Airway - EDExam
advertisement

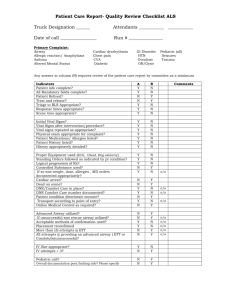
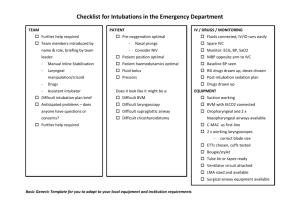
Trauma Notes Preparation Eye protection Gown Gloves Trauma Team Handover M Mechanism of injury I Injuries found S Signs (Obs) T Treatment Primary Survey – BEGINS WITH EXPOSURE OF PATIENT, then… A Airway (with Cspine control) B Breathing with O2 C Circulation (with control of bleeding) D Disability (Neuro status) E Exposure (body temp) Airway More important than C-spine Can remove collar to intubate with manual in line stabilisation Upper Airway – LOOK & FEEL o Burned Airway Do not delay with burned airway – intubate early Burns in/around mouth/lips/nose, edema of face/lips Resp distress Hoarse voice Beware CO poisoning – hyperbaric O2 if CO > 30% o Facial Injury Mid face fractures – slide backwards obstruct airway May be better to sit up (with collar) Fractured jaw Bleeding o Foreign Body Dentures/teeth Blood Other Lower Airway o Examine Neck 6 times when checking airway T Trachea – deviation Wounds – threatening airway/circulation (lacs/compression) Emphysema Larynx - ?intact Veins - ?distended (tamponade, PTX) DON’T FORGET to check under collar All patients with GCS < 9 need intubation Cricothyrotomy when all else fails o For upper airway obstruction o Beware subcut tracking of O2 – lose landmarks Pitfalls: 1. 2. 3. 4. Foreign body in the airway Mandibular or maxillofacial fracture Tracheal or laryngeal disruption Cervical spine injury Breathing Inspect Paplpate Auscultate All trauma patients are hypoxic: Mx = high conc. O2 o Airway compromise o Chest injury o Head injury o Hypovolaemia o Pain o Chronic Lung Disease = MORE HYPOXIC CO2 kills slowly, no O2 kills quickly 6 Life threatening chest conditions must be considered o Airway Obstruction o Tension Pneumothorax – needle decompression o Open pneumothorax – 3-sided seal dressing, or IPPV + ICC on suction o Massive haemothorax – FLUID BEFORE ICC o Cardiac Tamponade o Flail Chest Treat contusion (ventilatory support prn) ICC before ventilation (small PTX may tension) Pitfalls: 1. 2. 3. 4. Tension pneumothorax Flail Chest with pulmonary contusion Open pneumothorax Massive Hemothorax Circulation FEEL PULSE, CHECK BP, ATTACH MONITOR & SAT PROBE IV – SHORT & THICK (minimum 16G) Control Obvious Blood Loss o Control haemorrhage – pressure dressings o LOG ROLL to check BACK/BOWEL Hidden Blood Loss will CRAMP your style o C Chest - CxR o R Retroperitoneum – Check Urine o A Abdomen – FAST scan, CT, DPL o M Missed Long Bone Fracture o P Pelvis Fluid Resuscitation o Crystalloid o Colloid o O-Negative (NOT > 4 units if Bld Grp unknown) o X-matched blood Burns o Parkland Formula (crystalloid) weight (kg) x %burn x 4 = ml crystalloid in 1st 24hrs ½ in first 8 hours o Muir/Barclay (colloid) (weight (kg) x %burn) / 2 = ml colloid/unit time Unit Time = 4/4/4/6/6/12 hrs Urine Output o Adult 30-50ml/hr o Child: 1-2ml/kg/hr Head Injury alone does not cause hypotension o ↑ ICP – HYPERtension & bradycardia (Cushing Response) o Neurogenic shock is hypovolaemic shock until proved otherwise o ie high spinal injury – lose symp tone EMD o Hypoxia o Hypovolaemia o Hypothermia o Hypo/Hyperkalaemia o Tamponade o Tension PTX o Toxins, drugs/poisons o Thromboembolism (massive PE) Pitfalls: Hypovolemia resulting from 1. 2. 3. 4. Intra-abdominal or intrathoracic injury Fractures of the femur and/or pelvis Penetrating injuries with arterial or venous involvement External hemorrhage from any source. Disability (Neurologic Status) GCS o Does not measure prognosis o < 9 = intubation Pupils & Plantars Lateralising signs o Unilateral weakness/anaesthesia Agitation o BEWARE: Agitated patients calm down while deteriorating o Causes: Hypoxia Cerebral Irritation (cerebral oedema, intracranial haemorrhage) Pain Anxiety Full Bladder EtOH/Drugs o Sedating Pt to control airway is acceptable o MUST search for causes of agitation PAIN o It’s OK to give analgesia Reassurance Splints N20 – CI in CHEST INJURY/PTX Opiates/Ketamine (0.5-1.0mg/kg) – IV Local Anaesthetics/Nerve Blocks Exposure/Environmental Temperature o Hypothermia = core T < 35° Mild 32-35 Mod 30-32 Severe <30 Asystole @ 18-20 VF may not respond to DCR until T > 30 o Management Remove wet clothes/sheets, Dry Pt Cover – space blanket/warm blankets Warm IV fluids Bear Hugger Secondary Survey Bones Brain Back Bowel/Abdo Investigations Bloods ABG FAST Radiology Transferring Pt to radiology Tertiary Survey Penetrating Injury – In extremis: Number one concern: AIRWAY Head o Pressure on wound o Fluid o Cerebral Function Yes – CT +/- OR No – deceased Chest o Bilateral chest tubes o Thoracotamy prn o OR Neck/Abdo/Extremity o Pressure on wound o OR