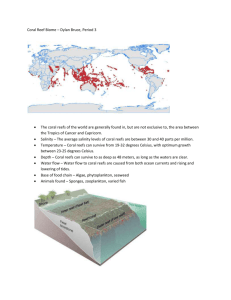
Coral reef bib - updated 5-19-10 — Ecosystem
advertisement

Skip to content Skip to navigation Site Map Accessibility Contact Search Site Search Advanced Search… Ecosystem-based Management Personal tools Log in Home » Working Groups » Valuation of Coastal Habitats » Meta-analysis » Papers for metaanalysis database » Coral List - Chris » Coral reef bib - updated 5-19-10 Navigation Document Actions Home Members News Events Projects Working Groups o Science Frameworks for EBM o Valuation of Coastal Habitats WG Member Models Meeting #1 - Jan 22-2th Papers Review of Social Literature as of 1/26/07 Relevant Short Format Papers Meta-analysis Papers for meta-analysis database Dune articles Coral reef Seagrass articles Kelp articles rocky intertidal Seagrass Articles - Chris Mangrove Dune articles - Chris Salt marsh articles - Chris Coral List - Chris Diaz-Pulido2002MEPS.pdf Coral reef bib updated 5-19-10 Download CoralChris_2_23_10.doc — 38Kb Preview Bellwood (CGB) N (not permanent)Baird AH, Marshall o o o o Garpe2006MEPS.pdf PA (2002) Hughes1987JEMBE.pdf Mortality, growth Liddell1986JEMBE.pdf and reproduction in Littler1993.pdf scleractinian corals Sammarco1982JEMBE.pdf following bleaching Carpenter1990MB.pdf on the Great Barrier Connell1997CoralReefs.pdf Reef. Marine Coral reef bib - updated 5- Ecology Progress 19-10 Series, 237, 133 Glynn1988Galaxea.pdf 141. coral maybe Mangroves - Chris Looks at speciesMeta-analysis database bibliography level bleaching Notes susceptibility. EBM Matrix EBM Marine Predators Distributed Graduate Seminar 2006 EBM Governance PrimaGIS Demo container Log in Login Name Password Log in Forgot your password? N (not permanent)Booth DJ, Beretta GA (2002) Changes in a fish assemblage after a coral bleaching event. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 245, 205-212. Damselfish assemblages after 1998 bleaching event. N (not permanent)Connell JH, Hughes TP, Wallace CC (1997) A 30-year study of coral abundance, recruitment, and disturbance at several scales in space and time. Ecological Monographs, 67, 461-488 Looks at recovery of corals after acute and chronic disturbances. Seems like a good paper . N (not permanent)Jones GP, McCormick MI, SrinivasanMet al. (2004) Coral decline threatens fish biodiversity in marine reserves. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 101, 82518253. Even when fish stocks are protected by marine reserves, significant coral decline can seriously impact abundance. REVIEW PAPER McManus JW, Polsenberg JF (2004) Coral-algal phase shifts on coral reefs: ecological and environmental aspects. Progress in Oceanography, 60, 263-279. No new data, but probably a good source. Paper works to develop a conceptual basis for the shifts. N - not permanentSano M (2000) Stability of reef fish assemblages: responses to coral recovery after catastrophic predation by Acanthaster planci. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 198, 121-130. Crown-of-thorn outbreaks cause long-term shift, but recovery does occur. Bellwood (CB) N - looking at rates of change in corals Bellwood, D.R., Hoey, A.S., and Choat, J.H. (2003). Limited functional redundancy in high diversity systems: Resilience and ecosystem function on coral reefs. Ecol. Lett. 6, 281-285. Looks at overfishing of coral-eating parrotfish and the effects on reef assemblage. Also considers “human impact.” Burke Glynn, P. W., 1988b. El Nino warming, coral mortality, and reef framework destruction by echinoid bioerosion in the eastern Pacific. Galaxea 7: 129-160. Cannot get PDF or abstract. (requested 3/20) Glynn, P. W., 1990. Coral mortality and disturbances to coral reefs in the tropical eastern Pacific. In Glynn, P. W. (ed.), Global Ecological Consequences of the 1982-83 El Nin oSouthern Oscillation. Elsevier, Amsterdam: 55-126. Book. REVIEW McCook, L. J., 1999. Macroalgae, nutrients and phase shifts on coral reefs: scientific issues and management consequences for the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 18: 357367. No new data but a good review paper. Chen Edmunds REVIEW - DONE TJ PHASE-SHIFTS IN CORAL-REEF COMMUNITIES AND THEIR ECOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE HYDROBIOLOGIA 247 : 121 1992 No new data. Good review. REVIEW KNOWLTON N THRESHOLDS AND MULTIPLE STABLE STATES IN CORAL-REEF COMMUNITY DYNAMICS AMERICAN ZOOLOGIST 32 : 674 1992 No new data. Good review. NO, not permanent - LAPOINTE BE Nutrient thresholds for bottom-up control of macroalgal blooms on coral reefs in Jamaica and southeast Florida LIMNOLOGY AND OCEANOGRAPHY 42 : 1119 1997 Looks at causes of shifts from coral to algae dominated systems. Hughes (Science) YES CARPENTER RC MASS MORTALITY OF DIADEMAANTILLARUM .1. LONG-TERM EFFECTS ON SEAURCHIN POPULATION DYNAMICS AND CORAL-REEF ALGAL COMMUNITIES MARINE BIOLOGY 104 : 67 1990 Effects of diadema loss on algae growth in reef communities. YES - HUGHES TP. HERBIVORY ON CORAL REEFS - COMMUNITY STRUCTURE FOLLOWING MASS MORTALITIES OF SEA-URCHINS JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MARINE BIOLOGY AND ECOLOGY 113 : 39 1987 Similar to the above. YES - LIDDELL WD CHANGES IN BENTHIC COMMUNITY COMPOSITION FOLLOWING THE MASS MORTALITY OF DIADEMA AT JAMAICA JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MARINE BIOLOGY AND ECOLOGY 95 : 271 1986 Similar to above. YES - experimental - SAMMARCO PW ECHINOID GRAZING AS A STRUCTURING FORCE IN CORAL COMMUNITIES WHOLE REEF MANIPULATIONS JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MARINE BIOLOGY AND ECOLOGY 61 : 31 1982 Similar to above. HUGHES (CB) Idjadi Ledlie YES - long term changes (eroded coral) Garpe KC, Yahya SAS, Lindahl U, O hman MC (2006) Long-term effects of the 1998 coral bleaching event on reef fish assemblages. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 315:237-247 Could not retrieve full paper, but abstract looks promising. (found 3/20) No - Gradient. Graham NAJ, Wilson SK, Jennings S, Polunin NVC, Bijoux JP, Robinson J (2006) Dynamic fragility of oceanic coral reef systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:8425-8429 Effects of climate change on coral ecosystems. No - Gradient. Mumby PJ (2005) Patch dynamics of coral reef macroalgae under chronic and acute disturbance. Coral Reefs 24:681-692 Macroalgae succession on patch reefs. Littler No - Bell, P., 1992. Eutrophication and coral reefs: some examples in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon. Wat. Res. 26, 555-568. Eutrophication might cause crownof-thorn outbreaks. Birkeland, C., 1987. Nutrient availability as a major determinant of differences among coastal hardsubstratum communities in different regions of the tropics. In: Birkeland, C. (Ed.), Comparison Between Atlantic and Pacific Tropical Marine Coastal Ecosystems: Community Structure, Ecological Processes, and Productivity. UNESCO Reports in Marine Science 46, pp. 45-97. Book N-Goreau, T.J., 2003.Waste nutrients: impacts on coastal coral reefs and fisheries, and abatement via land recycling. In: Proceedings of the UN Expert Meeting on Waste Management in small island developing states, Havana, Cuba. M - Littler, M.M., Littler, D.S., Lapointe, B.E., 1993. Modification of tropical reef community structure due to cultural eutrophication: the southwest coast of Martinique. In: Proceedings of the Seventh International Coral Reef Symposium 1. pp. 335-343. Nutrient enrichment causes phase shifts. N- Smith, J.E., Smith, C.M., Hunter, C.L., 2001. An experimental analysis of the effects of herbivory and nutrient enrichment on benthic community dynamics on a Hawaiian reef. Coral Reefs 19, 332-342. Nutrient enrichment in combination with reduced herbivory can cause abrupt phase shifts. N- (gradient analysis) Tomascik, T., Sander, F., 1987b. Effects of eutrophication on reef building corals. II. Structure of scleractinian coral communities on fringing reefs, Barbados, West Indies. Mar. Biol. 94, 53-75. Not really a phase shift, comparison along a gradient. Maliao YES - Connell JH (1997) Disturbance and recovery of coral assemblages. Coral Reefs 16:101113 A review of worldwide loss and recovery of coral reefs. REVIEW - Petraitis PS, Dudgeon SR (2004) Detection of alternative stable states in marine communities. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 300:343-371 Good review for the overall paper. Sergeeva YES - Diaz-Pulido, G. and McCook, L.J., The Fate of Bleached Corals: Patterns and Dynamics of Algal Recruitment, Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser., 2002, vol. 232, pp. 115-128. Looks at what leads bleached corals to be dominated by algae vs. recover. by Chris Kennedy — last modified 1905-2010 15:44 The Ecosystem-Based Management program is funded by the Packard Foundation. © 2005-2016 by the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Sythesis, UCSB Built with Plone