Quiz 3
advertisement

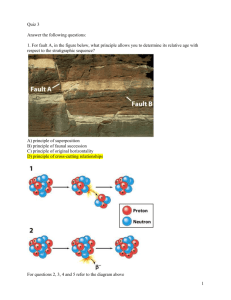
Quiz 3 1. What are the three main types of rock? B. Igneous,metamorphic,sedimentary 2. Which type of rock is formed when molten magma or lava solidifies? A. igneous 3. What is an igneous or sedimentary rock that has been changed by extreme pressure and heat? D. metamorphic 4. For fault A, in the figure above, what principle allows you to determine its relative age with respect to the stratigraphic sequence? D) principle of cross-cutting relationships For questions 5, 6, 7 and 8 refer to the diagram above 5. For the illustration above, what would be the change in atomic number from parent element to daughter element as a result of alpha emission? D) -2 6. For the illustration above, what would be the change in atomic number from parent element to daughter element as a result of beta decay? A) +1 7. For the illustration above, what would be the change in atomic mass from parent element to daughter element as a result of alpha emission? B) - 4 8. For the illustration above, what would be the change in atomic mass from parent element to daughter element as a result of beta decay? E) There will be no change in atomic mass. For questions 9 and 10 refer to the diagram above: 9. For the block diagram above, which of the following statements is(are) true? E) Both B and C are true statements. 10. What stratigraphic principle allowed you to answer question 9? D) principle of cross-cutting relationships 11. An isotope that is undergoing radioactive decay is called a _____, and an isotope that forms as a result of radioactive decay is called a _____. parent, daughter 12. In the process of alpha decay. How does the daughter element compare to the parent with respect to atomic number and mass? The daughter element reduces its atomic number by 2 and its atomic mass by 4 13. In beta decay a neutron becomes a proton inside the nucleus of an atom. What changes the atomic mass, atomic number or both? There is an increase in the atomic number, but the mass remains the same. 14. Numerical age is the age of a rock or geological feature in years. True 15. An unconformity is a gap in the stratigraphic sequence. True 16. In the photo (ABOVE) of the stratigraphic sequence of the Grand Canyon, the Redwall Limestone is the youngest layer. False For questions 17, 18, and 19 refer to the picture above 17. A(n) ______is a surface of erosion that separates younger strata above from older igneous or metamorphic rocks below. NONCONFORMITY 18. A(n) ______is a surface of erosion in which the orientation of the older strata, below, are parallel to the younger strata, above. DISCONFORMITY 19. A(n) ______is a surface of erosion between two groups of sedimentary rocks in which the older strata , below, are at angle to the younger strata, above. ANGULAR UNCONFORMITY 20. A(n) ______is a gap in the rock record across which there is a significant amount of missing time. UNCONFORMITY