Phase 2 Site Investigation Management Plan : Landfills
advertisement
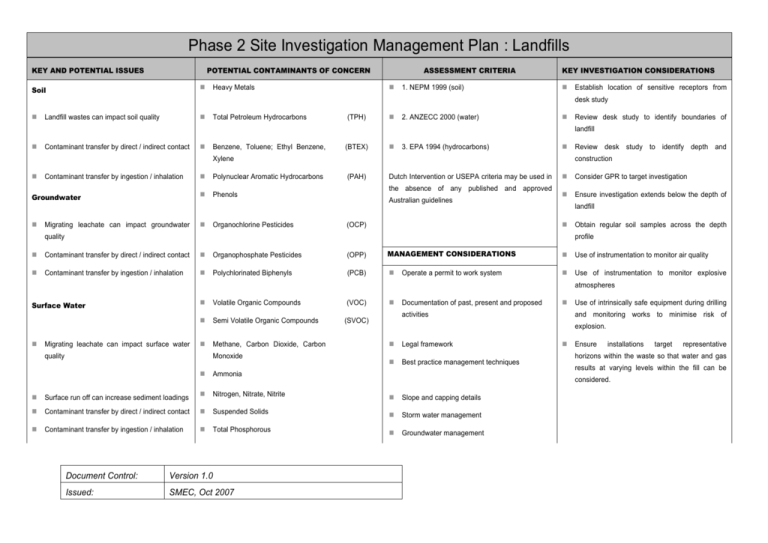
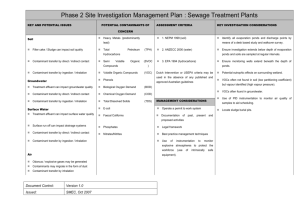
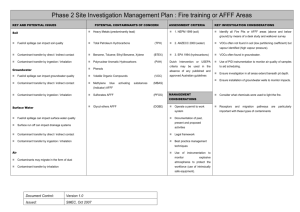
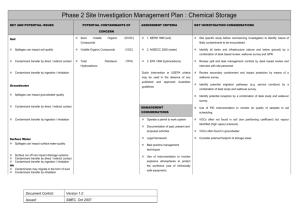
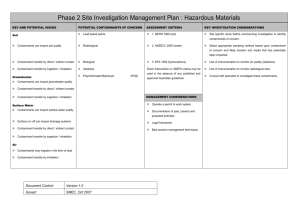
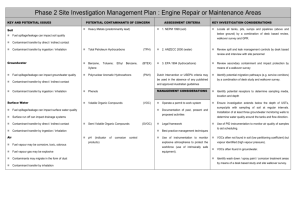
Phase 2 Site Investigation Management Plan : Landfills KEY AND POTENTIAL ISSUES POTENTIAL CONTAMINANTS OF CONCERN Soil ASSESSMENT CRITERIA Heavy Metals 1. NEPM 1999 (soil) KEY INVESTIGATION CONSIDERATIONS Establish location of sensitive receptors from desk study Landfill wastes can impact soil quality Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons (TPH) 2. ANZECC 2000 (water) Review desk study to identify boundaries of landfill Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact Benzene, Toluene; Ethyl Benzene, (BTEX) 3. EPA 1994 (hydrocarbons) Xylene Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Groundwater Migrating leachate can impact groundwater Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons construction (PAH) Dutch Intervention or USEPA criteria may be used in the absence of any published and approved Phenols Organochlorine Pesticides Review desk study to identify depth and Australian guidelines Consider GPR to target investigation Ensure investigation extends below the depth of landfill (OCP) quality Obtain regular soil samples across the depth profile Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact Organophosphate Pesticides (OPP) MANAGEMENT CONSIDERATIONS Use of instrumentation to monitor air quality Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCB) Use of instrumentation to monitor explosive Operate a permit to work system atmospheres Surface Water Migrating leachate can impact surface water Volatile Organic Compounds Semi Volatile Organic Compounds Methane, Carbon Dioxide, Carbon quality Monoxide Ammonia (VOC) Documentation of past, present and proposed (SVOC) Legal framework Best practice management techniques Nitrogen, Nitrate, Nitrite Slope and capping details Contaminant transfer by direct / indirect contact Suspended Solids Storm water management Contaminant transfer by ingestion / inhalation Total Phosphorous Groundwater management Issued: SMEC, Oct 2007 and monitoring works to minimise risk of Ensure installations target representative horizons within the waste so that water and gas results at varying levels within the fill can be considered. Surface run off can increase sediment loadings Version 1.0 Use of intrinsically safe equipment during drilling explosion. Document Control: activities Air Orthophosphate Gas management Landfill gas may be corrosive, toxic, odorous Anions and Cations Leachate management Asbestos Radiological contaminants Explosives Pathogens Nuisance (pest, vermin, weed) management Landfill gas may be explosive Landfill gas contributes to the ‘greenhouse effect’ Contaminants may migrate in the form of dust Fire prevention Contaminant transfer by inhalation Contaminant Monitoring Document Control: Version 1.0 Issued: SMEC, Oct 2007