Vocabulary
advertisement

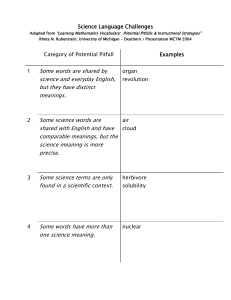
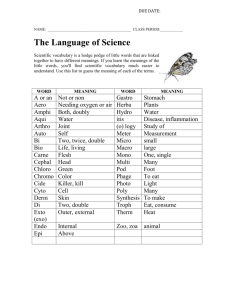
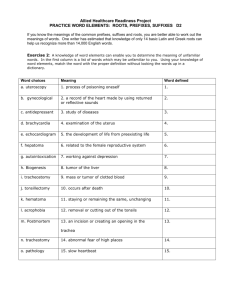
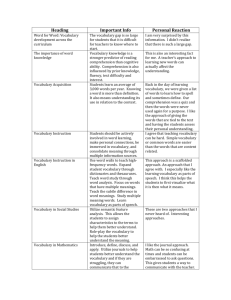
Vocabulary CTE READS! Developing Vocabulary Through Context Written by: Carilyn Knill, Peggy LaShier, Ann Tebo, Kathy Wooton School: Skyline Grade Level and/or Subject: High School Length of Study: 15-30 minutes Content Objective: TSW Examine different clues to use to determine the meanings of unknown words Construct meaning for unfamiliar words by using context clues Lesson or Performance objective: Students should try to figure out the meaning of the new words or phrases by the way they are used in passages, and the information that precedes and follows it. It is not always possible to create meaning from context, but it often is, so students should be made aware of the strategies involved. Knowing and using vocabulary strategies helps students become independent thinkers and learners. Standards Addressed: AIMS Connection: Strand 1: The Reading Process Concept 4: Vocabulary -Acquire and use new vocabulary in relevant contexts. PO 2. Infer word meanings from context (e.g., definition, example, restatement, comparison/contrast, cause/effect). Materials, Resources and Technology Needed: All that will be needed for this lesson are the handouts that follow the cover sheet. These strategies should be applied and modeled by the instructor with content-specific vocabulary as it comes up in reading assignments. Instructional Procedures or Anticipatory Set: Explain to students the fact that once they are out of school the predominant way they will learn new vocabulary is through reading, and that today’s lesson will illustrate some strategies to use to figure out the meaning of unknown words when they don’t have dictionaries handy. Presentation Skills: 1. Copy enough student handouts to distribute to the class. 2. Carefully go over and discuss the information prior to the sample problems on the student handout. 3. Have students do the problems, and go over the correct answers. Assessment: Students will complete the handout. Key: 1. A; 2. unlike, C; 3. B; 4. B; 5. and 6 – answers will vary. 1 Vocabulary Figuring out the Meaning of Unfamiliar Words Through the use of Context Clues Context is the environment in which something exists. In a reading passage, context refers to words and sentences that surround a particular word or phrase. Look for the following in the surrounding sentences to figure out the meanings of unknown words: Examples Descriptions or explanations Definitions or synonyms (words with similar meanings) Antonyms (words with opposite meanings) Causes and effects Grouping to make comparisons Conjunctions showing relationships (i.e. and, but, not only, whereas, etc.) Reading Strategy Tips in Practice: Look for words or phrases with meanings that might be similar to that of the unknown word. 1. Chemicals that destroy materials that they come in contact with are known to have corrosive qualities, and are referred to as corrosives. Which of the following is the closest meaning to the word corrosive as it is used in the sentence? A. destructive B. sarcastic C. cutting D. abrasive Look for words that might mean the opposite of the unknown word 2. Unlike the on-line school that offered no diploma certifying qualifications, Sandi chose to go through MCC’s accredited Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) program. Which word gives you the clue that you are to look for the opposite of the unknown word? ____________________ 2 Vocabulary In this sentence, what is the meaning of accredited? A. difficult to gain entry B. inexpensive C. certified as official D. technical Look for causes and effects related to the unknown word. 3. Since John went to the movies instead of writing the rough draft of his career search narrative, he felt like he had to fabricate a reason for coming unprepared to class. What does the word fabricate mean? A. to be happy about B. invent falsely C. write D. explain Try to fit the unknown word into a group by making comparisons. 4. Concerns for employee safety, comfort, ease of equipment use, and productivity are all related to ergonomic issues that should be considered by companies. Which is the best definition for ergonomic? A. work-based B. sanitation C. designing things for efficient use d. designing things to be most profitable Now try this on your own! Be prepared to come up with a description of what each of the underlined words is likely to refer to. 5. To avoid fraud, information in computers, cellular phones, ATMs, and Bluetooth devices can be transformed using encryption to protect consumers. encryption = _______________________________________________ The Culinary Arts students’ hypothesis for why their cupcakes were flat and smaller than the other kitchens was that they used baking powder instead of baking soda. 6. hypothesis = _______________________________________________ 3
![Word Study [1 class hour]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007905774_2-53b71d303720cf6608aea934a43e9f05-300x300.png)