9 - Transcription and Translation
advertisement
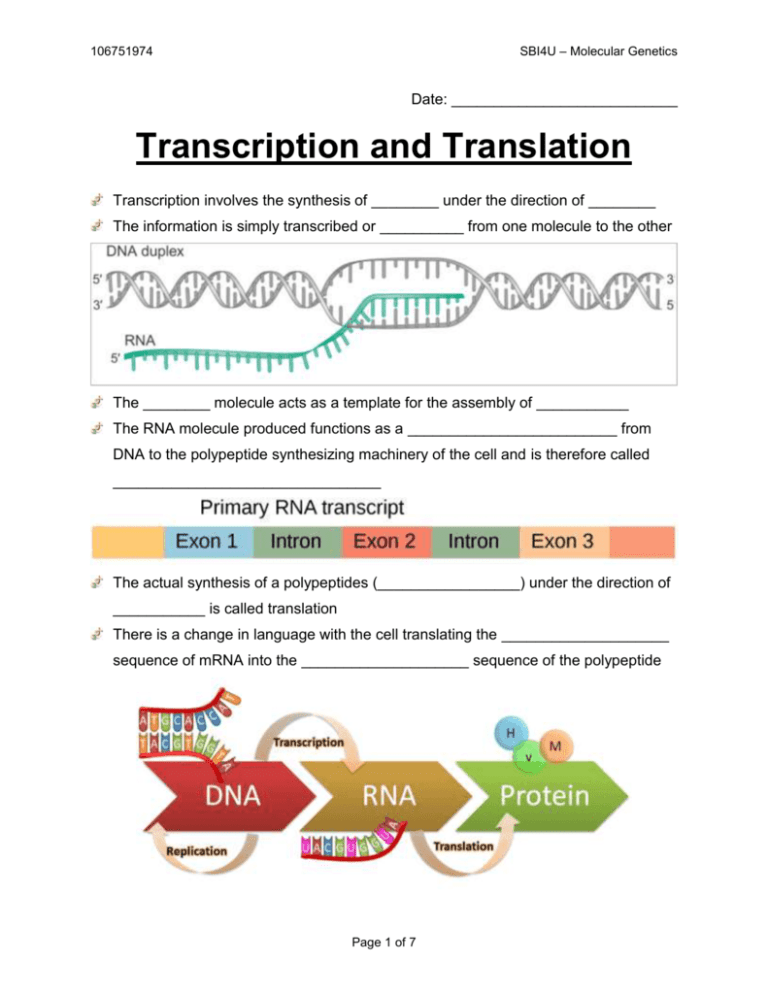
SBI4U – Molecular Genetics 106751974 Date: ___________________________ Transcription and Translation Transcription involves the synthesis of ________ under the direction of ________ The information is simply transcribed or __________ from one molecule to the other The ________ molecule acts as a template for the assembly of ___________ The RNA molecule produced functions as a _________________________ from DNA to the polypeptide synthesizing machinery of the cell and is therefore called ________________________________ The actual synthesis of a polypeptides (_________________) under the direction of ___________ is called translation There is a change in language with the cell translating the ____________________ sequence of mRNA into the ____________________ sequence of the polypeptide Page 1 of 7 SBI4U – Molecular Genetics 106751974 Transcription: The Details The enzyme responsible for transcription is ______________________________ Transcription occurs in three stages: 1. ________________________ 2. ________________________ 3. ________________________ Initiation RNA polymerase binds to regions of DNA called ________________________ The promoter region includes an _______________ Site where transcription begins Proteins called _________________________ aid RNA polymerase in searching for __________________ regions along the DNA molecule In eukaryotic cells, RNA polymerase recognizes a region called the ________________ (region rich in ______________ and _____________) to initiate transcription Once RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region it separates the DNA strands at the initiation site Page 2 of 7 SBI4U – Molecular Genetics 106751974 Elongation __________________________ moves along the DNA, unwinding it and separating the strands Enzymes add nucleotides to the _____ end of the growing mRNA molecule Goes from ____ end to the ____ end Termination Transcription proceeds until RNA polymerase reaches a ______________________ on the DNA mRNA molecule _________ away from the DNA ____________ and the non-coding strand reforms its __________________ shape Page 3 of 7 SBI4U – Molecular Genetics 106751974 The ends of the mRNA molecule are also modified with a ________________ and a __________________ added to inhibit _________________ of the mRNA molecule Translation: The Details Interpreting a genetic message encoded in mRNA requires another type of RNA molecule called ____________________________ tRNA functions to __________________ amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome Each tRNA associates with a particular mRNA ______________ and a particular ________________________ A codon is a sequence of _________________________ Page 4 of 7 SBI4U – Molecular Genetics 106751974 tRNA Structure tRNA is like a “_______________” with a "nucleic acid word" (________________) on one side and a "protein word" (___________________) on the other side Specific amino acids are added to each tRNA molecule with a specific enzyme called ___________________________ _____________________ The active site binds an amino acid and ATP to the tRNA Once ATP is bound it releases two phosphate molecules that drives the joining of the ____________________ to __________________ Translation occurs in three stages: 1. ________________________ 2. ________________________ 3. ________________________ Chain Initiation Initiation begins with two subunits of ribosomes, a mRNA molecule and the initiator tRNA anticodon: __________ amino acid: _____________________ Page 5 of 7 SBI4U – Molecular Genetics 106751974 Ribosome Anatomy A functional ribosome consists of two subunits a ___________ (________________) subunit a ___________ (________________) subunit It has a mRNA binding site and three tRNA binding sites known as the ___________ _________ sites The A site holds the tRNA carrying the next amino acid to be ________________ to the polypeptide chain The P site holds the tRNA attached to the ____________________________ The ___________________ tRNA leaves via the E site (___________) Elongation Amino acids are added one by one to the initial amino acid Page 6 of 7 SBI4U – Molecular Genetics 106751974 Termination Elongation continues until a _________________________ codon is reached Possible termination codons include: __________________________________ All these signal a “__________________” in translation Proteins called ________________________ cause the _________________ of completed polypeptide from tRNA in the P site Ribosomes separate into its subunits and are _________________ for further use Page 7 of 7