OBJECTIVE
advertisement
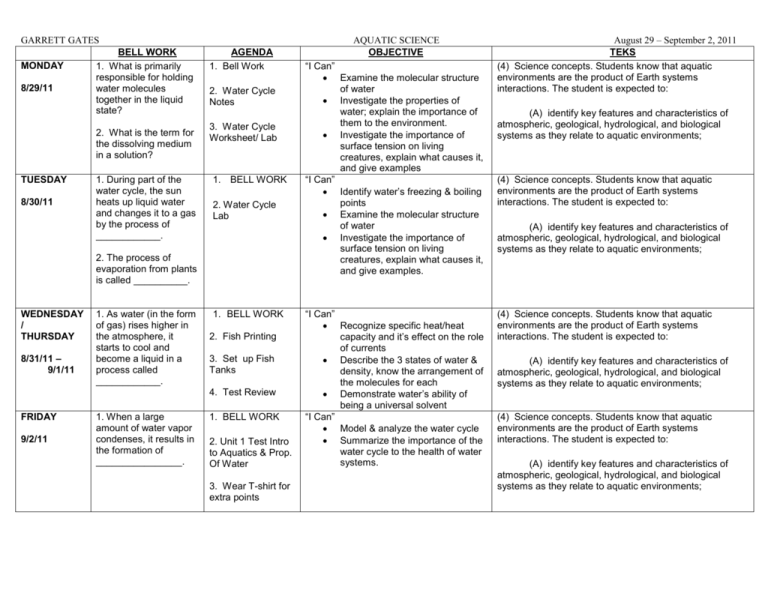
GARRETT GATES MONDAY 8/29/11 BELL WORK 1. What is primarily responsible for holding water molecules together in the liquid state? 2. What is the term for the dissolving medium in a solution? TUESDAY 8/30/11 1. During part of the water cycle, the sun heats up liquid water and changes it to a gas by the process of ____________. AGENDA 1. Bell Work 2. Water Cycle Notes 3. Water Cycle Worksheet/ Lab 1. BELL WORK 2. Water Cycle Lab 2. The process of evaporation from plants is called __________. WEDNESDAY / THURSDAY 8/31/11 – 9/1/11 1. As water (in the form of gas) rises higher in the atmosphere, it starts to cool and become a liquid in a process called ____________. 1. BELL WORK 2. Fish Printing 3. Set up Fish Tanks 4. Test Review FRIDAY 9/2/11 1. When a large amount of water vapor condenses, it results in the formation of ________________. 1. BELL WORK 2. Unit 1 Test Intro to Aquatics & Prop. Of Water 3. Wear T-shirt for extra points AQUATIC SCIENCE OBJECTIVE “I Can” Examine the molecular structure of water Investigate the properties of water; explain the importance of them to the environment. Investigate the importance of surface tension on living creatures, explain what causes it, and give examples “I Can” Identify water’s freezing & boiling points Examine the molecular structure of water Investigate the importance of surface tension on living creatures, explain what causes it, and give examples. “I Can” Recognize specific heat/heat capacity and it’s effect on the role of currents Describe the 3 states of water & density, know the arrangement of the molecules for each Demonstrate water’s ability of being a universal solvent “I Can” Model & analyze the water cycle Summarize the importance of the water cycle to the health of water systems. August 29 – September 2, 2011 TEKS (4) Science concepts. Students know that aquatic environments are the product of Earth systems interactions. The student is expected to: (A) identify key features and characteristics of atmospheric, geological, hydrological, and biological systems as they relate to aquatic environments; (4) Science concepts. Students know that aquatic environments are the product of Earth systems interactions. The student is expected to: (A) identify key features and characteristics of atmospheric, geological, hydrological, and biological systems as they relate to aquatic environments; (4) Science concepts. Students know that aquatic environments are the product of Earth systems interactions. The student is expected to: (A) identify key features and characteristics of atmospheric, geological, hydrological, and biological systems as they relate to aquatic environments; (4) Science concepts. Students know that aquatic environments are the product of Earth systems interactions. The student is expected to: (A) identify key features and characteristics of atmospheric, geological, hydrological, and biological systems as they relate to aquatic environments;