The NCSS Essentials of Social Studies Education
advertisement

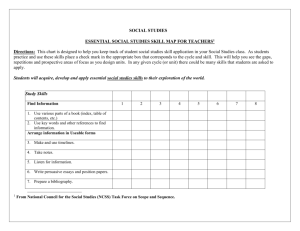
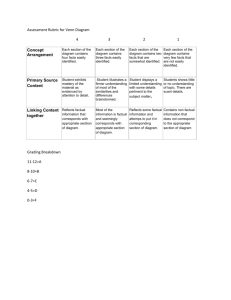
The NCSS Essentials of Social Studies Education Essential Skills of Social Studies Education Acquiring Information A. Reading Skills 1. Comprehension • Read to get literal meaning • Use topic and section headings, topic sentences, and summary sentences to select main ideas • Differentiate main and subordinate ideas • Select passages that are pertinent to the topic studied • Interpret what is read by drawing inferences • Detect cause-and-effect relationships • Distinguish between the fact and opinion; recognize propaganda • Recognize author bias • Use picture clues and picture captions to aid comprehension • Use literature to enrich meaning • Read for a variety of purposes: critically, analytically, to predict outcomes, to answer question, to form an opinion, to skim for facts • Read various forms of printed material: books, magazines, newspapers, directories, schedules, and journals 2. Vocabulary • Use usual word-attack skills: sight recognition, phonetic analysis, and structural analysis • Use context clues to gain meaning • Use appropriate sources to gain meaning of essential terms and vocabulary: glossary, dictionary, text, and word lists • Recognize and understand an increasing number of social studies terms 3. Rate of Reading • Adjust speed of reading to suit purpose • Adjust rate of reading to difficulty of the material B. Study Skills 1. Find Information • Use various parts of a book (index, table of contents, etc.) • Use key words, letters on volumes, index, and cross references to find information • Evaluate sources of information—print, visual, electronic • Use appropriate source of information • Use the community as a resource 2. Arrange Information in Usable Forms • Make outline of topic • Prepare summaries • Make timelines • Take notes • Keep records 533569412 Page 1 of 5 C. D. • Use italics, marginal notes, and footnotes • Listen for information • Follow directions • Write reports and research papers • Prepare a bibliography Reference and Information-Search Skills 1. The Library • Use card catalog to locate books • Use Reader's Guide to Periodical Literature and other indexes • Use COMCATS (Computer Catalog Service) • Use public library telephone information service 2. Special References • Almanacs • Encyclopedias • Dictionary • Indexes • Government publications • Microfiche • Periodicals • News sources: newspapers, newsmagazines, TV, radio, videotapes, and artifacts 3. Maps, Globes, and Graphics • Use map- and globe-reading skills: — Orient a map and note directions — Locate places on map and globe — Use scale and compute distances — Interpret map symbols and visualize what they mean — Compare maps and make inferences — Express relative location • Interpret graphs • Detect bias in visual material • Interpret social and political messages of cartoons • Interpret history through artifacts 4. Community Resources • Use sources of information in the community • Conduct interviews of individuals in the community • Use community newspapers Technical Skills Unique to Electronic Devices 1. Computer • Operate a computer using prepared instructional or reference programs • Operate a computer to enter and retrieve information gathered from a variety of sources 2. Telephone and Television Information Networks • Ability to access information through networks 533569412 Page 2 of 5 Organizing and Using Information These are form of Procedural Knowledge A. Thinking Skills 1. Classify Information • Identify relevant factual material • Sense relationship between items of factual information • Group data in categories according to appropriate criteria • Place in proper sequence: — order of occurrence — order of importance • Place data in tabular form: charts, graphs, and illustrations 2. Interpret Information • State relationships between categories of information • Note cause-and-effect relationships • Draw inferences from factual material • Predict likely outcomes based on factual information • Recognize the value dimension of interpreting factual material • Recognize instances in which more than one interpretation of factual material is valid. 3. Analyze Information • Form a simple organization of key ideas related to a topic • Separate a topic into major components according to appropriate criteria • Examine critically relationships between and among elements of a topic • Detect bias in data presented in various forms: graphics, tabular, visual, print • Compare and contrast credibility of differing accounts of the same event 4. Summarize Information • Extract significant ideas from supporting illustrative details • Combine critical concepts into a statement of conclusions based on information • Restate major ideas of a complex topic in concise form • Form opinion based on critical examination of relevant information • State hypotheses for further study 5. Synthesize Information • Propose a new plan of operation, create a new system, or devise a futuristic scheme based on available information • Reinterpret events in terms of what might have happened, and show the likely effects on subsequent events • Present visually (chart, graph, diagram, model, etc.) information extracted from print • Prepare a research paper that requires a creative solution to a problem 533569412 Page 3 of 5 • B. C. • Communicate orally and in writing 6. Evaluate Information • Determine whether or not the information is pertinent to the topic • Estimate the adequacy of the information Test the validity of the information, using such criteria as source, objectivity, technical correctness, and currency Decision-Making Skills • Identify a situation in which a decision is required • Secure needed factual information relevant to making the decision • Recognize the values implicit in the situation and the issues that flow from them • Identify alternative courses of action and predict likely consequences of each • Make decision based on the data obtained • Take action to implement the decision Metacognitive Skills • Select an appropriate strategy to solve a problem • Self-monitor one's thinking process Interpersonal Relationships and Social Participation A. Personal Skills • Express personal convictions • Communicate own beliefs, feelings, and convictions • Adjust own behavior to fit the dynamics of various groups and situations • Recognize the mutual relationship between human beings in satisfying one another's needs B. Group Interaction Skills • Contribute to the development of a supportive climate in groups • Participate in making rules and guidelines for group life • Serve as a leader or follower • Assist in setting goals for the group • Participate in delegating duties, organizing, planning, making decisions, and taking action in group setting • Participate in persuading, compromising, debating, and negotiating in the resolution of conflicts and differences C. Social and Political Participation Skills • Keep informed on issues that affect society • Identify situations in which social actions are required • Work individually or with others to decide on an appropriate course of action • Work to influence those in positions of social power to strive for extensions of freedom, social justice, and human rights • Accept and fulfill social responsibilities associated with citizenship in a free society 533569412 Page 4 of 5 Source: In 1989 NCSS adopted the Essential Skills of a Social Studies Education. See http://www.socialstudies.org/standards/ 533569412 Page 5 of 5