Exam ideas for aquatic biology
advertisement

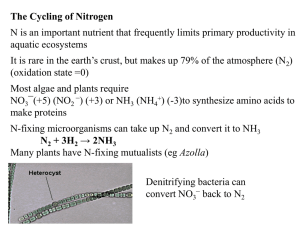
Practice Question for Mid-term I The gliding motion of Dugesia on a substrate a) does not require a hydrostatic skeleton/coelom b) is produced mainly by the cilia on its ventral surface c) involves cilia beating within a thin layer of mucous d) a, b and c are all true e) none of these are true The feeding of Dugesia and Hydra are similar in that a) their mouth also serves as the anus b) they are both carnivorous and feed on large prey c) they both have a muscular pharynx d) both a and b are true e) a, b, and c are all true Rhabdocoels are differ from Triclads a) in regards to their feeding mechanism b) in the shape of their intestine c) in that rhabdocoels are not carnivores whereas triclads are d) mainly in size e) none of these True or False The tentacles of Hydra and Plumatella function similarly. Mesostoma is a voracious predator on mosquito larvae and other zooplankton Fill in the blanks Freshwater sponges can withstand adverse conditions by producing asexual resistant stages called ____________ which are functionally analogous to the _____________ of freshwater bryozoans. The filter-feeding mechanism of a sponge is driven by the _________________, whereas that of the bryozoan uses its______________________. The name rhabodcoel refers to their _______________ gut cavity The antero-lateral sensory structures in triclads are called _______________. Explain—i.e give an explanation for the following: How a sponge moves water through its body and feeds itself. The function of the mesogloea in a sponge The lophophore of a bryozoan looks superficially like the polyp of a cnidarian, but they function very differently. Sponges and bryozoans both filter-feed but the way they do it is quite different. Animals that eat large prey often use the same opening as mouth and anus. Matching Aphanizomenon Azolla Bryophytes Ceratium Filamentous diatoms Halobacterium Mesostoma Platyhelminthes Raphed diatoms Rivularia Sagittaria Spirogyra Sulfate reducers Thiocapsa Triclads Vallisneria photoheterotroph metal reductases anaerobic photoautotroph short tapered filaments with basal heterocysts and akinetes filaments of tiny rectangular cells arranged in irregular sheets long spiral chloroplast capable of a gliding motion on a substratum cells joined at their valve faces mixotroph parasitic sporophyte heterosporous fern male and female flowers on separate shoots anthers and pistils in separate flowers on the same plant potential mosquito control agents free living flatworms, flukes and tapeworms simultaneous hermaphrodites. Short essays Mine wastes can have a devastating impact on aquatic ecosystems because. Explain the role of Thiobacillus in these effects, and how mine wastes should be handled to prevent this. Humans have always had a love-hate relationship with Cyanobacteria, Explain Many benthic diatoms exhibit a life cycle that alternates between a solitary motile phase and an attached filamentous phase. Explain how this would be advantageous for life in a stream or a wave washed shore. Although the mosses and pterophytes are quite dependent on water, they haven’t done nearly as well in the aquatic environment as flowering plants. Expand on this point, and using what you know about plant life cycles suggest an explanation for this pattern. Salvinia spp, most of which are polyploid and sterile are proliferating as pests in many parts of the world. Many other aquatic plants have also become major pests through vegetative proliferation. Suggest a mechanism by which an asexual fern can spread effectively enough to become major pests without being able to produce spores, which are required by most ferns for effective dispersal. Azolla, Salvinia, and Lemna all share the same basic growth form. Describe it and suggest some advantages and disadvantages to this growth form and in which types of aquatic habitat they are successful and where they are not. Ferns as a group remain at least partially dependent on water for reproduction, and, though they like wet places, few have become truly aquatic. Moreover, those that are aquatic have a growth form quite atypical for ferns. Expand on this, and based on your knowledge of the fern life cycle suggest and explanation for these observations. Altlhough Turbellarians are often considered to be very primitive organisms because they have no coelom, they are actually quite sophisticated animals functionally. Explain.