Massive Transfusion Guidelines 02
advertisement

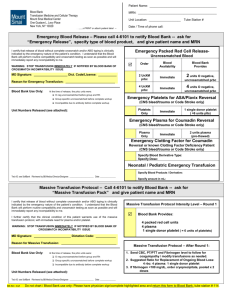
Massive Transfusion Guidelines Purpose: This document provides guidelines only for efficient and effective transfusion support for patients who have massive blood loss. As always, individual circumstances need to be considered for each patient. This document will be reviewed and updated periodically. Definition: Replacement of at least 1 blood volume (80cc/kg) in the first 24 hours of resuscitation. Triggers for massive transfusion: 1) Replacement of 20 ml/kg of RBCs within the first hour of resuscitation 2) Anticipated continued blood loss that would amount to 1 blood volume in 24 hours. Either the clinical team or the Blood Bank can activate the Blood Bank Massive Transfusion Protocol (see appendix K of the Patient Care Policy Blood and Blood Components” . At the Blood Bank, the following will be available once massive transfusion is called by the physician or triggered by the Blood Bank: Age (y) 0-3 4-7 8-12 >12 # units pRBC used in 24 h 4 6 8 10 # units FFP thawed and available 1 2 4 4 # units SDP platelet available 1 1 1 1 Overall management: 1. Restore circulating volume 2. Timely sample for blood type and crossmatch is required 3. Keep patient normothermic (core body temperature 36C; refer to Guidelines for Prevention and Management of Hypothermia in Trauma). 4. Anticipate and treat electrolyte imbalance (hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia) 5. Above parameters should be monitored at least every 6 hours post-stabilization and at 24 hours post stabilization. 6. Correct underlying cause of DIC if possible. Laboratory monitoring: 1) Initial: CBC, type and crossmatch, PT, PTT, fibrinogen, chemistry, glucose, blood gas 2) Ongoing: hemoglobin, platelet count, ICa, K, glucose, ABG (known as a surgical panel in the OR), PT, PTT, fibrinogen: Note Obtained by defined order set for intraoperative lab monitoring q1h In the PICU, obtained at least q 2-3h until stabilization. End points of resuscitation: In general, the goals of therapy are maintenance or restoration of tissue perfusion and oxygenation by restoring blood volume and hemoglobin and arrest of bleeding by surgical treatment of the source and correction of coagulopathy. Blood component therapy Blood product Packed red blood cells Frozen plasma Triggers - Hb < 8 gm/dl - If a third 20 ml/kg fluid bolus is required to maintain blood pressure Dose 15 ml/kg Comments - O neg RBCs are provided until sample is received for crossmatch, then group compatible uncrossmatched blood given - Blood bank may switch to Rh pos for males - FFP takes 20 min to thaw - If PT >15 sec (INR 20 ml/kg >1.5), PTT >40 sec - Once 40 ml/kg pRBC given, if still bleeding - Diffuse microvascular bleeding Platelets - If Weight - Platelet count ≥30 kg, 1 <75,000/ul if ongoing single donor bleeding pheresed - Once 40-80 ml/kg (SDP) unit; RBCs have been replaced, platelet count is if Weight <30 kg, ½ likely <50,000/ul (may SDP unit occur sooner) Cryoprecipitate - Fibrinogen <100 mg/dl 1 unit/10kg - Cryoprecipitate takes 20 - “Clinical” DIC: oozing, minutes to thaw major head injury, uncontrolled hemorrhage NOTE: It is Blood Bank policy to irradiate all blood products for children 12 months of age. Irradiation takes about 7 additional minutes per unit of blood product. The clinical team could instruct the Blood Bank to forego irradiation in urgent cases. Recombinant factor VIIa - May be considered if ongoing bleeding despite conventional therapy and surgical management 40-90 mcg/kg - Optimal dose is not known (there are studies showing beneficial effect with doses as low as 20 mcg/kg). There are no controlled studies that address benefit and safety in trauma. DIC is a relative contraindication. Stopping massive transfusion support When the patient is stabilized, the clinical team should inform the Blood Bank of the decreased need for support, so as not to waste resources. Developed by the Trauma Program at Children’s Hospital of Wisconsin Revisions 4/2008 Disclaimer for Release of Children’s Hospital and Health System Form Documents Children’s Hospital and Health System (CHHS) does not make any representation with respect to any sort of industry recognized standard of care for the particular subject matter of this/these document(s). Additionally, CHHS form documents are subject to change, revision, alteration and/or revocation without notice.