History of Administrative Reforms in Orissa
advertisement

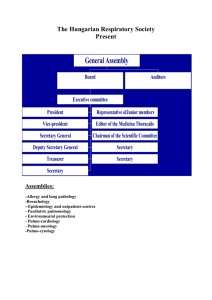
A Brief Note on AR Administrative Reforms In Orissa C o n t e n t s Sl.No Subject Page No. 1 History of Administrative Reforms in Orissa 1 2 Activities of Administrative Reforms Cell during 2002-05 3 Activities of Administrative Reforms Cell during 2005-06 3 3 4 Activity Plan for 2006-07 4 5 Strengthening of Administrative Reforms Cell 5 6 OMGI 5 7 Human Resources Management System 7 1 A Brief Note on AR A brief note on Administrative Reforms in Orissa _______________________________________________________ 1. History of Administrative Reforms in Orissa 1.1 The subject of Administrative Reforms was first dealt in the G.A. Department. In 1999 by an Amendment to the Rules of Business, the subject of Administrative Reforms was transferred to P.G & P.A Department. In 2000 Finance Department initiated the Fiscal and Governance Reform Programme. Under this programme a Task Force on Governance and Civil Services Reforms was set up on 01.11.2000 by the Finance Department. 1.2 The Task Force submitted its report on achieving Good Governance in Orissa by undertaking civil services reforms, anti-corruption measures, organizational review to distinguish core and non-core functions and identify surplus employees for re-deployment in other areas, stability of tenure by having a transfer policy, citizen charters, computerization, training, reward and punishment of employees, change in procedures, right to information, etc. 1.3 Basing on the report of the Task Force, on 17.10.2001 Finance Department set up a Fiscal and Civil Services Reforms Cell for the implementation of the Fiscal and Governance Reforms Programme. The Cell was headed by Chief Secretary. 1.4 On 16.3.2002, Finance Department requested G.A. Department for the constitution of the Administrative Reforms Department. It also submitted a 2 A Brief Note on AR list of businesses basing on the report of the Task Force to be transacted by the new Department of Administrative Reforms. It suggested the structure of the new Department as comprising one Special Secretary, one Joint Secretary, two Deputy Secretaries and ten Section Officers / Assistants. 1.5 On 17.4.2002 G.A. Department set up an Administrative Reforms Cell that was headed by a Special Secretary (Administrative Reforms). The Cell was also proposed to have one Joint Secretary/Deputy Secretary/ Under Secretary and some staff. 1.6 On 29.8.2002 the Rules of Business was amended for the creation and allocation of business of Administrative Reforms Cell in G.A. Department. 1.7 The different positions and incumbents in Administrative Reforms Cell from 2002 onwards may be seen in the tables given below: 2002 Sri P.K. Mishra, I.A. & A.S Sri R.N. Rout, OAS Special Secretary Joint Secretary 2003 Sri P.K. Mishra, I.A. & A.S Sri D.N. Mishra, IAS Sri R.N. Rout, OAS Miss Banani Mohanty, OAS Special Secretary Additional Secretary Joint Secretary Under Secretary 2004 Sri P.K. Mishra, I.A. & A.S Sri D.K. Mohanty, OAS Sri R.N. Rout, OAS Miss Banani Mohanty, OAS Special Secretary Additional Secretary Joint Secretary Under Secretary October, 2004 Smt. Madhur Sarangi, IAS Sri P.K. Mishra, I.A. & A.S Principal Secretary Special Secretary 3 A Brief Note on AR Sri K.C. Mishra, OAS Sri Girish S.N., IAS Joint Secretary Under Secretary 2005 Sri T.K. Pandey, IAS Sri N. Chandra, IAS Sri S. Sukla, OAS Special Secretary Additional Secretary Under Secretary 1.8 At present there are three Assistants and one Sr. Grade Typist in the Cell. 2. Activities of Administrative Reforms Cell during 2002-05: 2.1 Over three thousand surplus employees were re-deployed in different Departments. A proposal was made for the merger of the office of Special Relief Commissioner with the Revenue Department and renaming of the Revenue Department as Revenue and Disaster Management Department. Organizational Review was taken up in eight Departments; Agriculture, Transport, Panchayati Raj, School & Mass Education, Forest & Environment, Health & F.W., Government Printing Press of Commerce Department and Commercial Taxes. 3. Activities of Administrative Reforms Cell during 2005-06: 3.1 The programme for Orissa Modernizing Government Initiative was finalized. HRMS in six districts on a pilot basis was started. Transparency and Accountability Programme on a pilot basis was taken up in nine Departments and nine Districts. e-Governance Programme Document was prepared in collaboration with the I.T. Department. Proposal for amendment to Rules of Business and Rules for Rationalization of Government Personnel was prepared. Proposal for Composite Directorate in Textile and Handloom, Sports and Youth Services, Tourism and Culture Departments was submitted. Performance 4 Appraisal System of A Brief Note on AR Government employees was revamped. Anti-corruption Action Plan was prepared. Training of Government employees for computer literacy was provided. 4. Activity Plan for 2006-07: 1. HRMS (Human Resources Management System) in six districts to be grounded on a pilot basis. 2. Preparation and implementation of Reform Action Plans in select Departments under OMGI (Orissa Modernizing Government Initiatives) 3. Expansion of e-Governance. a. State Information Services Board b. District Information Services Council c. Mission Mode Projects 4. Transparency and Accountability Programme. 5. Citizen’s Charter to be initiated in Municipality, Tahsils, RTO, Urban Development Authority, etc. 6. Review of Codes 7. Delegation of powers 8. Meeting Monitoring System 9. Project Management 10. E-procurement 11. Simplification of Land Acquisition 12. Use of Oriya Language 13. Strengthening of Planning Organization 14. Organizational Review. 15. Zero-based Review of Personnel 16. Reorganization of Departments 17. Training of employees 5 A Brief Note on AR 18. Amendment of Secretariat Instructions. 19. Strengthening of District Administration 20. Best Practices Dissemination. 21. PM Award for excellence in Public Administration. 22. Civil Services Census. 23. Litigation Management System. 24. Institutional Development of A.R. Cell and OCAC. 25. Setting up of State Centre for Good Governance. 26. Implementation of Action Plan of Inter-State Council 5. Strengthening of Administrative Reforms Cell: There is going to be significant increase in the work load of the Cell during 2006-07. It is therefore proposed that the Cell be strengthened by induction of more officers and staff in the Cell. It needs to have a Project Management Unit and a Team of Consultants to take up the new responsibilities. For the implementation of HRMS Project a Project Management Unit consisting of at least four Gr. ’A’ or Gr. ‘B’ officers is required. Consultants having domain expertise in the areas of Information Technology, Management, Law, Procurement and Finance will be required. In addition a few more Deputy/Under Secretaries, Section Officers, Assistants and Data Entry Operators will be required. A detailed organizational plan for Strategy and Performance Innovation Unit has been prepared. Currently, the Procurement and Contracting Unit has been set up. Staffing of other personnel is in progress. 6. OMGI 6.1 OMGI stands for Orissa Modernizing Government Initiative. OMGI Programme has been conceived with the assistance of DFID under its larger Orissa Public Sector Reform Programme. It is a multi-sectoral 6 A Brief Note on AR cross-cutting initiative that aims at development of Reform Action Plans in selected Departments and their implementation on a pilot basis for the purpose of improving the service delivery system. Priority has been assigned to such Plans that have the maximum impact on the poor. The programme duration is for three years from 1.4.06. Total investment will be of the order of Rs 948.08 lakhs to be funded entirely by DFID. 6.2 Under the programme critical gaps in the selected Departments will be identified that hinder the achievements of the goals of the Department. These gaps may be related to process, technology or the human resources employed in the Department. Measures will be formulated to overcome the constraints. The implementation of the measures will be undertaken on a pilot basis. 6.3 The programme will run under the strategic direction of the Steering Committee headed by Chief Secretary. A Management Committee has been constituted for taking operational decisions. 6.4 A Strategic and Performance Innovation Unit (SPIU) will be set up consisting of domain experts who will critically study the nature of process, technology and human resources employed in the selected Departments and prepare the Reform Action Plan in consultation with the Departments and other stakeholders. Each SPIU will consist of a Workstream Facilitator, MIS Development Specialist and Technical Specialists (Programmer). 6.5 In order to streamline the Government procurement of goods and services OCAC will be strengthened under OMGI to act as the nodal agency to provide the contracting services. For this purpose, a team of Procurement Specialists will be housed in OCAC. 6.6 The programme coordination will be done by the State Project Coordination and Monitoring Unit (SPMU) set up in General Administration Department. It will act as the Secretariat of the Steering Committee of the Programme. 7 A Brief Note on AR 6.7 Special emphasis has been laid on the training of Government employees in order to improve the human resources within the Government. They will be exposed to the best practices, acquainted with modern office management procedures and ICT, statutes, rules and regulations of the Government, techniques of project management, specialized subject matters, etc. 6.8 OMGI provides for the scoping study of Human Resources Management System, District Modernization Plan, Food Grain Tracking, MDM MIS, Property Tax MIS, Allotment System in BDA. These components are subject to revision during the continuance of the programme. 7. Human Resources Management Information System 7.1 Government of Orissa have identified human resource management function as a common thread that binds all the Departments. At present, the Government have about 4.70 lakh employees on their rolls. The Government recognizes the need for an information technology solution to address the needs and streamline its complex and dispersed Human Resource Management System. The problems in the personnel system have negative repercussions upon the activities of the rest of the organization. Mismanagement of the personnel system imposes a serious burden and distracts the energy of the leadership from core departmental activities to solving grievances of the employees. It also causes distortion in the personnel structure as delays occur in recruitment and promotion and vacancies remain unfilled for a considerable period of time. Delays also occur in sanction of pensions that cause grave hardship. The Administration often gets involved in solving employee grievances and substantial manpower efforts are diverted to these issues. In addition, there are over 50,000 pending litigation cases which take away crucial 8 A Brief Note on AR senior officials’ time and attention. All these problems require an immediate remedy. Given the size of the personnel in the State Government and the complexities of the problems related to personnel, the modernization of the Human Resources Management System will be a major enabler for an efficient, effective and citizen-centric administration. 7.2 Government have identified Human Resource Management System (HRMS) as one of the core initiatives as a part of its ongoing modernizing initiatives and e-governance plans, eventually culminating into a Government to Employee (G2E) portal. An Employee Life Cycle Approach will be adopted while capturing the employee data in a dynamic real-time basis through the proposed system right from the stage of the recruitment of the employee to the stage of her retirement (in fact, even for postretirement pension related issues) all the relevant facts in connection with the employee will be recorded in the proposed database. This is a project aimed at modernization of the human resource management system that may facilitate creation of an optimal personnel regime which simultaneously, satisfies the employees, and furnishes the necessary means for the fulfillment of broader organizational goals. The optimal personal strength would in turn lead to reduction in the salary cost of the Government. This would make the system leaner and efficient and in turn would help in better management of finances of the state. The resources which would be freed can be deployed into programs which would have a wider social impact for the state as a whole. The outcome of the same shall be more time for the senior officials as well as employees to devote to relevant development work and operation issues thereby serving the citizens better, particularly the weaker sections. It will cover all the offices including the Departments, Heads of Departments, other subordinate Field offices. 9