Earth and Space Science Chapter 19 Notes – Air Pressure and Wind
advertisement

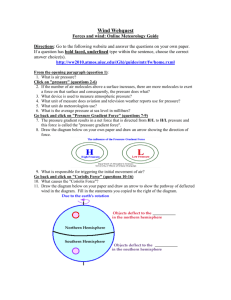
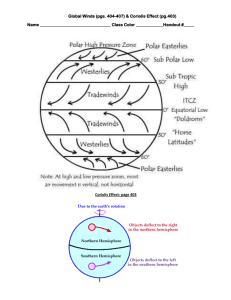
E&S Science Chapter 19 Notes – Air Pressure and Wind Name __________________________ Air Pressure - pressure exerted by the weight of air __________ Air pressure is exerted in all _____________ - Down, up, sideways o Pressure pushing down on an object balances air pressure pushing up on the object! Average air pressure at ______ level: 1 kg/cm2 or 1 atmosphere Measuring Air Pressure o ___________ – a device used for measuring air pressure Measured in units called ___________ Two types ____________ – glass tube, dish of mercury o when air pressure increases, mercury in tube rises o when air pressure decreases height of mercury decreases ____________ – partially emptied metal chamber sensitive to variations in air pressure o Provides continuous record of pressure changes over time Factors affecting Wind Wind – result of _______________ differences in air pressure o Air flows from areas of higher pressure to lower pressure Unequal ____________ of Earth’s surface generates pressure differences o Solar radiation is source o If Earth did not rotate, air would flow in a ____________ line from areas of higher to lower pressure Three factors combine to control wind: o Pressure differences, Coriolis effect, friction Pressure Differences ______________ – lines on a map that connect places of equal pressure Pressure ______________ – pressure changes indicated by spacing of isobars o A steep pressure gradient causes greater ____________________ of air o Closely spaced isobars indicate ___________ pressure gradient and _________ winds o Widely spaced isobars indicate _________ pressure gradient and _________ winds ____________ gradient is driving force of wind!!! Direction of force is always from areas of higher to lower pressure and at _________ angles to isobars Coriolis Effect Describes how Earth’s rotation affects moving objects All free-moving objects, including wind, are ______________ to the ________ of their path of motion in the N.H. o In the S.H. they are deflected to the left Northern Hemisphere – ___________________ motion __________________ Hemisphere – clockwise motion A rocket launched from North Pole toward a large target on equator o It will land 15° West of its target o The Earth would have rotated 15° East under the rocket in one hour This deflection: o Always directed at right angles to direction of ______________ o Affects ___________ wind direction, not wind speed o Is affected by wind speed – ______________ wind, greater deflection o Strongest at poles and weakens toward _____________ becoming non-existent Friction Friction of wind is only important within a few ____________ of Earth’s surface o _________ air movement – changes wind direction o When air above friction layer, pressure gradient causes air to move across isobars o Pressure gradient and Coriolis effect ______________ in high-altitude air and wind flows parallel to isobars Pressure Centers and Winds Centers: o _________ pressure – lows or cyclones Pressure ______________ from outer isobars toward the center o High pressure – highs or anticyclones Values of isobars ______________ from outside toward center _____________ and Anticyclonic Winds o When pressure gradient & Coriolis effect applied to pressure centers in _______________ Hemisphere: Around a ________ – winds blow counterclockwise Around a high – winds blow ______________ o _____________ Hemisphere: Around a low – winds blow _____________ Around a ________ – winds blow counterclockwise o Both Hemispheres friction causes: Cyclone – net flow of air ______________ Anticyclone – net flow of air _____________ Weather and Air Pressure Cyclonic flow – horizontal convergence on ____________ (pushes air up) o Divergence aloft (above air system) o Related to unstable systems and __________ weather Anticyclonic flow – horizontal divergence on surface o _______________ aloft (pushes air down) o Related to clear skies and ________ weather Weather Forecasting Low pressure centers – produce bad weather in any _______________ o __________________ direction across U.S. o Take a few days, up to more than a week o Paths can be unpredictable Global Winds ____________ regions – ___________ solar radiation is received than is radiated back to space Polar regions – ___________ solar energy is received than lost Giant Heat Transfer System: o ________ air moved toward high latitudes o Cool air moved toward __________ Non-Rotating Earth Model o Smooth surface o Heated air at equator would rise until reaching _______________ o Tropopause would deflect hot air towards _________ o Air would reach poles, sink, spread out in all directions and move back towards ______________ Rotating Earth Global Winds o __________ and tropical cells retain earlier characteristics ____________ latitudes are different o Equatorial low – region characterized by ________________ precipitation Produced by rising air o ____________ N or S latitude of equator Hot, arid conditions due to sinking air Great deserts of Australia, Arabia, Sahara __________ winds – two belts of wind that blow almost constantly from ____________ directions o Located between subtropical highs and equator ___________ – air that travels to the poles and is deflected, generating _____________ wind of middle latitudes o Dominant west-to-east motion of atmosphere in regions on _____________ side of subtropical highs Polar _________________ – winds that blow from polar high toward ________________ low o Not constant o Cold polar air sinks and spreads towards ____________ Polar Front – interaction of warm and cool air masses o Produce a _____________ belt Circulation in 4 Pressure Zones Subtropical and Polar regions – areas of dry sinking air that flows _______________ toward surface o Produces ____________ winds o __________ pressure zones Equatorial and subpolar regions – associated with _____________ and ____________airflow o Accompanied by clouds and precipitation o ________ pressure zones Influence of Continents Only continuous belt without influence of land is _________ ______ in S.H. At other latitudes, particularly N.H., seasonal temp changes disrupt pressure pattern Large land masses: o become _________ in winter – seasonal ________ pressure system develops (airflow off land) o _________ in summer – seasonal ________ pressure system develops (airflow onto land) Monsoons – seasonal changes in wind __________ o Summer - ________ o Winter - _______ Regional Wind Systems Local Winds – caused by topographic effects or variations in surface composition (________ and ________) o _______ breezes – cooler air over sea (higher pressure) blows to land (lower pressure) Breeze develops before ________ and goes to late afternoon Can also develop on shores of lakes o _______ breeze – cooler air over land (higher pressure) than sea (lower pressure) cooler air blows towards the sea Happens at ________ o _________ breeze – warmer air on mountain slopes tends to ________ Daytime More dominant in warmer seasons o ___________ breeze – cooler air on mountain slopes ________ to valley Nighttime Coldest pockets of air usually found in lowest spots More dominant in __________ seasons How Wind is Measured __________ – winds labeled direction _________ which they blow o I.E. – North (north to south) o Wind vane used to measure o _____________ wind – when wind blows _____________ from one direction to another Westerlies consistently move weather from west to east (winds vary) ___________ - measured by an _______________ o Read from dial like a speedometer El Niño Cold ___________ current – flows towards ____________ along coasts of Ecuador and Peru o upwelling of cold nutrient-rich waters o Near end of year, __________ current replaces cold current & lasts a few weeks Every _______ yrs, countercurrents unusually strong, replacing cold offshore waters with warm equatorial waters o Marked by ____________ weather patterns o Normally arid inland areas receive lots of ________ o Part of a global circulation La Niña - When temps in eastern pacific are ___________ than normal Blows colder than normal air over Pacific Northwest and northern Great Plains Warms much of rest of U.S. Northwest – greater precipitation Also can increase ___________ activity Different effects all over globe Global Distribution of Precipitation ___________ region on Earth – ___________ region dominated by equatorial ________ o Rainforests of South America and Africa o Warm, humid trade winds converge ___________ – areas dominated by subtropical _______-pressure cells ___________ of large land masses – decreased precipitation