison of Subatomic Particles Subatomic Particle Charge Location Proton, p+ positive Nucleus Neutron, no neutral Nucleus Electron, enegative Electron cloud Mass (amu) 1 1 1/1840 Number in atom Same as atomic number Mass number – atomic number Same as number of protons Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 41 of 84 Practice Activity: Complete the table below using the information provided and a periodic table. Element 1 Symbol Atomic Number Atomic mass Number of protons Number of neutrons Number of electrons 238 92 238 92 146 92 8 16 8 8 8 30 66 30 36 30 14 27 14 13 14 53 126 53 73 53 79 118 79 Uranium-238 92U 2 Oxygen-16 16 8O 3 Zinc-66 66 30Zn 4 Silicon-27 27 14Si 5 Iodine-126 126 53 6 Gold-197 I 79 197 79 197 Au Practice Questions: Hint: Use the Periodic Chart in the Resources section to help you answer these questions. 1. An atom of radium (Ra) with mass number 222 has ______ neutrons. A. 222 B. 88 C. 134 D. 310 2. A neutral atom of iron will have _________ electrons. A. 26 B. 56 C. 30 D. 55.847 3. A carbon atom with mass 14 (C-14) and carbon with mass 12 (C-12) are called ____ of carbon. A. ions B. allotropes C. isotopes D. compounds 4. How is an ion formed? A. An atom gains protons B. An atom gains electrons C. A compound loses electrons D. An atom loses neutrons Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 42 of 84 Concept #4: Periodic Chart Elements on the periodic chart are arranged in periods (rows) and families or groups (columns). Elements in the same group share many chemical and physical properties. Metals appear on the left and center of the chart and nonmetals appear on the far right. The most reactive metals are in group 1 (or IA) and are called the alkali metals. The most reactive nonmetals are in group 17 (or VIIA) and are called the halogens. The elements in group 18 (or VIIIA), the noble gases, are the least reactive since they have eight electrons in their valence level (highest energy level). Metals lose electrons during chemical reactions to form positive ions called cations. They often lose all of their valence electrons. Nonmetals gain electrons during chemical reactions to form negative ions called anions. They will gain enough electrons to complete the octet (8 electrons) in their valence (outer) level. The periodic law states that there is a periodic repetition of properties when elements are placed in order of increasing atomic number. This means that there are trends in periods and families on the periodic table. o The atomic radius is the radius of atoms. Atomic radius increases as you move down a family due to the addition of an energy level with each element. Atomic radius decreases across a period due to increased nuclear charge attracting the same valence level. o Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom. Ionization energy decreases as you move down a family. Valence electrons are not held as tightly in large atoms and take less energy to remove. Ionization energy increases across a period due to increased nuclear charge exerting a greater pull on valence electrons. Valence electrons are held more tightly and take more energy to remove. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 43 of 84 Practice Activity: Get to know the arrangement. Identify each of the numbered regions on the periodic table shown below. 1 2 3 4 8 5 7 6 1. Metals 5. Alkaline Earth Metals 2. Nonmetals 6. Transition Metals 3. Metalloids 7. Halogens 4. Alkali Metals 8. Noble Gases Practice Questions: Hint: Use the Periodic Chart in the Resources section to help you answer these questions. 1. Which of these elements will form a positive ion after a chemical reaction takes place? A. Mg B. He C. F D. Kr 2. Which element would be most similar to sodium (Na) in properties? A. Mg B. K C. Ne D. H 3. Potassium (K) would likely react with which of the following elements? A. Kr B. Ca C. U D. Cl Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 44 of 84 4. Which element is in the same period as Tin (Sn)? A.Y B. Pb C. W D. C 5. Which atom has the greatest radius? A. Na B. Mg C. Al D. S 6. Which atom has the greatest radius? A. Li B. Na C. K D. Rb 7. Which element has the greatest ionization energy? A. Ca B. Mg C. Sr D. Ba 8. Referring to the periodic chart, how many electrons are in the 2nd energy level in a phosphorus atom? A. 2 B. 5 C. 8 D. 15 Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 45 of 84 Concept #5: Matter has two types of properties: A physical property is observed with the five senses without destroying the object. Examples of physical properties are color, shape, mass, density, malleability, solubility, taste, odor, and ductility. Most measurements such as mass, length, temperature, and volume are also physical properties. A chemical property is how a substance reacts with another substance. In order to observe a chemical property, a chemical change must have occurred and produced a new substance. There are many signals that a chemical change has occurred such as a change of color, production of gas, exchange of energy, and the formation of a precipitate. Practice Questions: 1. Joe makes observations about an unknown solid. He observes that it is a white crystal that dissolves in water and changes to a brown color when it reacts with an acid. The observation that it reacts with an acid is an example of a ________________. A. physical change B. chemical property C. physical property 2. Gold has a density of 19.3 g/cm3. This can be determined using a balance to measure mass and a graduated cylinder to measure volume. Density is an example of a(n) ____________. A. physical property B. chemical property C. energy change D. qualitative data Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 46 of 84 Concept #6: There are two types of ways you can change matter. In a physical change, the original substance still exists (it has only changed in form). For example, you can tear a piece of paper into small pieces. The remains are still paper. You have changed the way it appears, but you have not made a new substance. A physical change does not change the way the atoms are linked. Energy changes usually do not accompany physical changes. No energy is taken in or given off unless there is a change of state. For example, if you heat a beaker of water until it boils to form steam, an energy change is required to change the water from a liquid to a gas but it is still water (just in a different state). There are six phase changes: Phase change Melting Vaporization (boiling or evaporation) Sublimation Freezing Condensation Deposition What happens Solid becomes liquid Liquid becomes gas Energy change Absorbs heat Endothermic Absorbs heat Endothermic Solid become gas Liquid becomes solid Gas becomes liquid Gas becomes a solid Absorbs heat Releases heat Releases heat Releases heat Endothermic Exothermic Exothermic Exothermic In a chemical change, a new substance is produced. This new substance has different properties from the old substance. When atoms change the way they link up, we say a chemical reaction has taken place. Energy changes always take place during a chemical reaction. Energy is either given off or taken in. A reaction in which energy is absorbed is called an endothermic reaction. A reaction in which energy is given off is called an exothermic reaction. Some example of changes: Physical changes Melting Dissolving Evaporating Condensing Cutting Boiling Sublimating Tearing Stretching Freezing Chemical changes Rusting Tarnishing Decomposing Reacting Burning Fermenting Oxidizing Spoiling Cooking Electrolyzing Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 47 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. Boiling can be defined as a_____________. A. chemical change B. phase change of liquid to gas C. substance undergoing sublimation D. change from gas to a liquid that requires absorption of energy 2. A container of sugar water is heated. The solution boils and produces steam. As the liquid evaporates, a black substance begins to form. What reason would explain why this is a chemical change? A. A phase change of liquid to gas occurs. B. An energy change occurs. C. A color change indicates a new substance is produced. D. Evaporation causes the liquid to disappear. 3. A solid, white crystal is added to a liquid. As the solid dissolves, the solution turns cloudy and the container feels hot to the touch. This would be an example of a(n) ________________. A. physical change B. endothermic reaction C. exothermic reaction 4. Which of the following is a chemical change? A. sugar dissolving in water B. paper burning C. ice melting D. water boiling 5. Which of the following phase changes requires a loss of energy? A. melting B. condensation C. sublimation D. boiling Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 48 of 84 Domain 3: Structure and Properties of Matter Acids and Bases Acids are substances that dissociate to produce H+1 ions in solution. Examples of common acids are HCl, HBr, HNO3, H2SO4, H3PO4, citric acid, and vinegar. Bases are substances that dissociate to produce OH-1 ions in solution. Examples of common bases are NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2, antacids, and lime. Substances that produce neither H+1 ions nor OH-1 ions are called salts or neutral substances. Ions Produced Taste Litmus Reaction Reactions Acids H+1 ions Sour Turn blue litmus red React with metals to produce hydrogen; react with bases in neutralization Bases OH-1 ions Bitter Turn red litmus blue React with grease and dirt; denature proteins (feels slippery on skin); react with acids in neutralization The scale that measures the concentration of hydrogen ions (also known as hydronium ions) is called the pH scale. A pH less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH greater than 7 (up to 14) is basic/ alkaline. The lower the pH, the greater the acidity and the higher the pH, the greater the alkalinity. Indicators are substances that change color in the presence of an acid or a base. Common indicators are phenolphthalein and litmus. Phenolphthalein is colorless in acids and neutral substances, but turns pink in bases. Red litmus remains red in acids and neutral substances, but turns blue in bases. Blue litmus remains blue in bases and neutral substances, but turns red in acids. When an acid and a base are combined together, they undergo neutralization. They produce water and a salt. Salts are formed from the cation (positive ion) of the base and the anion (negative ion) of the acid. The water is formed from the OH-1 of the base and the H+1 of the acid. Example: HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O acid base salt water Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 49 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. Lemons taste sour. They are probably a(n) ___________. A. acid B. base C. salt D. indicator 2. Which of the following would be an acid? A. NaOH B. NaCl C. HCl D. Mg(OH)2 3. Beth performs several tests on a clear liquid. She finds that the liquid turns blue litmus red, but does not cause red litmus to change color. Beth most likely has a liquid that would have a pH of __________. A. 2 B. 7 C. 8 D. 12 4. Which of the following is a product formed during a neutralization reaction? A. acid B. base C. indicator D. salt Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 50 of 84 Domain 4: Energy Transformations Concept #1: Energy is not created or destroyed but is conserved. This is the Law of Conservation of Energy. Energy can change from one form of energy to another. For example, when you use a hairdryer, electrical energy is changed into heat energy. Concept #2: Heat exchange always takes place from regions of high temperature to regions of lower temperature and can occur in three ways: Radiation is when heat is transferred by electromagnetic waves (such as being warmed by the sunlight). Conduction is when heat is transferred by the collision of particles (such as when a stove heats a pan to cook food). Metals are good conductors and transfer heat easily. Insulators do not transfer heat easily. Glass, rubber, and plastic are good insulators. Convection is when heat is spread by gas or liquid particle movement (such as when the heating system in your house warms the air). www.g9toengineering.com Concept #3: There are two main types of energy: Potential energy is stored energy. Gravitational potential energy is dependent upon the position of an object. A rock at the top of a hill has more stored energy due to its position than the same rock at the bottom of the hill. Other examples of potential energy include chemical and nuclear energy. Kinetic energy is energy of motion. A motionless rock at the top of the hill has its greatest amount of potential energy and its least kinetic energy. As the rock begins to roll down the hill, its potential energy changes into kinetic energy. At the point when the rock is rolling the fastest, it has its greatest kinetic energy and its least amount of potential energy. Examples of kinetic energy include electricity, light, mechanical, and sound. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 51 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. An example of an energy transfer in which chemical energy is transferred into light energy would be a ______________. A. microwave B. flashlight C. solar calculator D. hairdryer 2. Which of the following best defines radiation? A. Marshmallows roasting over a fire B. A hot air balloon C. A lizard warming in the sun D. Burning your finger on a hot pan 3. Why does a skier travel to the highest point on the ski slope? A. He is attempting to increase his potential energy in order to increase his speed. B. He is increasing his kinetic energy in order to decrease his potential energy. C. He decreases his kinetic energy in order to increase his potential energy. 4. An icepack contains ammonium nitrate. When this is dissolved in water it gets considerably cold. This is an example of heat energy being converted into _____ energy. A. light B. mechanical C. chemical D. nuclear 5. Energy is added in the form of heat to a pot of water on the stove. This causes the water to _________. A. decrease kinetic energy B. increase kinetic energy C. decrease potential energy D. increase potential energy Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 52 of 84 Concept #4 : Nuclear Energy Radioactive decay is a spontaneous process where unstable nuclei lose energy by emitting radiation. Nuclear stability depends on the ratio of protons to neutrons in the nucleus. There are 3 basic types of radiation involved in radioactive decay: alpha, beta, and gamma rays. When a nucleus emits alpha or beta particles, a different element is formed. www.who.int Alpha +2 Made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons (same as the nucleus of a helium atom) Penetration Absorbed by paper or 5 cm of air Charge Nature Beta -1 A very fast moving electron Absorbed by 3 mm of aluminum Gamma 0 Electromagnetic waves of high frequency and energy Needs > 10 cm of lead to stop Half-life is the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay into another element. During each half-life that occurs, half the sample has decayed into another element. Example: If an element Z has a half-life of 5 minutes and you have a sample of 40 grams of Z, then after 5 minutes (one half-life) the sample of Z remaining would be 20 grams (1/2) with the other half having been converted into another element. After another 5 minutes (a second half-life), the sample of Z remaining would be 10 grams (1/4). The other half would have been converted into another element. www.coolschool.ca Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 53 of 84 Nuclear Fission is the splitting of large atoms. This releases large amounts of energy. These types of reactions occur in nuclear reactors. Nuclear Fusion combines small nuclei into larger nuclei. This also releases large amounts of energy. These types of reactions occur in the sun. Practice Questions: 1. A sample of radioactive radium decays to form radon and emits 2 protons and 2 neutrons. Which of the following should be used to absorb the radiation? A. Paper B. Aluminum foil C. Lead sheet D. All of the choices above will absorb the radiation. 2. A 50 gram sample of a radioactive element has a half-life of 2 years. If 6.25 grams remain how many years have passed? A. 2 years B. 4 years C. 6 years 3. The nucleus of a large atom splits and two smaller atoms are formed. What is the name of the process? A. friction B. fusion C. fission D. binary multiplication 4. 750 million years ago, there was enough Uranium-235 in Oklo, Gabon to have a natural fission reaction occur and generate a chain reaction. If these is currently 50 kg of U-235 present in Oklo, how much must have been present 750 million years ago when the reaction took place? A. 200 kg B. 100 kg C. 50 kg D. 25 kg Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 54 of 84 Forces Domain 5: Forces, Waves, and Electricity Concept #1: A force is simply a push or a pull; it is anything that changes the velocity of an object by causing the object to start moving, stop moving, or change its motion in any way. This change in motion is called acceleration. Forces are measured in the metric unit called the Newton. Some types of forces include: o Friction is an example of a force that exists between surfaces that move past each other. Air resistance is one type of frictional force. o Gravity is the force that exists between all objects, and is determined by the objects’ masses and the distance between them. o Magnetism is the force that includes the attraction of iron for a magnet, and is associated with the motion of electric charge. The force that results from combining all forces acting on an object is the net force. If the combined forces result in a net force of zero, the object is said to be in equilibrium. o Newton’s 1st Law of Motion (The Law of Inertia) is stated as follows: An object at rest will stay at rest and object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by some outside net force. Newton referred to this tendency of objects to remain in motion or stay at rest as inertia, which is measured by an object’s mass. The greater the mass of an object, the greater its inertia and its tendency to maintain its current state. So, an object in equilibrium, with a net force of zero, will not accelerate. o If the combined forces acting on an object result in a value that is not zero, the object will accelerate according to Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion (The Law of Acceleration): F = ma (force = mass x acceleration). The greater the applied force, the greater the acceleration of the object. The larger the mass of an object, the smaller the acceleration. o Newton’s 3rd Law of Motion states that for every action there is an equal but opposite reaction. If object A exerts a force on object B, then object B exerts an equal force on object A but in the opposite direction. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 55 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. Two forces, 25 N and 14 N, both act in the same direction on an object. What is the net force acting on the object? A. 25 N B. 39 N C. 11 N D. 14 N 2. If the forces in #1 above are acting in opposite directions on an object, what is the net force acting on the object? A. 25 N B. 39 N C. 11 N D. 14 N 3. What will be the acceleration of an object with a mass of 12 kg when it is acted upon by a net force of 5 Newtons? A. 0.4 m/s2 B. 60 m/s2 C. 2.4 m/s2 Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 56 of 84 Concept #2: Speed is the rate at which distance is covered; velocity is speed with direction. When an object accelerates, its velocity changes. Consequently, acceleration can include a change in speed (either increasing or decreasing) and/or a change in direction. To calculate the velocity of an object, the following equation will be used: d v (Velocity is displacement divided by time.) t To calculate the acceleration of an object, the following equation will be used: v f vi (Acceleration is the change in velocity divided by time.) a t When an object is in free fall, the only force acting on the object is the force of gravity (air resistance is not considered). The acceleration due to gravity, g, is -9.8 m/s2. Practice Questions: 1. In 35 seconds, a cyclist rides 0.10 km. What is the velocity of the cyclist in km/s? A. 3.5 km/s B. 0.0029 km/s C. 350 km/s D. 0.29 km/s 2. What is the acceleration of a plane that changes velocity from 75 m/s to 140 m/s in 15s? A. 4.3 m/s2 B. 14 m/s2 C. 5 m/s2 D. 135 m/s2 3. A stone falls from rest until its velocity is -4.5 m/s. Not considering air resistance, how long did the stone fall? A. 44 s B. 0.46 s C. 0.22 s Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 57 of 84 Concept #3: Mass is the amount of matter in an object. Weight is the response of mass to gravity. Mass is measured in kilograms and mass does not change due to location. Mass is measured by using a balance that compares a known amount of matter to an unknown amount of matter. mass weight acceleration due to gravity (acceleration due to gravity on earth = -9.8 m/s2 ) Weight is a force measured in Newtons and weight is affected by location. Weight is measured on a scale. weight mass x acceleration due to gravity Practice Questions: 1. A certain cube has a mass of 95 kg and weight of 931 N on Earth. What will be its mass and weight on another planet that has an acceleration due to gravity of 4.5 m/s2 ? A. Mass of 95 kg and weight of 931 N B. Mass of 931 kg and weight of 95 N C. Mass of 95 kg and weight of 428 N D. Mass of 428 kg and weight of 95 N 2. A cube of 11 kg is moved to Venus. What will be its new mass on Venus if Venus has an acceleration due to gravity of 8.6 m/s2? A. 11 kg B. 94.6 kg C. 8.6 kg D. 108 kg 3. A cube of 11 kg is moved to Venus. What will be its new weight on Venus if Venus has an acceleration due to gravity of 8.6 m/s2? A. 11 N B. 94.6 N C. 8.6 N D. 108 N Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 58 of 84 Concept #4: There are two major formulas that govern gravity: Universal Gravitation tells us that each particle of matter attracts every other particle of matter with a force equal to the product of the masses of the two particles of matter divided by the square of the distance between the centers of mass of the particles. In other words, the force of gravity between two objects increases as the mass of either object increases and decreases as the distance between the objects increases. Gravitational Force G m1m2 d2 On earth the force of gravity is called the weight of the object. All objects on the earth experience a force directed toward the center of the earth. The formula for weight equals the mass of the object multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity. The accepted value for the acceleration due to gravity, g, here on earth is -9.8 m/s2. Force of Weight mg Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 59 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. You weigh 526 N on Earth. Planet Y has twice the mass of Earth and twice the radius of Earth. What is your weight in Newtons on planet Y? A. 53 N B. 263 N C. 526 N D. 1040 N 2. An imaginary dense Star X has ½ the earth’s radius but 1000 times the earth’s mass. What would a mass weighing 1.0 N on Earth weigh on Star X? A. 2000 N B. 4000 N C. 500 N D. 1000 N 3. An object weighing 40 N on the earth’s surface would weigh only 10 N when its distance from the center of the earth is ______________. A. doubled B. halved C. tripled D. quadrupled 4. What is the weight on the surface of the earth of an object with a mass of 10 kg? A. 10 N B. 9.8 N C. 98 N D. 980 N 5. An object with a weight of 19.6 N would have a mass of what value on the surface of the earth? A. 1 kg B. 2 kg C. 10 kg D. 9.8 kg Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 60 of 84 Concept #5: Work is accomplished when an applied force causes an object to move in the direction of the force. Work can be made easier by using simple machines. When a machine puts out more force than is put in, the machine is said to have mechanical advantage. w f xd The unit for work is the newton meter = joule. No work is done if the object does not move in the direction of the applied force. Simple machines are devices that only require the application of a single force to do work. A simple machine does not multiply the work done but instead it multiplies the force. A traditional list of simple machines includes: 1) Inclined plane- examples: ramp, staircase 2) Lever- examples: seesaw, hammer, bottle opener, door on hinges 3) Screw- examples: bolt, spiral staircase 4) Pulley- examples: flag pole, crane, mini-blinds 5) Wheel and axle- examples: door knob, wagon, toy car 6) Wedge- examples: axe, zipper, knife Mechanical Advantage (MA) is the factor by which a mechanism multiplies the force put into it. o There are two types of mechanical advantage: Ideal mechanical advantage (IMA) does not consider frictional loss. Effort Length IMA Resistance Length Actual mechanical advantage (AMA) takes into account frictional loss. F AMA R FE Where FR is Force due to resistance and FE is Force due to effort. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 61 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. Work is done when a(n) _____________. A. object is at rest B. force is applied to an object C. force causes an object to move 2. Which of the following is a unit for work? A. Newton B. Joule C. Watt D. Joule/Second 3. A person prevents an 8000 N car from rolling down a hill by pushing with a force of 280 N. How much work has the person done? A. 0 J B. 5000 J C. 150000 J D. 2240000 J 4. A crate rests on a hill that is 12 m long and 3 m high. The crate weighs 80 N and it takes 25 N to push it up the 12 m hill. What is the IMA of the hill? A. 1.25 B. 3 C. 3.2 D. 4 5. What is the AMA of the hill? A. 1.25 B. 3 C. 3.2 D. 4 6. Which of the following is NOT an example of a lever? A. a broom B. a crowbar C. a knife blade D. a bottle opener Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 62 of 84 Waves Domain 5: Forces, Waves, and Electricity Concept #1: Waves are a way to transfer energy without transferring the matter. There are two major types of waves: o Electromagnetic waves can travel in a vacuum (they do not require a medium). Example: light o Mechanical waves can only travel in a material medium. Example: sound Waves can disturb the particles of a medium parallel to the direction of the energy. Such a wave is called longitudinal. Example: sound www.ddart.net Waves can disturb the particles of a medium perpendicular to the direction of the energy. Such a wave is called transverse. Example: water waves and waves on a string. Waves have different properties: www.ddart.net o o o o Frequency is the number of disturbances per unit of time. Period is the time for one wave to pass by a given point. Wavelength is the distance between successive in-phase particles. Amplitude is the maximum displacement from equilibrium and is related to the energy of the wave. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 63 of 84 Label the indicated parts of the wave pictured below. wavelength amplitude crest equilibrium amplitude Waves have characteristic behaviors: trough o Reflection is the bouncing back of a wave from the edge of a boundary. The angle of incidence formed between the boundary and the incoming wave is equal to the angle of reflection between the boundary and the outgoing wave. www.dosits.org o Refraction is the bending of a wave as it enters a new medium obliquely. The refraction occurs because the wave has a different speed in the new medium. Refraction is why a pencil looks broken when it is placed in a glass of water. Incident ray Air Water reefkeeping.com o Diffraction is the spreading of a wave as it moves around the edge of a boundary. Diffraction explains how sound can be heard around corners. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 64 of 84 Diffraction of waves through a slit o Interference occurs when two or more waves occupy the same space at the same time and they add together as vectors. Interference can be constructive or destructive because of the direction of the waves. library.thinkquest.org Practice Questions: 1. Waves provide a means of transferring ______________. A. matter B. particles C. liquids D. energy 2. Waves that do not require a material medium to travel are called ______________. A. electromagnetic B. mechanical C. diffraction D. reflection 3. The bouncing back of a particle or wave that strikes a boundary is called ______________. A. reflection B. refraction C. diffraction D. interference Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 65 of 84 Concept #2: Wave energy is dependent on the frequency and wavelength of an electromagnetic wave. Frequency (f) and wavelength () are inversely proportional, so the higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength. Higher frequency waves are more energetic and therefore potentially more damaging. The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into regions based on frequency and wavelength. The spectrum ranges from radio, microwaves, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-rays, and gamma rays. Radio waves have the longest wavelength and the lowest frequency, so they are the least dangerous because of their low energy. Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength and the highest frequency, so they are the most dangerous because of their high energy. www.centennialofflight.gov Practice Questions: 1. Which wave has the longest wavelength? A. Microwaves B. X rays C. Visible waves 2. Which wave would be most energetic? A. Gamma rays B. X rays C. Visible 3. As frequency of a wave gets larger, what else happens? A. Wavelength gets larger. B. Energy gets lower. C. Wavelength gets smaller. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 66 of 84 Concept #3: Sound waves require a material medium to travel. This type of wave is known as a mechanical wave. Sound waves follow characteristic patterns: Sound travels faster in denser mediums (such as steel) than they do in less dense mediums (such as air). Sound travels faster in warmer mediums (such as hot air) than they do in cooler temperatures (such as cold air). Different sound waves appear different because they have different pitch or frequency. The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch. The volume of a sound wave is determined by the amplitude and is measured in decibels. The Doppler effect occurs when the sound wave produced by a moving object seems to have a higher pitch as the object approaches the observer and a lower pitch as they move away. This phenomenon is due to the compression and spreading out of sound waves created by the movement of the source of the sound. Sonic booms are created when the source of the sound wave catches up to and passes the front of the sound wave. Practice Questions: 1. A person puts an ear to a railroad track while another person standing close by listens for the train through the air. Which person will hear the sound of the train first? A. The person standing beside the track listening through the air B. The person with an ear to the steel track C. Both will hear the train at the same time 2. A sound wave is sent through warm air while another sound wave is sent through very cold air. Which sound wave will travel faster? A. The wave in warm air B. The wave in the cool air C. Neither since temperature doesn’t affect speed of sound. 3. The pitch of the siren on an ambulance appears to be getting higher. The ambulance is A. moving toward the observer. B. moving away from the observer. C. at rest. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 67 of 84 Concept #4: Light waves can be reflected from mirrors and can be refracted through lenses. Light waves have certain properties: When light reflects from mirrors it does so in a predictable manner. The angle of incidence formed between the incoming wave and the perpendicular to the mirror is equal to the angle of reflection formed between the outgoing wave and the perpendicular to the mirror. When light passes from air into a glass lens, the light will bend or refract as a result of the change in speed it experiences. Light does not require a medium to travel, so the glass actually slows down the light as compared to its speed in air. Light bends towards the normal (perpendicular) when traveling from less dense air into glass, which is denser than air. When light passes from the glass lens back into the air, it will refract or bend again as it changes speed. As the light speeds up returning to the medium of the air, it will bend away from the normal. The speed of light in a vacuum is 3.0 x 108 m/s. (All electromagnetic waves travel at this speed). Visible light consists of seven colors, each having a different wavelength. From longest wavelength to shortest, the colors are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. (ROYGBIV) Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 68 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. The speed of light is greatest in _______________. A. air B. water C. steel D. a vacuum 2. When light passes into a lens from air, the light ________________. A. bends towards the normal B. bends away from the normal C. does not bend as it does not change speed 3. Rear view mirrors can be adjusted to reflect light to a predictable spot because ______________. A. the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection B. the angle of incidence does not equal the angle of reflection Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 69 of 84 Domain 5: Forces, Waves, and Electricity Electricity and Magnetism Concept #1: Magnetism is a result of moving charged particles. Magnets exert forces on objects made of iron and a few other elements because a magnetic field exists around a magnet. This magnetic field is represented by magnetic field lines that show the direction and magnitude of this force field. The magnetic field is strongest at the magnet’s poles, which are usually at the ends of a magnet. Some important concepts to remember are: Magnets have a north pole and a south pole. o A single pole has never been found; magnetic poles always come in pairs. o Even if you cut a magnet in half, each half will have two poles. Like poles repel and unlike poles attract. A magnetic field surrounds the earth. A compass, which is used to locate the earth’s North Pole, is actually a magnet that is freely suspended and able to move. Concept #2: A magnetic field also exists around a wire carrying a current. If a wire is looped to form a coil, and current flows through the coil, an electromagnet has been formed. The coil of current carrying wire has a north pole and a south pole just like a bar magnet. When the current is stopped, the coil no longer behaves as a magnet. Electromagnets are very beneficial. For one thing, electromagnets can be very strong; additionally, they are beneficial because their magnetism can be turned off and on. Electromagnets are used in lots of everyday devices such as radios, doorbells, and stereo speakers. The strength of an electromagnet can be increased by: increasing the number of loops of wire. increasing the current through the wire. inserting an iron core into the center of the loops of wire. Interestingly, if wire is looped to form a coil, and a magnet is moved back and forth in the coil, current is produced in the wire. The process of generating a current in this way is called electromagnetic induction. Moving the magnet faster increases the current, as does increasing the number of coils. Motors and generators use the concept of electromagnetic induction but perform opposite tasks: Motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 70 of 84 Practice Questions: 1. All magnets ________________. A. are shaped like a horseshoe B. have two north poles C. have two south poles D. are surrounded by a magnetic field 2. An electromagnet ________________. A. can be formed when a magnet moves in and out of a coil of wire B. can be turned on and off C. can be strengthened by increasing the number of loops in the coil of wire D. All of the above are correct. 3. A magnetic field _________________. A. exists around a current carrying wire B. can be detected by a compass C. surrounds the earth D. All of the above are correct. 4. A ceiling fan uses a motor that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. A. True B. False 5. In most electric power plants, magnets are moved through a coil of wire. This motion causes current to flow through the wire. The equipment that does this is called a _________. A. motor B. generator C. circuit D. amplifier Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 71 of 84 Concept #3: Charge (measured in coulombs) flows when there is a potential difference, or voltage, across the ends of a conductor. To sustain a potential difference, a voltage source is required. Examples of voltage sources include batteries and generators. The alternator in a car is an example of a generator. Electric current is the rate of flow of charge and is measured in amperes, which is defined as the flow of 1 coulomb of charge per second. Electric resistance is the resistance of a substance to the flow of electric charge. Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance and is stated mathematically as follows: V = IR V = voltage, measured in volts I = current, measured in amperes R = resistance, measured in ohms (Ω) Concept #4: An electrical circuit is any pathway along which charge may flow. There are two types of circuits that we will review: Series circuits form a single path for the flow of charge. o Because there is a single path, if one device fails, charge is no longer able to flow, and none of the devices will work. Some older (or less expensive) holiday lights are like this. If one bulb quits working, the entire string goes out! o The diagram below is an example of a series circuit. Note that the circuit forms a single pathway for the flow of electric charge. o In a series circuit, the overall resistance of the circuit increases as more resistors are added. In this example, the total resistance of the circuit is 34 ohms, which is the sum of the individual resistors. (Rtotal = 6 + 14 + 14 = 34 ohms) o If lights are added in series, the bulbs become dimmer with each addition. R1 = 6 R2 = 14 60v R3 = 14 Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 72 of 84 Parallel circuits form branches which provide separate paths for the flow of charge. o Because there are separate paths for the flow of charge, if one device fails, devices in other paths will still work. Good for us that our homes are wired in parallel! o The diagram below is an example of a parallel circuit. Note the two branches in which the 20 ohm resistors are placed. If one device goes out, the other will still work because it is in a separate branch. o In a parallel circuit, the overall resistance of the circuit decreases as more branches are added. The equivalent resistance for the diagram below is 10 ohms, which is less than either resistor alone based on the formula: 1 1 1 1 = + … R1 R2 R3 Req 1 = 1 + 1 = 1 Req 20 20 10 If the voltage remains unchanged, the brightness of each individual bulb remains the same despite the addition of each additional bulb. o If too many devices are being used, the overall resistance of the circuit decreases. According to Ohm’s Law, decreasing the resistance increases the current. This can create a dangerous condition called overloading which could possibly cause a fire to start if the insulation on the wires were to melt. As a safety feature, fuses or circuit breakers open the circuit when too much current causes overloading. 4a R1 = 20 R2 = 20 Practice Questions: 1. Calculate the current in a 12 volt battery that powers a 10 ohm resistor. A. 1.2 amps B. 120 amps C. 8.3 amps 2. In the diagram of the parallel circuit above, what will happen to R1 if R2 “goes out”? A. R1 will go out as well. B. R1 will continue to work since it is in a separate pathway than R2. Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 73 of 84 Resources The following 2 pages will be provided for you on the day of the GHSGT. Use them! SCIENCE FACTS AND FORMULAS Some of the questions in this test require you to solve problems. This page contains all the basic facts and formulas you will need to solve those problems. You may refer to this page as often as you wish while you take the test. Some questions may require information from the Periodic Table. This table can be found at the end of the test booklet. Basic Facts Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 meters/second/second (9.8 m/s2) Weight = Mass (m) Acceleration due to gravity (g) (W = mg) Density = Mass/Volume Volume of a Rectangular Solid = Length Width Height 1 newton = 1 kilogrammeter/second/second 1 joule = 1 newtonmeter 1 watt = 1 newtonmeter/second = 1 joule/second Motion Velocity = distance/time v d t Acceleration = Change in Velocity/Time Elapsed a v f vi t Force, Mechanical Advantage, Power, Work Force = Mass Acceleration (F = ma) Mechanical Advantage F AMA R , FE where FR is Force due to resistance and FE is Force due to effort. Actual Mechanical Advantage: Effort Length Ideal Mechanical Advantage: IMA Resistance Length Power = Work/Time Work = Force Distance w P t (W = Fd) Electricity Voltage = Current Resistance (V = IR) Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Carrollton High School Page 74 of 84 Practice Test 1. A car starts from rest at a stop light and reaches 20 m/s in 3.5 seconds. Determine the acceleration of the car. a. 3.5 m/s2 b. 5.7 m/s2 c. 20 m/s2 d. 70 m/s2 2. The atomic number of magnesium is 12. Its nucleus must contain a. 6 protons and 6 neutrons b. 6 neutrons and 6 electrons c. 12 protons and 0 electrons d. 12 neutrons and 0 protons 3. An icepack contains ammonium nitrate. When this is dissolved in water, it gets cold. This is an example of heat energy being converted into a. light b. mechanical c. chemical d. nuclear 4. Malaria is caused by ___. a. bacteria b. mutations c. Giardia d. a protist 5. Fleas living on a dog are an example of ___. a. parasitism b. mutualism c. commensalism d. predator-prey 6. The acceleration of gravity is about -10 m/s2. This means that… a. the velocity of a falling body increases by 10 m/s every second b. the velocity of a falling body increases by 1 m/s every 10 seconds c. the distance of a falling body increases by 10 m every second d. the time of a falling body increases by 1 second every 10 meters 7. Which of the following is an example of something that would be separated by a filter and a funnel? a. a mixture of sand and water b. salt water c. Kool-aid d. Coca-cola Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 76 of 84 8. Which of the following is not a form of electromagnetic radiation? a. AM radio waves b. Beta particles c. Ultraviolet light d. Gamma rays 9. If each normal body cell of a human contains 46 chromosomes, then the number of chromosomes in a human egg will be ___. a. 46 b. 24 c. 23 d. 36 10. If a population grows larger than its environmental carrying capacity, then… a. birth rate may rise significantly b. death rate may rise c. death rate may fall significantly d. immigration rate may increase 11. Mike traveled for 4 hours at a rate of 55 mph. How far did he travel? a. 110 miles b. 11 miles c. 220 miles d. 55 miles 12. In an electrically stable atom of any element, there are equal numbers of ___. a. protons and neutrons b. electrons and neutrons c. electrons and protons d. atomic number and atomic mass 13. Which phase of matter has the most kinetic energy? a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. telophase 14. A farmer cut a branch from his favorite tree and planted it in a bucket of soil which grew to be a new tree. The farmer’s method of growing a new plant is a type of: a. Meiosis b. Asexual reproduction c. Succession d. Sexual reproduction Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 77 of 84 15. In marine food chains, the ___ are microscopic organisms called phytoplankton. a. consumers b. producers c. heterotrophs d. herbivores 16. In most electric power plants, magnets are moved through a coil of wire. This causes current to flow through the wire. The equipment that does this is called a ___. a. motor b. generator c. circuit d. amplifier 17. Stranded at sea in a life raft with no drinkable water, which of the following items would be useful? a. funnel and filter b. chromatography paper c. distillation apparatus d. $3,000,000 18. Americium 241 is a radioactive substance used in smoke detectors. The half life of Americium 241 is 432 years. If a smoke detector initially contains 1 gram of Americium 241, how much will remain in 432 years? a. 2.0 g b. 1.5 g c. 1.0 g d. 0.5 g 19. The products of photosynthesis that begin cellular respiration are ___. a. organic compounds and oxygen b. carbon dioxide and water c. NADPH and hydrogen d. AARP and water 20. What is a group of organisms of different species living together in a particular place called? a. community b. population c. biome d. habitat 21. When light enters a pair of glasses, it ___ when it hits the glass. a. speeds up b. refracts c. diffracts d. reflects Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 78 of 84 22. Where is over 99% of the mass of an atom located? a. the nucleus b. the electron cloud c. the protons d. the neutrons 23. The nucleus of a large atoms splits and two smaller atoms are formed. What is the name of the process? a. friction b. fusion c. fission d. binary multiplication 24. What is the function of the cell organelle known as the Golgi apparatus? a. houses the cell’s DNA b. movement c. houses the digestive enzymes d. packages proteins for transport out of the cell 25. A relationship between a producer and a consumer is best illustrated by a ___. a. snake eating a rodent b. bird eating an insect c. barnacle attached to whale d. zebra eating grass 26. The need for seatbelts in automobiles is due to what law? a. Law of Conservation of Energy b. Newton’s First Law of Motion c. Newton’s Second Law of Motion d. Newton’s Third Law of Motion 27. Sugar, flavoring, and water are mixed together to make a child’s drink. What is the sugar? a. Solute b. Solvent c. Mixture d. Element 28. As a roller coaster goes downhill ___ is converted into ___. a. electrical energy, potential energy b. kinetic energy, potential energy c. potential energy, kinetic energy d. potential energy, electrical energy 29. What name is given a large and varied group of molecules that are usually not soluble in water? a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Amino acids Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 79 of 84 30. What characteristic does the tundra and a desert share? a. warm temperatures b. estivation by animals c. low annual precipitation d. large numbers of reptiles 31. Through what medium do sound waves travel fastest? a. solid b. liquid c. gas d. plasma 32. Uranium-235 has an atomic number of 92. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons does an atom of U-235 have? a. 92 protons, 235 neutrons, 143 electrons b. 92 protons, 235 neutrons, 92 electrons c. 92 protons, 143 neutrons, 143 electrons d. 92 protons, 143 neutrons, 92 electrons 33. The heat from the sun reaches the Earth by ___. a. conduction b. convection c. radiation d. all of the above 34. The process of copying DNA to make new identical DNA molecules is called ___. a. replication b. transcription c. transformation d. translation 35. What is an organism called that feeds only on producers? a. herbivore b. carnivore c. omnivore d. saprophyte 36. A broom is an example of what type of simple machine? a. lever b. pulley c. wheel and axle d. inclined plane 37. Oxygen has an atomic number of 8. How many electrons does the ion O2- contain? a. 2 b. 6 c. 8 d. 10 Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 80 of 84 38. A ceiling fan converts ___ energy into ___ energy. a. mechanical, wind b. chemical, electrical c. electrical, mechanical d. light, mechanical 39. Which of the following is not found in DNA? a. adenine b. guanine c. thymine d. uracil 40. Most autotrophs store energy in the form of ___. a. starches b. carbon dioxide c. water d. nucleic acids 41. A simple machine has an input force of 5 N and an output force of 100 N. What is the mechanical advantage of the machine? a. 0.05 b. 2 c. 20 d. 95 42. Which statement best describes a chemical property? a. The crystals are a metallic gray. b. It dissolves in alcohol. c. It forms a violet-colored gas. d. It reacts with hydrogen to form a gas. 43. The half-life of carbon-14 is 5730 years. How much carbon-14 would remain after 11,460 years? a. none b. one-eighth c. one-fourth d. one-half 44. An animal cell is placed in a solution of distilled water. If left overnight, this cell will ___. a. shrivel and die b. swell and burst c. undergo plasmolysis d. remain the same Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 81 of 84 45. Which food chain correctly lists the steps according to energy flow? a. Sun grass deer mountain lion b. Mountain lion deer grass sun c. Grass sun mountain lion deer d. Deer mountain lion grass sun 46. In which of the following cases is work being done? a. Joe carries a box across the room. b. Sally pushes on a wall. c. Mike lifts a box off the floor. d. All of the above. 47. Which substance cannot be decomposed into simpler substances? a. ammonia b. aluminum c. methane d. methanol 48. The greater the mass of the object, a. the less force it can exert. b. the more space it takes up. c. the more balanced it is. d. the greater the inertia. 49. In squirrels, the gene for gray fur (G) is dominant over the gene for black fur (g). If 50% of a large litter of squirrels are gray, what is the most likely parental cross that produced this litter? a. GG x Gg b. GG x GG c. Gg x gg d. gg x gg 50. In a terrestrial ecosystem, the trophic level that would contain the largest biomass would be the ___. a. producers b. primary consumers c. secondary consumers d. decomposers Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 82 of 84 Answer Key Following is a key of the answers to the Practice Questions. Please attempt to answer the questions on your own before you use the key. This will help you better prepare for the GHSGT! p. 5 1. D 2. D 3. A p. 7 1. D 2. D 3. A p. 9 1. surface area, pressure 2. surface are, pressure 4. inverse p. 16 1. cell wall 2. mitochondria 3. vacuole 4. Golgi appartus 5. cytoplasm 6. nuclear membrane 7. nucleolus 8. nucleus 9. chromosome 10. endoplasmic reticulum 11. chloroplast 12. centriole 13. lysosome p. 25 25% RR 50% Rr 25% rr 75% rough 25% smooth p.26 1. B 2. A 3. B 4. B 5. C p. 40 1. B 2. B 3. B 4. A 5. A p. 42 1. C 2. A 3. C 4. B 6. C 7. B 8. C 9. D 10. A 11. B 12. D 13. D 14. C p. 44 1. A 2. B 3. D 4. A p. 10 1. C 2. C 3. B p. 19 1. C 2. C 3. B 4. D 5. B 6. A p. 29 1. D 2. C 3. A 4. B 5. A 6. B 5. A 6. D 7. B 8. C p. 11 1. C 2. A 3. B 4. B p. 24 1. Mitosis 2. Meiosis 3. Meiosis 4. Mitosis 5. Mitosis 6. Meiosis 7. Meiosis 7. B 8. A 9. A 10. B 11. B 12. D 13. A p. 31 1. C 2. B 3. A 4. B 5. C 6. A p. 34 1. C 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. D 6. A p. 44 p. 46 1. metals 1. B 2. nonmetals 2. A 3. metalloids 4. alkali metals 5. alkaline earth metals 6. transition metals 7. halogens 8. noble gases p. 52 1. B 2. C 3. A 4. C 5. B p. 54 1. D 2. C 3. C 4. B p. 56 1. B 2. C 3. A p. 57 1. B 2. A 3. B p. 58 1. C 2. A 3. B p. 66 1. A 2. A 3. C p. 67 1. B 2. A 3. A p. 69 1. D 2. A 3. A p. 71 1. D 2. D 3. D 4. A 5. B p. 73 1. A 2. B p. 13 1. C 2. B 7. D 8. C 9. D p. 37 1. B 2. D 3. B 4. A p. 48 1. B 2. C 3. C 4. B p. 60 1. B 2. B 3. A 4. C 5. B Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 83 of 84 8. Mitosis 9. Meiosis 10. Mitosis 11. Mitosis 12. Both 13. Mitosis 14. Meiosis p. 38 1. B 2. A 3. A p. 50 1. A 2. C 3. A 4. D 5. B p. 62 1. C 2. B 3. A 4. D 5. A p. 65 1. D 2. A 3. A Georgia High School Graduation Test Content Review Guide: Science Buford High School Page 84 of 84