In situ Hybridization - Washington State University
advertisement

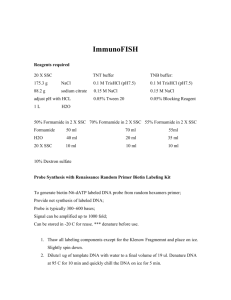
Franceschi Microscopy & Imaging Center Washington State University 2/17/16 1 In situ Hybridization Paraffin: Use slides with 1 or 2 sections close together (this reduces the amount of solutions needed). Deparaffinization: 2x, 5m - Hemo De 2x, 5m - 100% EtOH 1x, 5m - 50% EtOH, air dry completely, circle sections with rubber cement to keep solutions on sections and for sealing coverslip. Resin: Slides - no special preparations except keep sections close together, circle sections with rubber cement to keep solutions on sections and for sealing coverslip. Grids - do following steps in microfuge tubes, 50 - 100 ul Pretreat Proteinase K (25 mg/ml) 5m, room temperature (rt) (0.002g in 1 ml TE buffer) - protease treatment increases accessibility by digesting protein around target nucleic acids. Wash TE buffer 50 mM TRIS 5 mM EDTA in DEPC water pH 7.4 - to remove proteinase K 2x, 5m, rt 20x SSC Deionized Formamide (100%) 3M NaCl 50 ml formamide w/5g mixed bed ion exchange resin 300mM NaCitrate stir 30m, rt. filter 2x whatman #1 filters pH 7 (w.10N NaOH) 500 ul aliquots store at -20 C 50x Denhardts Solution 1% PVP 1% Ficoll 400 1% BSA store at -20C Dextran Sulfate (50%) 50 mg Dextran Sulfate 65 ul dH2O Prehybridization Hybridization solution + 1 ul Dextran Sulfate -prehybridization is to prevent background staining tRNA 10 10 mg/ml ssDNA 10 mg/ml 15m, rt-55 C 4. Hybridization (see also notes*) Hybridization Buffer + probe (1 ng/ul) + 1 ul Dextran sulfate - temp 30 - 65 C - time 10 -24 h - may also preheat probe to 70 C, 5m in water bath to remove secondary structures Franceschi Microscopy & Imaging Center Washington State University 5. Washes Method I 1X SSC RNase 4X SSC 2X SSC 1X SSC ddH2O 3x, 5m 20m, rt 5m 5m 5m jet washes Method II 4X SSC 2X SSC 1X SSC 0.1X SSC 2/17/16 2 5m, 50 C 5m, rt 5m, rt 5m, rt -posthybrization washes help remove non-specific hybrids. Probe may bind to sequence which bears homology but not entirely homologous. Wash with various stringencies, can vary formamide conc., salt conc., and/or temp. 6. Secondary antibody (if using DIG labeled probe) Block with TBST-BSA (500 mM NaCl) 30m Incubate; TBST-BSA : Sheep-anti-DIG 1.5h 1 : 50 Wash; TBST-BSA 10m TBST 10m ddH2O 2x, 5m & jet wash * Notes on hybridization; hybridization depends on ability of denatured DNA to reanneal with complementary strands in environment just below their melting point (Tm = temp at which 1/2 DNA is present in single strand form (denatured)). Stability of DNA directly dependent on GC content, increase molar ratio of GC pairs = increase melting point (Tm). Renaturation of DNA and Tm influenced by: temperature, pH, concentration of monovalent cations, presence of organic solvents. pH: increase pH above 6.5-7.5 to produce more stringent hybridization conditions Monovalent cations (sodium ions): interact electrostaticly with nucleic acids (i.e. phosphate groups). Increase salt conc. = decrease electrostatic repulsion between the 2 strands & increase stability of hybridization Decreased salt concentration affects Tm and renaturation rate. Formamide: Organic solvent, reduces melting temp of DNA/DNA, DNA/RNA duplexes so that hybrid can occur at temp below 65- 75 C (normal temp for in situ to work, but causes trouble with morphology) with 50% formamide in mix. Dextran Sulfate: strongly hydrated, macromolecules have no access to water- increases hybridization rates by apparently increasing probe concentration. Other variables; Probe length - increase probe length = increase renaturation rate Probe conc. - increase probe concentration = increase reanneal rate