Electronic Supplementary Material
advertisement

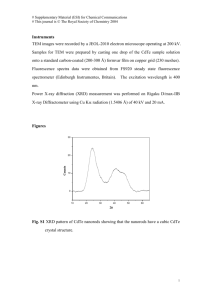
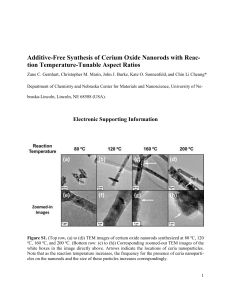
Electronic Supplementary Material A luminescence enhancement method for the immediate determination of vitamin B1 using long-wavelength emission water-soluble CdTe nanorods 2500 A 1.5h, 5.5h, 12h, 24h 2000 1500 1000 500 0 480 560 640 Wavelength (nm) 720 Luminescence intensity (a.u) Luminescence intensity (a.u) Yan Li, Peng Wang, Xin Wang, Ming Cao, YunSheng Xia, Chun Cao, MeiGui Liu, ChangQing Zhu* Anhui Key Laboratory of Chemo-Biosensing, College of Chemistry and Materials Science, Anhui Normal University, Wuhu, 241000, P. R. China. E-mail: zhucq@mail.ahnu.edu.cn; 3000 CdTe nonarods + VB 1 B CdTe nonarods 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 0 480 540 600 660 720 780 Wavelength (nm) Fig. S-1 (A) Luminescence spectrum of four CdTe nanorods obtained at pH 11 after different refluxing time, (B) Luminescence enhancement effects for various CdTe nanorods upon addition of 2.0 μmol L-1 vitamin B1 at pH 10.83 with the emission maximum wavelength of CdTe nanorods (from left to right) at 550, 600, 665 and 720 nm, respectively, The molar ratio of Cd2+:TGA:Cys:HTe− of the nanorods used is set at 1:1.8:0.6:0.5. Counts B A A 0 200 400 600 800 1000 Time (ns) Fig. S-2 Luminescence decay curves of CdTe nanorods with the emission wavelength of 665 nm at pH 10.83 in the absence (A) and presence (B) of 2.0 μmol L-1 vitamin B1. The measurements were performed at room temperature with the excitation and emission wavelength at 530 nm and 665 nm, respectively. The molar ratio of Cd2+:TGA:Cys:HTe− 2000 (I0) 1600 220 A (I) (I- I0) B 200 1200 I - I0 Luminescence intensity (a.u) of the nanorods used is set at 1:1.8:0.6:0.5. 800 180 400 160 0 6 8 10 pH 12 14 0 5 10 15 20 25 -3 Na2CO3-NaHCO3 (1×10 M) Fig. S-3 Effect of pH (A) and the concentration of buffer solution (B) on luminescence enhancement. [CdTe]= 1.0×10-5 mol L-1, [VB1] = 2.0 μmol L-1. The excitation and emission wavelengths are 530 nm and 665 nm, respectively. Table S-1 Interference of some coexisting substances Coexisting substances Molar ratio to thiamine Relative error (%) Ca2+ 7.5 -4.8 Zn2+ 22.5 -3.9 Pb2+ 38 -4.78 Mg2+ 15 -4.06 K+, I- 35 -3.7 Al3+ 14 -3.1 Cu2+, Mn2+ 0.25 -4.7 Hg2+ 0.03 -4.8 Glycine 25 -4.6 Glutamic acid 25 -4.9 Vitamin C 4 -4.0 Riboflavin 2 -2.9 Nicotinic acid 150 -3.4 Pyridoxine hydrochloride 25 -4.3 Folic acid 2 -3.7 Tartaric acid 7.5 -4.6 Biotin 10 -3.9