113 Genetics notes
advertisement

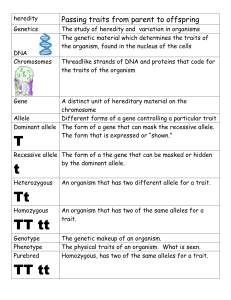
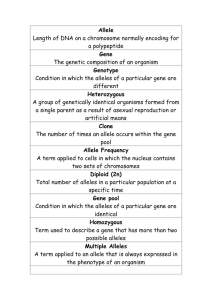
GENETICS POWERPOINT NOTES #113 Name______________________________ Use pages 76-89 in textbook Life Science Standards: 7. Recognize that every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits. These instructions are stored in the organism’s chromosomes. Heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another. 8. Recognize that hereditary information is contained in genes located in the chromosomes of each cell. A human cell contains about 30,000 different genes on 23 different chromosomes. 9. Compare sexual reproduction (offspring inherit half of their genes from each parent) with asexual reproduction (offspring is an identical copy of the parent’s cell). Slide 2 1. Traits : __________________________________________________ of an organism inherited from parents and passed on from one generation to the next. 2. Heredity: The passing of the traits from __________________ to ____________________. 3. Genetics: Study of _______________________ Slide 3 4. Name 3 of your traits (be specific- don’t say “skin color”, say “medium brown skin color” __________________________ ____________________________ ___________________________ 5. Name 2 specific traits that could be found in a plant (again, be specific- use adjectives) ____________________________ ______________________________ 5a. Many traits are unseen- they have to do with _________________________________ in cells. Slide 7 6. How many chromosomes are in each of our body cells? ________ found in ________ pairs. 7. How many chromosomes are in human egg and sperm cells? _________; ________ pairs 8. How many genes do we have in all on our chromosomes? ________________________ STOP and THINK: answer #9 with your partner using the diagram on the slide 9. Arrange the order of the following structures from largest to smallest: nucleus gene cell chromosome DNA base pair __________________________________________________________________________________ Slide 8: 6. What controls traits? ______________________ 7. Gene: a segment of ______________ on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait. 8. Genes hold the instructions (in the DNA nucleic base “code”) used to make a specific ___________________. Slide 9: 9. Where do we get the 2 alleles of each gene that we have? One from ________; one from ________ Slide 11: 10. Allele: different forms of a ___________________. 11. A dominant allele is _______________________ expressed no matter what other copy of gene is. 12. A recessive allele is ____________ expressed if the other allele for that gene is _______________. 13. A dominant allele is expressed with a _________________letter; recessive with a ____________. STOP and THINK: For each of the allele pairs below, write whether the organism will show the dominant or recessive trait bb _____________________ CC ________________________ Dd ________________________ How many alleles do you have for each gene? ________ Slide 12: 14. Give an example of a purebred dominant trait: __________ a purebred recessive: ____________ a hybrid _________ Slide 13: 15. phenotype- _____________________ or physical appearance of an organism 16. genotype- ______________________________ of an organism- its allele combination 17. For each of the following examples, write whether it is a phenotype or genotype: green pea pods ___________________; Bb ____________________; dimples __________________ Slide 15: 18. (Female gametes) (Male gametes) Genotype: ______% Hh Phenotype: ______% Hitchhiker’s thumb Slide 16: 19. The “father of genetics” was the Austrian monk named ____________________________. 20. He worked with ______________ plants. Slide 17: Mendel’s F1 generation 21. Mendel’s F2 generation Genotype = __________________ Genotype = __________________ Phenotype = __________________ Phenotype = __________________ Slide 18: 22. Mendel’s work wasn’t looked at widely until it was rediscovered in _________________. Slide 21: 23. Probability: a number that describes how ________________ it is that an event will occur 24. The results of one offspring do not affect the other offspring. Think of this: If you get 5 “heads” in a row, that ____________________ mean the 6th toss is more likely to be heads. Slide 22: 25. Homozygous- 2 ________________ alleles; purebred example: ________ Slide 23: 26. Heterozygous- 2 ________________ alleles; hybrid example: ________ Slide 24: 27. Incomplete Dominance- alleles not _______________________ nor _______________________ 28. The phenotype is a ____________________ of the two alleles. Example: pink flower Slide 25: 29. Codominance- neither allele is dominant or recessive. The two different traits appear _____________________ in the organism. Example: ABO __________ types