learning styles
advertisement

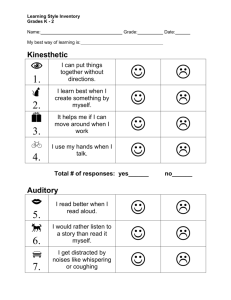
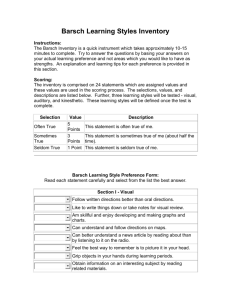
What's YOUR Learning Style? Learning styles are various approaches or ways of learning[1]. They involve educating methods, particular to an individual, that are presumed to allow that individual to learn best. Most people prefer an identifiable method of interacting with, taking in, and processing stimuli or information. Based on this concept, the idea of individualized "learning styles" originated in the 1970s, and acquired "enormous popularity".[2] Look at Visual Learners: A typical visual learner uses visualization techniques to remember things. They often have a good sense of direction because they visualize maps and directions in their mind. Many prefer to read information in a textbook or on the whiteboard rather than listen to the teacher lecture. They also enjoy doodling and drawing. Visual learners typically use sight words in their everyday terminology. For example, they might say "Let's take a look at this." or "Let's look at this from a different perspective." They remember details including colors and spatial arrangements. Auditory learning is a learning style in which a person learns through listening. An auditory learner depends on hearing and speaking as a main way of learning.[1] Auditory learners must be able to hear what is being said in order to understand and may have difficulty with instructions that are written. They also use their listening and repeating skills to sort through the information that is sent to them. [2] Purpose: To learn about learning styles. To understand the differences between auditory, visual and kinesthetic learners To identify your own learning style There are three basic types of learning styles. The three most common are visual, auditory, and kinesthetic. To learn, we depend on our senses to process the information around us. Most people tend to use one of their senses more than the others. Today's lesson will help you determine which of these learning styles you rely on the most. There is a series of 16 questions that are related to the three main learning styles. Read the question and select the answer that closest fits your answer. Don't think about the questions too much. Go with your first choice. After you answer each of these questions, just click on the submit button at the bottom of the page. If you are connected to the internet, the computer will evaluate the results and display how many of each answer you selected. Once the computer has evaluated your answers, it will show your primary learning style. Sometimes people have two or three that all have about the same number of choices. Some people depend on two or more types of learning styles. It is not unusual to use different learning styles for different tasks. That's why people can respond so differently to the same thing. Three Different Learning Styles If you scored mostly a's you may have a visual learning style. You learn by seeing and looking. Visual Learners take numerous detailed notes tend to sit in the front are usually neat and clean often close their eyes to visualize or remember something find something to watch if they are bored like to see what they are learning benefit from illustrations and presentations that use color are attracted to written or spoken language rich in imagery prefer stimuli to be isolated from auditory and kinesthetic distraction find passive surroundings ideal If you scored mostly b's, you may have an auditory learning style. You learn by hearing and listening. Auditory Learners sit where they can hear but needn't pay attention to what is happening in front may not coordinate colors or clothes, but can explain why they are wearing what they are wearing and why hum or talk to themselves or others when bored acquire knowledge by reading aloud remember by verbalizing lessons to themselves (if they don't they have difficulty reading maps or diagrams or handling conceptual assignments like mathematics). If you had mostly c's, you may have a kinesthetic learning style. You learn by touching and doing. Kinesthetic Learners need to be active and take frequent breaks speak with their hands and with gestures remember what was done, but have difficulty recalling what was said or seen find reasons to tinker or move when bored rely on what they can directly experience or perform activities such as cooking, construction, engineering and art help them perceive and learn enjoy field trips and tasks that involve manipulating materials sit near the door or someplace else where they can easily get up and move around are uncomfortable in classrooms where they lack opportunities for hands-on experience communicate by touching and appreciate physically expressed encouragement, such as a pat on the back Understanding and Identifying Auditory, Visual and Kinesthetic Learning Styles Auditory Visual Kinesthetic Identify sounds related to an experience Have a sharp, clear picture of an experience Develop a strong feeling towards an experience I hear you clearly, Do you make pictures in your head I want you to listen . . . This sounds good Do you have visual images in your head as you are talking and Do you feel what you are saying? Are you in touch with what I am saying? listening to me? Can you see what I am saying? How do you hear this situation going? What do you hear that is stopping you? Sounds heavy. How do you see the situation? What do you seestopping you? This looks good. Do you see what I amshowing you? How do you feel about this situation? I'm getting a handle on this material. Let's move together. Does what I am putting you in touch with feelright? Sounds heavy. Word Selections Word Selections Word Selections tinkling silent squeal blast screaming choking color clear spiral showed vivid notice felt body sensations feel pain touch Fantasies Lecture Do you love me? Auditories complain: Kinesthetics don't listen. Visuals complain: Auditories don't pay attention to them because they don't make eye contact. Kinesthetics complain: "Auditory and visual people are insensitive." LEARNING STYLES Students preferentially take in and process information in different ways: by seeing and hearing, reflecting and acting, reasoning logically and intuitively, analyzing and visualizing, steadily and in fits and starts. Teaching methods also vary. Some instructors lecture, others demonstrate or lead students to self-discovery; some focus on principles and others on applications; some emphasize memory and others understanding. When mismatches exist between learning styles of most students in a class and the teaching style of the professor, the students may become bored and inattentive in class, do poorly on tests, get discouraged about the courses, the curriculum, and themselves, and in some cases change to other curricula or drop out of school. Professors, confronted by low test grades, unresponsive or hostile classes, poor attendance and dropouts, know something is not working. They may become overly critical of their students (making things even worse) or begin to wonder if they are in the right profession. Most seriously, society loses potentially excellent professionals. To overcome these problems, professors should strive for a balance of instructional methods (as opposed to trying to teach each student exclusively according to his or her preferences.) If the balance is achieved, all students will be taught partly in a manner they prefer, which leads to an increased comfort level and willingness to learn, and partly in a less preferred manner, which provides practice and feedback in ways of thinking and solving problems which they may not initially be comfortable with but which they will have to use to be fully effective professionals. This site contains resources for a model of learning styles generally referred to as the Felder-Silverman model. The model was originally formulated by Dr. Felder in collaboration with Dr. Linda K. Silverman, an educational psychologist, for use by college instructors and students in engineering and the sciences, although it has subsequently been applied in a broad range of disciplines. This chart helps you determine your learning style; read the word in the left column and then answer the questions in the successive three columns to see how you respond to each situation. Your answers may fall into all three columns, but one column will likely contain the most answers. The dominant column indicates your primary learning style. When you.. Visual Auditory Kinesthetic & Tactile Spell Do you try to see the word? Do you sound out the word or use a phonetic approach? Do you write the word down to find if it feels right? Talk Do you sparingly but dislike listening for too long? Do you favor words such as see, Do you enjoy listening but Do you gesture and use are impatient to talk? Do expressive movements? you use words such Do you use words such Concentrate picture, and imagine? as hear, tune, and think? as feel, touch, and hold? Do you become distracted by untidiness or movement? Do you become distracted Do you become distracted by sounds or noises? by activity around you? Do you forget faces but Do you forget names but Meet someone remember names or Do you remember best remember faces or remember again remember what you talked what you did together? where you met? about? Contact people Do you prefer direct, face-toon business face, personal meetings? Read Do something new at work Do you prefer the telephone? Do you like descriptive scenes Do you enjoy dialog and or pause to imagine the conversation or hear the actions? characters talk? Do you like to see demonstrations, diagrams, slides, or posters? Put something Do you look at the directions together and the picture? Need help with a Do you seek out pictures or computer diagrams? application Do you prefer verbal instructions or talking about it with someone else? Do you talk with them while walking or participating in an activity? Do you prefer action stories or are not a keen reader? Do you prefer to jump right in and try it? Do you ignore the directions and figure it out as you go along? Do you call the help desk, Do you keep trying to do it ask a neighbor, or growl at or try it on another the computer? computer? Understanding Different Learning Styles What is the best way to learn? The best way for a person to learn depends on the person, of course. It is well know that people have different leaning styles that work best for them. The best approach for an instructor to take is to address a variety of learning styles with their teaching plan. It is also helpful to encourage students to understand their preferred leaning style. By the time students reach the college level it is often assumed that they have figured out the best and most productive way to study to retain information. Of course, this is not a correct assumption. Teachers should make students aware of the various learning styles and encourage them to consider their preferred style as they complete their studies. Providing the right environment conducive to learning The classroom environment can also have a big effect on the amount of learning that occurs. Here again, people are different and have different environmental preferences. Nevertheless, understand what effects the learning process is important to know. Some of the common learning styles and environmental factors that should be considered when attempting to create the best learning conditions are listed below. (This following information was adapted from: Moore, Carol. (1992). Learning Styles - Classroom Adaptation<based primarily on Carbo Learning Styles>. Learning Styles DESCRIPTION Structure of Lessons Most students learn best when there is a logical sequential, delineated lesson that provides the objective and systematic steps to do the assignment. This type of student benefits from the use of rubrics so that they can better follow lectures and assignments. However, some students do not like much structure and appreciate being given choices and allowed to be creative. Sociological Some students benefit greatly from group activities and other do not. For those who are peer learners, pair them with another student when possible. For those who are self learners, do not force them into a group/peer-learning situation all the time. Cooperative learning is an important learning tool but some students are more introverted than others and may have difficulty participating in group activities. Auditory Some students learn best by listening. Auditory learners do well with lecture, class discussions, etc. While lecture is considered the least effective teaching method, some students learn best by simply listening. These students may also be more sensitive to outside noises. Visual Visual learners benefit from a variety of ocular stimulation. One example would be the use of colors. These students like images and written information. They like to be able to read instructions or the text on their own to increase their understanding. When studying it is helpful for these student to use different color highlighters or pens as they are reading and taking notes. These students may also be more sensitive to visual distractions. Tactile Most people learn best with hands-on activities, but some gain a lot more from it than others. Some students really increase their learn potential when they are give they opportunity to do something by themselves Especially in a science classroom there should be plenty of opportunities to learn by doing. Environmental Factors Formal vs. Informal A formal setting would be the traditional desk and chair or possibly a table. An informal setting would be the floor, a couch, a beanbag, etc. Every student's brain will not function the same in the same postural position. So when you see a student slouching in a traditional desk or chair, it may simply mean that they would learn better in more of a informal setting. Some students find sound distracting and some find it calming. It may be beneficial to have several study areas established. One Noise vs. Quiet where the noise level is kept to a minimum and one where some background noise is present. Temperature Room temperature also plays a key role in learning. If a student is too cold or too hot, they will have more of a hard time concentrating on what their learning task is. It is recommended that the classroom temperature be cool if possible. This way those who do not like being cold can simply wear another layer of clothing and be comfortable. Everybody's eyes react differently to light. Some students may need to sit by a bright reading lamp while others may get a Bright vs. Dim headache when too much light is present. A light level that all students find comfortable should be sought. Kinesthetic Some people need to have continuous movement as they are studying, such as tapping there fingers or foot on the floor, fooling with their hair, using a stress ball, or chewing gum. This is absolutely natural but if they are not alone studying, make sure they do not distract others. Mobility The human body is built to move and it does particularly like to sit still for long periods of time. Have students to stand, stretch, and take short breaks as needed during studying. It is good to study in 20-30 minute increments with a brief break between each block of time. Research has shown that it only takes 30 seconds to rest and recharge the brain. http://homeworktips.about.com/od/homeworkhelp/a/learningstyle.htm